Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Analysis, Troubleshooting runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax wireless network adapter.
What is Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA)?
WiFi standards continue to evolve to support our growing need for faster, more reliable wireless connectivity. One of the latest features is called Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA).
Let's together untie the meaning of this tongue twister to explain how it works and why it's such a good idea to buy a router with OFDMA support.
To better understand why the OFDMA WiFi technology exists, you can imagine a single-lane road where only one car can pass at a time. Any obstruction on the road that causes any of the cars currently driving on it to slow down or stop will delay all other cars on the same road. That's not ideal considering how many users are typically connected to the same router these days. Unfortunately, that's exactly how older routers work.

When you enable OFDMA on your WiFi 6 or WiFi 7 router, you essentially increase the number of available lanes for cars to drive on, allowing multiple devices to communicate with the router at the same time without the possibility of one device slowing down all other devices.
What's the Difference Between OFDM and OFDMA?
Before OFDMA there was OFDM (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiplexing). Both of these WiFi technologies are designed to improve the efficiency and reliability of wireless communication, but OFDMA takes things to the next level by allowing more than one device to transmit data at the same time.
How Does OFDMA Work?
The analogy above creates a helpful mental model of what OFDMA is in WiFi, but it doesn't really explain how it works under the hood. So let's open it and have a quick peek, shall we?
As you may know, WiFi frequency bands (such as 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz) are divided into multiple channels to prevent signal interference. An OFDMA router takes a WiFi channel and partitions it into multiple sub-channels. It then dedicates these sub-channels (called sub-carriers) to specific devices, allowing them to communicate with the router simultaneously.
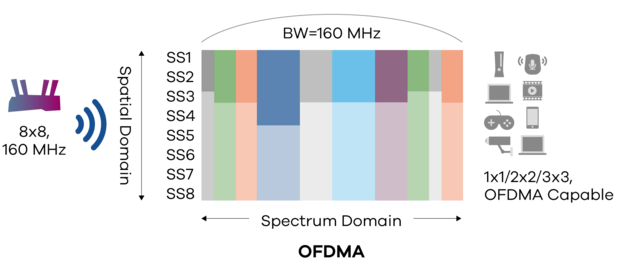

MU-MIMO and OFDMA are most effective when used together. That's because MU-MIMO is more effective for high-bandwidth applications like high-definition video streaming and online gaming thanks to its ability to increase network capacity, while OFDMA's latency-reducing capabilities make it ideal for low-bandwidth applications, such as connecting IoT devices.
| OFDMA | MU-MIMO | |
|---|---|---|
| Full name | Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access | Multi-User Multiple Input Multiple Output |
| Operating principle | Sub-divides a channel | Uses different spatial streams |
| Use of antennas | Not antenna-based | Primarily based on antennas |
| Benefit | Better frequency reuse, reduced latency, and increased efficiency | Increases capacity and efficiency |
| Application | Low-bandwidth applications | High-bandwidth applications |
| First implemented | WiFi 6 (802.11ax) | WiFi 6 (802.11ax) |
Advantages and Disadvantages of OFDMA
OFDMA is often described as the most important technology enhancement introduced in WiFi 6 because it offers many useful benefits. That said, the technology also has a few downsides you should be aware of.
Advantages
- Lower latency: Arguably the biggest advantage of OFDMA routers is their reduced latency, which is especially important in real-time applications such as IoT, online gaming, or audio/video conferencing.
- Higher throughput: By dividing a single channel into multiple subcarriers and assigning them to different users, OFDMA can increase the total maximum throughput of a network.
- Increased network capacity: By allowing multiple users to simultaneously transmit and receive data, OFDMA can increase network capacity, allowing for more devices to connect to a network without compromising performance.
- Improved power efficiency: OFDMA can help reduce power consumption in mobile devices by enabling them to transmit and receive data more efficiently, leading to longer battery life.
- Backward compatibility: When you enable OFDMA on your wireless router, you don't prevent legacy devices that don't support WiFi 6 or WiFi 7 from connecting to your network.
Downsides
- Requires a WiFi 6 or newer router: OFDMA is a feature of the WiFi 6 (802.11ax) standard and is not supported by older routers. As such, you may need to purchase a new router to take advantage of it.
- Higher CPU usage: The increased complexity of OFDMA compared with OFDM means that OFDMA-enabled routers need beefier CPUs to process the same amount of data.
Of course, the advantages of OFDMA will manifest only if your wireless network is designed and implemented correctly. That's why you should always perform a wireless network assessment using an easy-to-use WiFi analyzer app like NetSpot.
