The Noise level is the amount of outside interference detected at each measurement point. Noise negatively affects your Wi-Fi signal. Sources of noise can include microwave ovens, cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, wireless video cameras, wireless game controllers, fluorescent lights, and more.
Your noise level is best understood in comparison to your signal strength (see What is the signal-to-noise ratio?). Other Wi-Fi networks are not counted as noise — they are counted as interference (see the Signal-to-Interference Ratio). If you hover over the measurement markers on the map and look at the AP names on the left, you can see the exact noise levels for each location.
The Noise Level visualization is one of the PRO visualizations available only for the Pro and Enterprise versions of NetSpot on macOS.
If your noise levels are too high, see Troubleshooting High Noise Level for strategies to correct this issue. NetSpot PRO and Enterprise users also have access to Automated Troubleshooting, to help identify and fix noise issues.
There are several ways you can adjust this heatmap view:
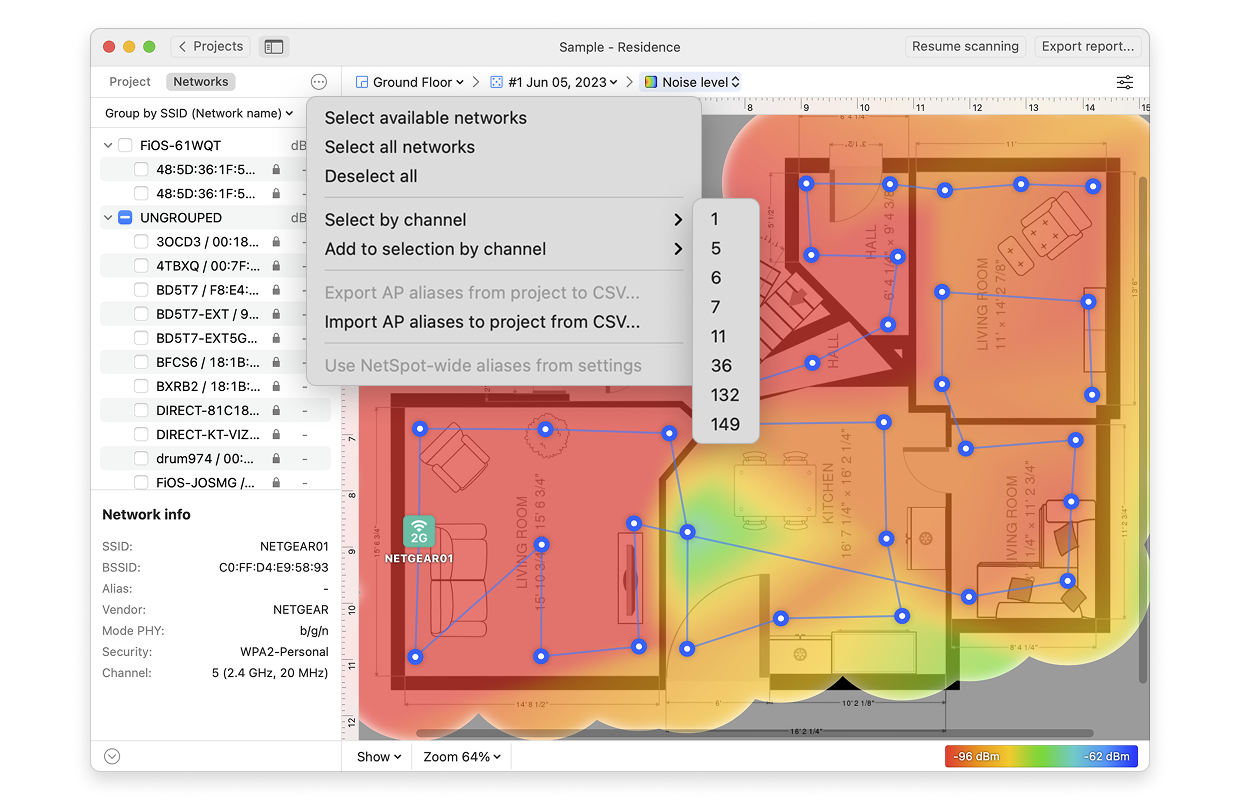
- Wi-Fi Network: Each Wi-Fi network detected can be mapped individually. Simply check the box next to the network(s) you wish to view on the left-hand side of the NetSpot window.
- Wi-Fi Channel: Click (
 ) at the top of the left panel in NetSpot (above the networks list) to visualize networks broadcasting on certain channels.
) at the top of the left panel in NetSpot (above the networks list) to visualize networks broadcasting on certain channels.
