Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Analysis, Troubleshooting runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11be/ax/ac/n/g/a/b wireless network adapter. Read more about the 802.11be support here.
How to troubleshoot Wi-Fi Interference with NetSpot
Wi-Fi might feel like magic, but it’s all about science and radio waves. Even this advanced technology can be disrupted by Wi-Fi interference. With NetSpot, you can easily identify the causes of interference and optimize your Wi-Fi.
When your devices use WiFi to connect to Internet the signals are sent with radio waves and despite of all advanced features wireless interference can happen. As a result your wireless connection may become weak and unreliable.
- What Is Wireless Interference and How Does It Affect Wi-Fi Performance?
- Positioning of a Wireless Router
- Physical obstacles
- Frequency Interference (Other wireless appliances)
- Interference from competing Wi-Fi networks
- Other Obstacles
- How to Detect and Eliminate WiFi Interference with NetSpot
- WiFi Interference — FAQs
What Is Wireless Interference and How Does It Affect Wi-Fi Performance?
Wireless interference occurs when external factors disrupt the radio waves your Wi-Fi relies on to communicate with devices. These disruptions, known as radio frequency interference, can lead to delays in connection and data transfer, slow network speeds, and poor signal strength, making your internet experience frustrating and unreliable.
Wi-Fi signals are transmitted via radio frequencies, similar to how radios or TVs receive signals. When other devices or obstacles interfere with these frequencies, the connection weakens or becomes unstable. Here are some common sources of wireless interference:
- Router Placement: Proper router positioning, as described in the dedicated section, is essential to avoid signal loss and interference.
- Physical Barriers: Walls, floors, and materials like concrete or metal absorb or block Wi-Fi signals, causing dead zones.
- Competing Devices: Baby monitors, cordless phones, and garage door openers often operate on the same frequencies as Wi-Fi, disrupting the signal.
- Appliances: Kitchen devices like microwaves can emit signals that interfere with Wi-Fi, particularly on the 2.4 GHz band.
- Overlapping Networks: In crowded spaces like apartment buildings, multiple Wi-Fi networks on the same channel create congestion and interference.
By understanding the nature of signal interference and what causes WiFi interference, you can address these issues effectively.
Positioning of a Wireless Router
Obviously the way you position your wireless router will have effect on your coverage area and WiFi signal strength. Incorrect placement can lead to weak signals, dead zones, and slow network speeds.
How to troubleshoot :
- Position your wireless router in the middle of the space where the network is needed. If the router is placed off-center, the signal won't be even, leaving some areas with poor coverage.
- Ensure the router antenna is vertical. While many antennas can be adjusted, a straight-up position typically provides the best performance. For routers with multiple antennas, angling them differently, such as one vertical and one diagonal, can enhance signal coverage.
- Place your router on an elevated surface. A desk or shelf will provide better reception compared to placing it on the floor. Avoid positioning it near electronic devices like microwaves or cordless phones, as well as metal objects or mirrors, which can cause radio frequency interference.
- If you have multiple floors, position your wireless router on a higher floor. This helps the signal radiate downward more effectively, improving coverage across all levels.
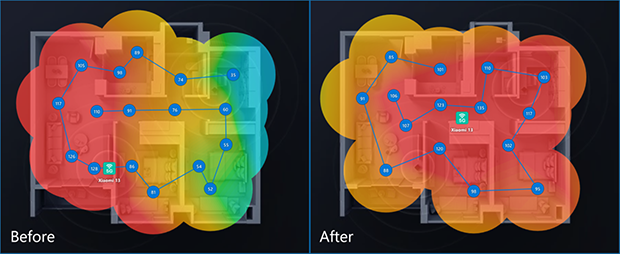
To get the most out of your Wi-Fi setup, use tools like NetSpot to analyze your network and create a heatmap. This allows you to visualize signal strength and make data-driven adjustments to position your wireless router optimally.
Physical obstacles
The construction of a building, whether it’s a home or office, significantly affects the range and speed of wireless communication. One of the main WiFi interference causes is the presence of physical obstacles that weaken or block the radio waves used by Wi-Fi. Understanding what interferes with WiFi is critical for optimizing your network’s performance.