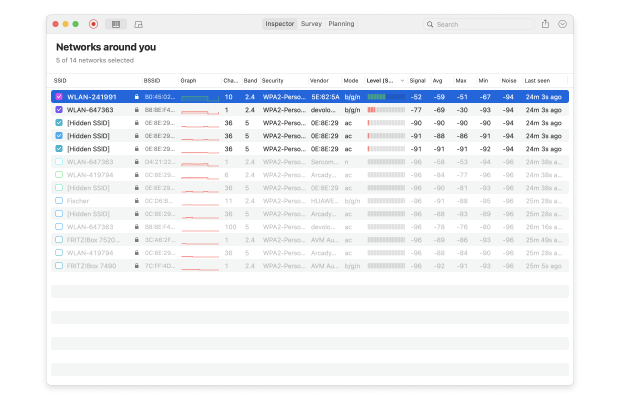
With the help of NetSpot, you can perform a site survey to identify the perfect location for your router, and you can also analyze other networks in your area so that you know how to adjust your network settings in order to reduce signal interference.
Where is OFDMA used?
Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) is used in various communication systems and technologies, owing to its efficiency in handling high data rates and supporting multiple users. Here are some primary areas where OFDMA is utilized:
- 4G LTE and 5G Networks: OFDMA is a key modulation and multiple access technique used in 4G LTE (Long Term Evolution) and 5G networks. It enables these cellular networks to offer high-speed internet and support multiple users simultaneously by dividing the spectrum into narrowband channels at different frequencies.
- Wi-Fi: Starting with the Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax) standard, OFDMA has been adopted to improve efficiency and capacity, especially in environments with high demand on bandwidth and multiple users. It allows for more efficient use of the available spectrum by allowing multiple users to share the same channel, thereby improving throughput and reducing latency.
- Broadband Wireless Access (BWA): OFDMA is used in various broadband wireless access technologies, including WiMAX (Worldwide Interoperability for Microwave Access). WiMAX, grounded in the IEEE 802.16 standard, employs OFDMA technology to provide high-speed internet across extensive regions, offering an efficient option for last-mile broadband connections.
- Digital Broadcasting: OFDMA is also employed in some digital broadcasting systems. It is beneficial in scenarios where multiple signals need to be transmitted over the same channel without interference, as it can efficiently manage the available spectrum and improve the quality of service.
- Military and Secure Communications: The robustness of OFDMA against interference and its efficient spectrum usage make it suitable for military and secure communication systems. It is used to ensure reliable communication in various conditions, including jamming environments.
OFDMA's ability to efficiently allocate bandwidth to multiple users, support high data rates, and resist interference makes it a foundational technology for modern wireless communication systems.
What cellular networks use OFDMA and OFDM?
Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and Orthogonal Frequency-Division Multiplexing (OFDM) are closely related technologies used in modern cellular networks. OFDM modulates a digital signal across multiple channels to minimize interference, whereas OFDMA, a variation of OFDM, enables concurrent network access for multiple users by distributing subsets of subcarriers to each user. Here's how they are used in cellular networks:
- 4G LTE (Long Term Evolution):
- OFDMA is used in the downlink (base station to device) to allow multiple devices to access the network simultaneously by dividing the available spectrum into smaller frequency bands or subcarriers. This increases efficiency and capacity.
- Single Carrier-Frequency Division Multiple Access (SC-FDMA), a variant of OFDM, is used in the uplink (device to base station). SC-FDMA is selected for uplink purposes due to its lower Peak-to-Average Power Ratio (PAPR) compared to OFDM, which makes it more power-efficient for battery-operated devices.
- 5G NR (New Radio):
- OFDMA is utilized for both the uplink and downlink in 5G NR, providing greater flexibility and efficiency compared to 4G LTE. This is essential for supporting the vastly increased data rates and the massive number of connections required by next-generation mobile networks.
- OFDM serves as the basic modulation scheme upon which OFDMA is built, ensuring that 5G networks are capable of supporting a wide range of services, from high throughput applications like video streaming to low latency applications critical for autonomous driving and industrial IoT.
Both OFDM and OFDMA are foundational to the operation of modern cellular networks, enabling them to support the growing demand for mobile data and connectivity. The choice of these technologies reflects a balance between the need for high spectral efficiency, capacity, and the ability to serve a large number of users and devices while optimizing for power consumption and minimizing interference.
To Sum It Up
The evolution of WiFi standards goes hand in hand with the evolution of our wireless needs. Even standard home routers now regularly connect dozens of devices to the internet, including computers, mobile devices, video gaming consoles, and smart home appliances.
OFDMA helps eliminate performance bottlenecks by assigning each connected device its own dedicated sub-channel. This makes OFDMA routers worth the extra cost for all users that seek to achieve the best online experience possible.
Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) — FAQs
OFDMA means Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access.
If you're planning to buy a new WiFi router, then you should prioritize models that offer OFDMA support because the technology can significantly increase the efficiency of your WiFi network.
Yes, OFDMA makes a huge real-world difference, especially when it comes to network latency. In fact, the technology has been demonstrated to deliver a latency reduction of up to 99 percent.
Definitely! If your WiFi router supports OFDMA, then we strongly recommend you enable it to take advantage of its latency-reducing and efficiency-increasing benefits.