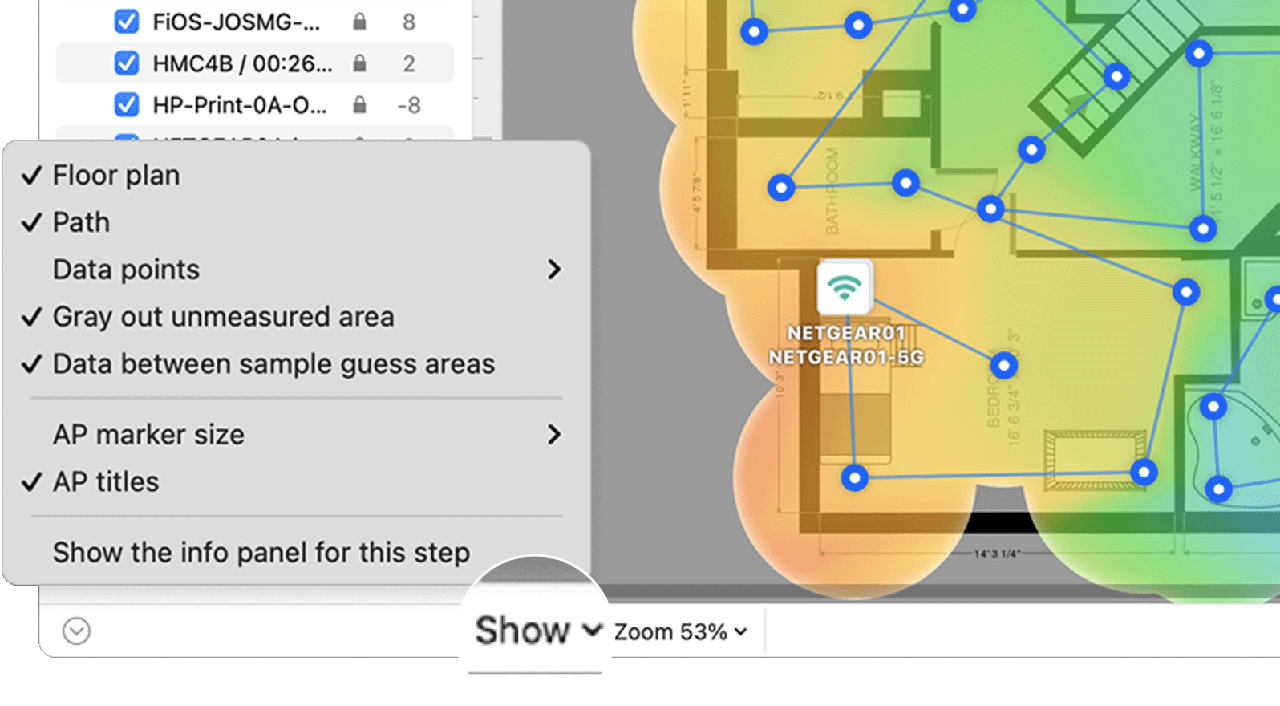
- View: By clicking on the Show menu in the bottom left corner of the canvas, you can choose whether to show your floor plan, path, sampling points, and AP titles on the heatmap, as well as several other adjustments.
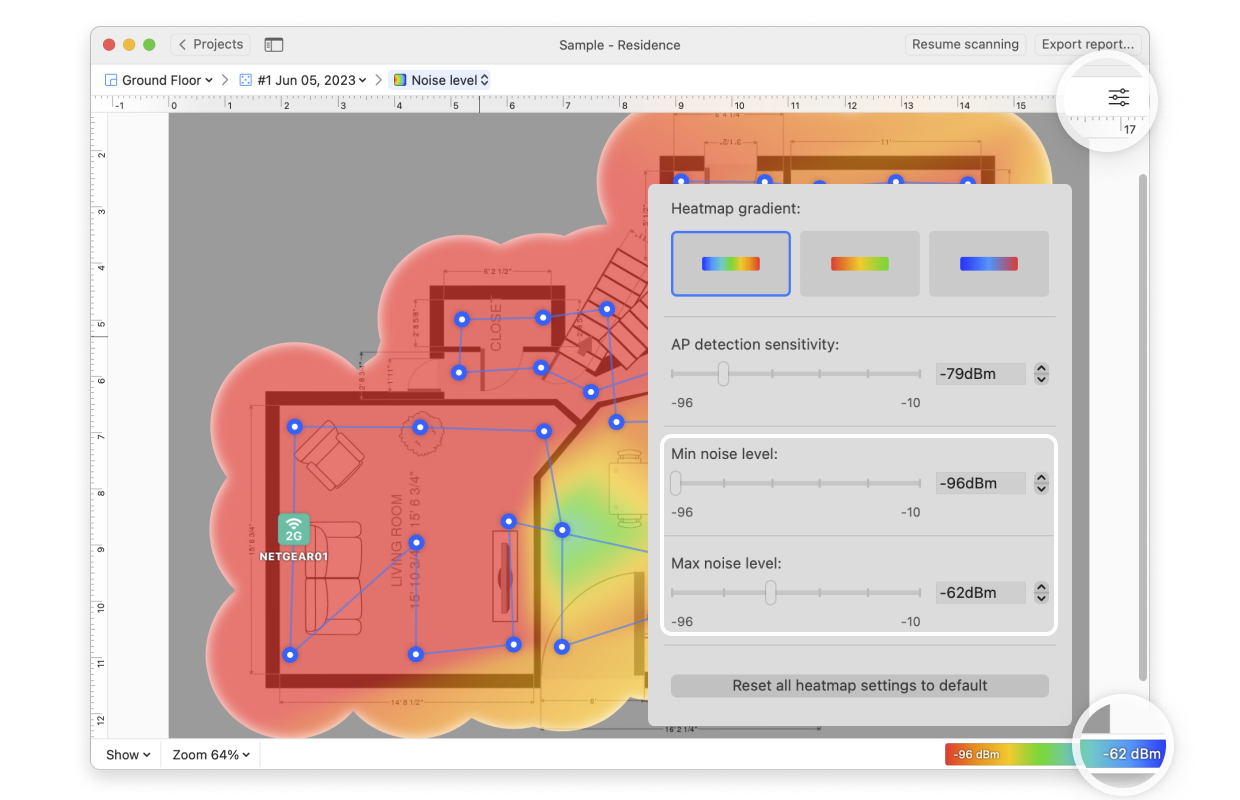
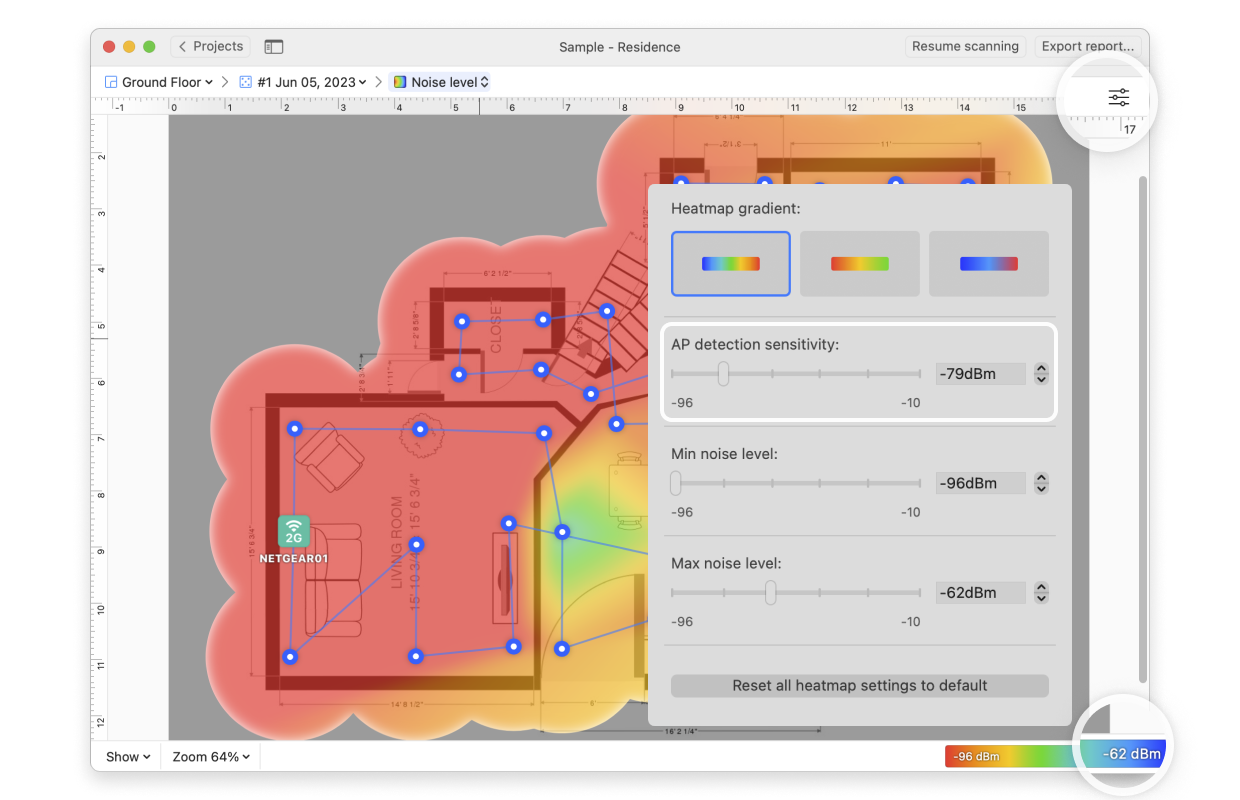
- AP Detection Proximity: By clicking the Heatmap Settings icon at the top right or by clicking on the gradient on the lower right, you can filter out weaker access points (APs) by adjusting the AP detection proximity slider. The default value is -50dBm.
- Min/Max Noise Level: By clicking the Heatmap Settings icon in the upper right corner of the app window or by clicking on the gradient on the lower right, the color scheme of the noise level heatmap can be adjusted to a more convenient range. You can change the color combination by choosing from the three gradient options, and then the intensity can be changed by tweaking the visualized noise levels. The default range is set to -96dBm (minimum) and -10dBm (maximum).