Powerful advanced tool for multiple Wi-Fi networks Surveys, Analysis and Troubleshooting.
6 Ways To Secure Your WiFi Network
From hackers to network leeches, learning how to secure your WiFi network is crucial to prevent unauthorized access to your WiFi network to either steal your bandwidth or your money.
To keep people out of your home or business’s wireless network, use these steps to tighten up security and protect yourself.
How To Secure WiFi Network: Quick Steps
Getting a new router from your internet provider might make you want to quickly plug it in and start browsing immediately. But properly securing your WiFi network is just as important as installing new locks after you move into a new house — it’s crucial to protecting your online safety.
Use these simple guidelines to strengthen your WiFi security:
#1 Change the Default Router Login
If you’re wondering “How to Secure My WiFi”, start here: don’t use the default password. Too often the default password is “000” or “password” or in the case of routers, it’s the serial number, which is on the side of the router.
So the first thing to do when looking to secure a WiFi router:
- Connect to the router via an Ethernet connection. Do not use a WiFi connection to get to the administrative access. Check the manual, but usually, the Admin interface for a router is at http://192.168.0.1 or http://192.168.1.1.
- Once in, log in with the default admin username and password. Even though you want to change it, you still have to get in the first time.
- Depending on your router, the steps to change the administrative username and password will be different. For Arris, this is listed under Login settings:
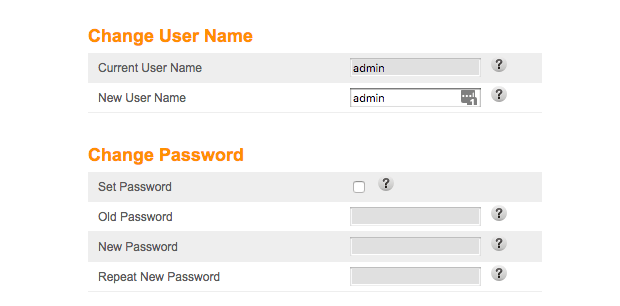
- Change both the username and the password. Write these down and store them in a secure location, like a home safe. Don’t give it to your kids — you know that will end badly.
That’s the first step to securing your WiFi network. But it’s not the last.
#2 Change and Hide your SSID
The SSID is the identity for your secure WiFi network. It’s the name people use to find it and connect to the network, and how to set it apart. It’s also set by default by your router, usually some combination of its serial number like “F27N37552” or, even worse it identifies what kind of router it is like “NetGear001” or the provider with “VerizonBox”.
All of these are bad for different reasons. With the SSID telling the user what kind of network or router is being used makes it easier for hackers to figure out the best way to attack your network.
Stop them by changing the SSID.
Some routers even let you specify multiple networks (more on that in a moment).
Check your manual, but the typical steps are:
- Log into your router (you did set up a new username and password from Step 1, right?).
- Select your WiFi network.
- Change the SSID, and turn off “Broadcast Network Name.”
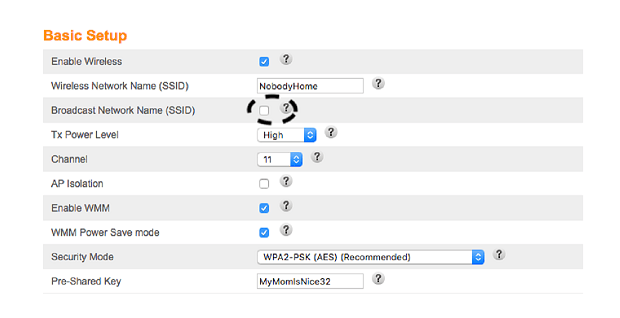
Save those settings. The WiFi network will still work, it just won’t tell everyone about it. While you’re at it, make sure that the Pre-Shared Key is something unique.
Expert Tip: Use memorable phrases rather than simple words or numbers.
Now we’re hidden and people just can’t get in without permission. But hiding your SSID doesn’t make your network completely invisible or fully secure. Specialized WiFi analyzer apps such as NetSpot can detect hidden networks, although they won’t display the hidden SSID itself.
#3 Use Strong Wi-Fi Encryption
Most modern routers automatically enable Wi-Fi encryption by default. But — are you sure your router’s encryption is enabled and properly configured? Don’t assume it is — you should always verify your router’s security settings.
Previously, the common standard was WPA2, which uses an encryption algorithm called AES. Think of it as having millions of locks protecting your data, unlike the outdated WEP, which could easily be cracked by hackers.
However, Wi-Fi security standards have advanced. Ideally, set your router encryption to WPA3-Personal if available, as this is the latest Wi-Fi encryption standard and provides the strongest protection available today. WPA3 offers improved defense against brute-force attacks, better encryption of passwords, and overall enhanced security for home and business networks.
The steps for configuring your WiFi network encryption differ slightly between router models, but generally, follow these instructions:
- Log into your router.
- Set Security Mode or Encryption Level to WPA3-Personal. If WPA3 is not supported by your router, use WPA2-PSK (AES) instead.
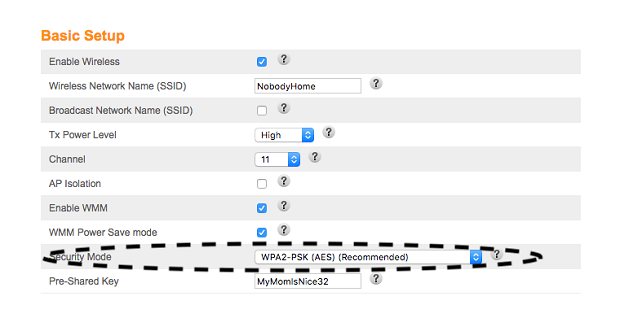
- Avoid using WPA2-AES/TKIP unless absolutely necessary, as TKIP is less secure and intended only for older, legacy devices.
