Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Analysis, Troubleshooting runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax wireless network adapter.
MU-MIMO: What It Is and How It Make WiFi Better
In our ongoing series about WiFi standards, we've discussed various advancements that have shaped the way we connect to the internet. Today, we're focusing on a game-changing innovation: Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output (MU-MIMO).
Let's explore what MU-MIMO is, why it matters, and how to make the most of it.
What Is MU-MIMO?
WiFi speeds have increased significantly in the last two decades. Until 2008, the maximum link rate was 54 Mbit/s. In 2025, you can easily buy a WiFi 6 router that can theoretically max out at 9.6 Gbps.
These speed gains have been unlocked in no small part thanks to MU-MIMO technology, but what exactly is it?

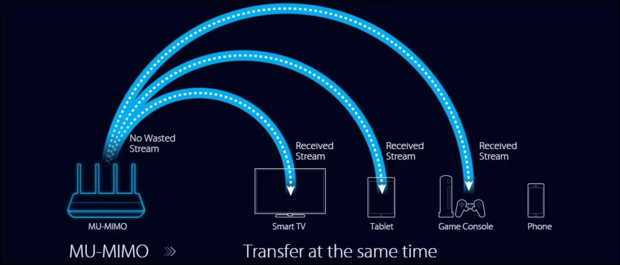
MU-MIMO, short for Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output, is a wireless technology designed to improve the efficiency of WiFi networks by enabling multiple devices to receive data simultaneously without queueing up for their turn.
It's a successor to traditional single-user MIMO (SU-MIMO), which was introduced with the release of the 802.11n standard (2008) to divide network resources spatially so they could be transmitted simultaneously through multiple antennas. In other words, MIMO made it possible to send data packets in parallel across multiple lines of communication to increase throughput.
However, regular MIMO requires the receiving device to have the same number of antennas as the transmitting access point to fully utilize the available channels and maximize data transfer rates. This rarely happens in the real world because smartphones and laptops usually have fewer antennas compared to the AP.
MU-MIMO (first introduced with the 802.11ac standard, commonly referred to as WiFi 5) addresses this imbalance by allowing the router to split its attention and antennas among multiple devices simultaneously. This way, each device gets a portion of the router’s bandwidth and antennas, which aligns more closely with the actual capabilities of typical consumer electronics.
How Does MU-MIMO Work?
Multi-User MIMO routers come in different configurations, such as 2x2, 3x3, or 4x4. These numbers describe the number of antennas used for sending and receiving data. For example, a 2x2 MU-MIMO router has two antennas for sending data and two for receiving it, while a 4x4 setup includes four antennas for both sending and receiving.
To better understand how the number of antennas impacts MU-MIMO transmission, think of a restaurant with multiple waitstaff serving customers. In a traditional SU-MIMO setup, there's only one waiter serving tables one at a time. With MU-MIMO, multiple waitstaff are available to serve several tables simultaneously. The more waitstaff (antennas) there are, the more tables (devices) can be served concurrently.
What Are the Advantages and Disadvantages of MU-MIMO?
MU-MIMO technology promises several attractive benefits, but it also has some drawbacks that impact its real-world usefulness, especially for home users:
Advantages of MU-MIMO:
- Improved speed and throughput: As we've explained, MU-MIMO allows multiple devices to communicate with the router simultaneously, and this leads to better overall network performance and faster data transfer rates.
- Reduced latency: By serving multiple devices at once, MU-MIMO helps reduce latency, so you can enjoy smoother online gaming, video chatting, and other real-time applications that require quick and responsive connections.
- Enhanced connection stability: Because MU-MIMO maintains a stable link to the network for more than one device at a time, the overall connection stability is enhanced in environments where multiple devices are operating simultaneously.
Disadvantages of MU-MIMO:
- Client device support: To take full advantage of MU-MIMO, your client devices must also support the technology. Unfortunately, many devices currently don't support MU-MIMO (more about that in the next section).
- Diminished returns in smaller networks: In environments with few devices, or where devices don't support MU-MIMO, the benefits of enabling MU-MIMO are less noticeable because the technology shines in settings with high device density.
Which WiFi Devices Support MU-MIMO?
On the transmitter (router) side, support for MU-MIMO is widespread as most WiFi 5 (802.11ac) and WiFi 6 (802.11ax) routers support MU-MIMO.
Popular examples of routers with MU-MIMO support include:
- TP-Link Archer AX55 (2x2)
- Asus RT-AX86U (4x4)
- Asus ROG Rapture GT-AX6000 (4x4)
- Netgear Nighthawk RAXE300 (4x4)
- Synology RT6600ax (2x2)
On the receiver (device) side, the situation is, unfortunately, much bleaker as MU-MIMO support is usually found only in high-end devices, such as the Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra or recently released iPhone models.
The good news is that even if your devices don't support MU-MIMO, having a router with MU-MIMO support can still benefit you. MU-MIMO's biggest selling point is its ability to handle multiple devices simultaneously, reducing congestion and improving overall network performance. This means that even devices without MU-MIMO support can experience a more stable and efficient connection when using a MU-MIMO-enabled router.
To Sum It Up
MU-MIMO technology represents a significant advancement in WiFi networking. By enabling more efficient use of network resources, it helps improve speed, reduce latency, and stabilize connections. While the technology requires compatible devices to fully exploit its benefits, even non-MU-MIMO devices can enjoy improved network performance when connected to MU-MIMO-enabled routers, which are now readily available at increasingly affordable prices.
