What is WiFi network security?
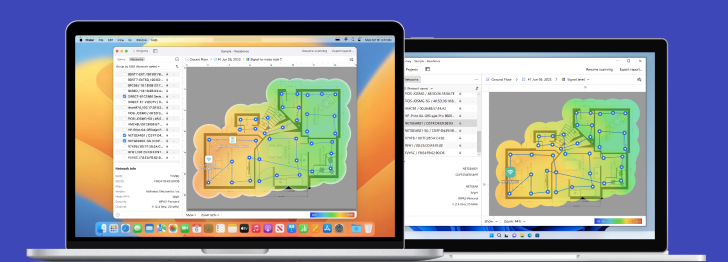
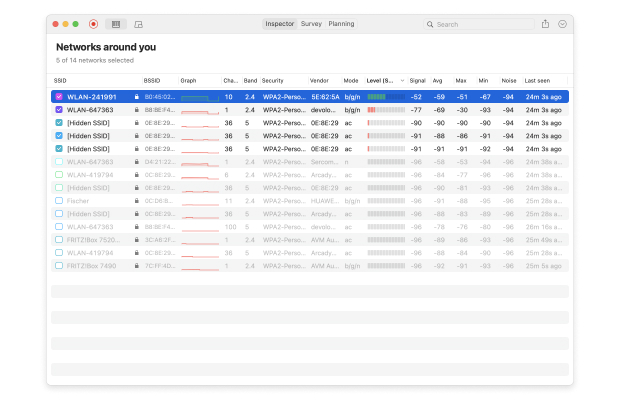
WiFi network security, or sometimes wireless network security, deals with the prevention of unauthorized access to data transmitted across WiFi networks and other wireless network security risks.
As such, it’s a subset of computer network security, which also deals with wired networks that connect computers, servers, and other devices together using physical cables.

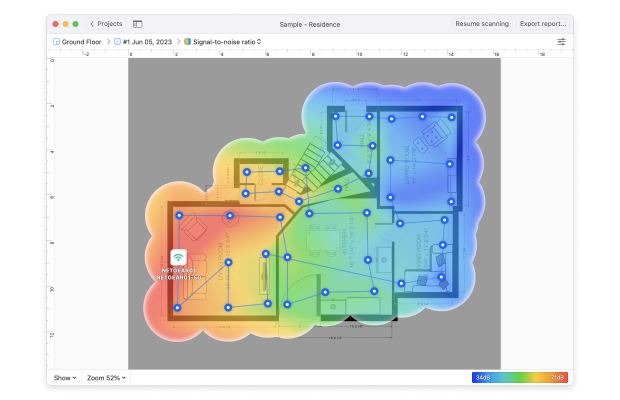
WiFi security has never been more important than it is today because the networks it aims to protect play a critical role in virtually all aspects of our lives. Without them, we wouldn’t be able to communicate with our loved ones, collaborate with work colleagues, browse the web, stream music and movies, and so on.
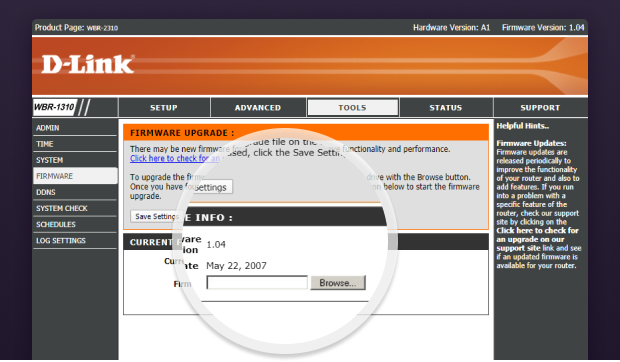
Thanks to wireless security, we can do these and many other activities without our personal data falling into the wrong hands and being used for all kinds of malicious purposes — at least if the right wireless security network standard is used to encrypt transmitted data.