Enabling the strongest available encryption helps protect sensitive data when you’re banking online, making secure transactions, checking personal information,or binge-watching the latest episodes of “Pretty Little Liars” (I’m not judging you).
Expert Tip: Regularly update your router’s firmware to ensure support for the latest security protocols like WPA3.
#4 Set Up A Guest Network
Sometimes you’ll have friends or family over. And when they’re with you, they’ll ask one of two dreaded questions “What’s your WiFi password?”.
Instead of sharing your main WiFi network credentials — which could expose sensitive information — there’s a safer solution: set up a separate guest WiFi network. Many modern routers support multiple networks, making this easy to implement.
A guest WiFi network lets visitors access the internet without giving them direct access to your home devices, personal files, or smart home gadgets. Think of it as offering guests their own safe, digital room — isolated but convenient.
Why is setting up a guest network important? It’s not that you don’t trust your family. Except maybe Aunt Edna, who never seems to update her antivirus. But if their devices may be compromised without their knowledge. If someone’s device has malware or spyware, your entire network could be vulnerable if they’re logged onto your primary WiFi.
Best practices to secure your guest network:
- Activate your guest network only when needed. Turn it off when your guests leave to minimize security risks.
- Regularly update your guest network credentials. Change the guest SSID and password periodically — ideally each time you activate the network.
- Limit permissions on the guest network. Enable internet-only access and disable file sharing or network device visibility.
Expert Tip: Many routers from popular brands like Netgear, TP-Link, or ASUS have easy-to-use apps or web interfaces for setting up secure guest networks in minutes. Check your router’s instructions or app for quick setup guides.
Implementing these tips helps you understand how to secure your WiFi network better, significantly reducing the risk of cyber threats from guest devices.
Powerful advanced tool for multiple Wi-Fi networks Surveys, Analysis and Troubleshooting.
-
Get NetSpot
macOS 11+, Windows 7/8/10/11
#5 Set Up The Firewall
A firewall functions as a defensive mechanism that regulates network traffic coming into and going out of a system based on established security rules.
- Rule 1: Reject all inbound connections that were not explicitly requested (Any: DENY).
- Rule 2: Permit inbound connections solely when they are responses to outgoing requests initiated by devices within the network (stateful firewall).
- Rule 3: Enable “Ping Blocking” to prevent your router from responding to external ping requests (ICMP Echo requests). Hackers often ping networks to identify active systems. By blocking ping responses, you make your network less visible.
Another setting is to block “fragmented packets.” A packet is a bit of network, containing a header saying where the packet is going and what information it carries. It’s like a letter that computers send each other on the network. The envelope shows where the letter came from and where it’s going to, and inside the letter is the actual information.
But sometimes a hacker will send a fragmented packet. This is a packet that is formed badly on purpose to confuse the router or computers into accepting bad information that they usually would deny. It can trick the computer into granting access because the computer will do it’s best to guess what the fragmented traffic is trying to get to. By denying these, it prevents those issues in the first place:

Expert Tip: Regularly review firewall logs to rapidly identify and address possible security risks by monitoring suspicious behavior.
#6 Monitor Nearby Wi-Fi Networks Regularly
Locking down the network with the five steps listed are a good start to good wireless network security.
Past just locking it down, you should also know what’s out there on the network, and in your building. Sometimes a clever hacker can get into a business and plug in a small WiFi router into the Ethernet network so they can access it from outside the building.
You’re going to want a good network analyzer to find any rogue WiFi networks in your building. Download NetSpot — the free version can show the different networks it detects. If there are networks that are coming on strong or aren’t ones you know about, it can help you find them and shut down.
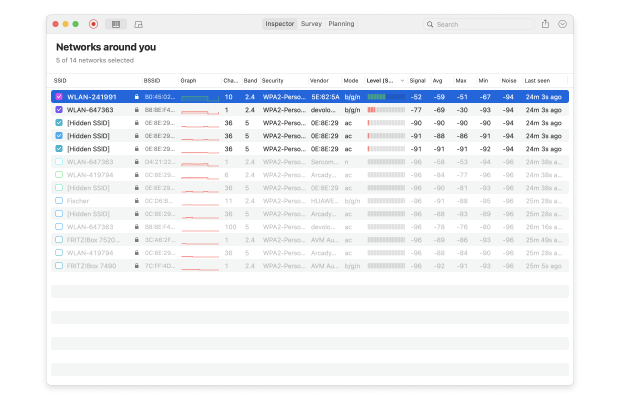
Secure your network with a bit of simple locking down of the system, and using NetSpot to find anything that doesn’t belong and turn it off so people can snitch on what your network is doing without your authorization. It’ll grant peace of mind and save a lot of heartaches after.
Powerful advanced tool for multiple Wi-Fi networks Surveys, Analysis and Troubleshooting.
-
Get NetSpot
macOS 11+, Windows 7/8/10/11
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions on Wi-Fi Security
To maximize Wi-Fi security, it’s best practice to change your Wi-Fi password every three to six months, especially if you frequently share network access with guests or experience suspicious activity.
No. Although hiding your SSID can help prevent casual discovery, hackers can still detect hidden networks with specialized tools. Always combine SSID hiding with robust WPA3 encryption and a strong, unique password to enhance your Wi-Fi security.
WPA3 encryption is currently the most secure method for protecting WiFi networks. It considerably lowers the likelihood of brute-force hacking attempts and unauthorized access, making it highly recommended for securing sensitive data.
WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup) can be exploited by attackers through various known vulnerabilities, allowing unauthorized access to your network. Disabling WPS is a simple step to prevent these common Wi-Fi security threats.