Different materials have varying levels of impact on Wi-Fi signals. While wood and glass cause minimal disruption, materials like concrete, brick, and metal can drastically degrade signal quality and lead to slow network speeds. For example, mirrors can create high levels of wifi signal interference by reflecting and scattering radio waves. Here’s a breakdown of how different barriers affect Wi-Fi:
| Type of Barrier | Interference Level |
| Wood | Low |
| Plaster | Low |
| Synthetic Material | Low |
| Glass | Low |
| Water | Medium |
| Bricks | Medium |
| Marble | Medium |
| Concrete | High |
| Metal | High |
| Mirror | Very High |
How to troubleshoot :
If you suspect physical obstacles are causing wireless interference, there are a few simple steps you can take to improve signal strength:
- Relocate the Wireless Device: Even moving a Wi-Fi routers or device a few feet can have a noticeable impact on signal quality. Adjusting the antenna direction can also help reduce WiFi interference.
- Add a Wi-Fi extender : For spaces where physical obstacles cannot be avoided, a Wi-Fi extender can re-transmit the signal, ensuring better coverage even in remote areas. This is particularly useful for overcoming WiFi signal interference caused by thick walls or multiple floors.
- Consider Powerline Adapters: In larger spaces with challenging layouts, Powerline adapters use your existing electrical wiring to extend the network. Pairing them with a Wi-Fi extender provides a reliable solution for areas with high wireless interference.
By understanding what causes WiFi interference and how to address it, you can significantly improve your network performance. Tools like NetSpot can help you detect WiFi interference by providing detailed insights into signal strength and coverage, making it easier to overcome obstacles and maintain a reliable wireless connection.
Frequency Interference (Other wireless appliances)
Many devices, even those not directly connected to your Wi-Fi network, can cause frequency interference by operating on the same 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz spectrum. This interference disrupts the radio waves your Wi-Fi depends on, meaning the network may be slower or disconnect, resulting in frustratingly poor performance. Recognizing what causes WiFi interference and addressing it is key to maintaining a reliable connection.
Devices such as Bluetooth gadgets, cordless phones, and baby monitors commonly operate on the 2.4 GHz band, directly competing with your Wi-Fi for bandwidth. Similarly, appliances like microwaves emit radio frequency noise that disrupts signals, especially for older routers. Even less obvious culprits, like poorly wired satellite dishes, power sources, or external monitors, can cause WiFi signal interference, further degrading network quality.
To help you identify and address what interferes with WiFi, here’s a detailed table showing the most common interference sources, their impact on your network, and practical solutions:
| Interference Source | Impact on Wi-Fi | Solution |
| Microwave | Causes interference, especially in the 2.4 GHz spectrum, slowing the network or causing disconnects when in use. | Place the router away from the microwave, especially for older routers operating on 2.4 GHz. |
| Cordless Phonee | Interferes with 2.4 GHz spectrum during active calls, leading to large signal disruptions. | Use DECT phones or move the router away from cordless phones. |
| Poorly Wired Satellite Dish | Can cause significant signal interference if improperly wired or with deteriorating cables. | Ensure proper wiring and replace deteriorating cables for satellite dishes. |
| Other Wireless Devices | Generates interference from wireless speakers, baby monitors, and devices on 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz. | Keep devices like wireless cameras and speakers away from the router; switch to 5 GHz if possible. |
| Power Sources | Creates interference from nearby power lines, electrical tracks, or breaker boxes. | Avoid placing the router near power lines or electrical equipment. |
| Poorly Shielded Cables | Introduces interference if cables are poorly shielded; can be resolved by replacing cables. | Replace poorly shielded cables and avoid running cables parallel to power lines. |
| External Monitors and LCD Displayss | Causes interference in the 2.4 GHz band (channels 11-14), worsened with connected external monitors. | Move the router to a different location or switch to 5 GHz or lower 2.4 GHz channels. |
| Neighbors' WiFi | Strong overlapping networks can create signal congestion and reduce network performance. | Change your Wi-Fi channel or use 5 GHz to avoid overlapping interference. |
How to troubleshoot :
- It is always a good idea to turn off and unplug electronic devices temporarily to see how it affects the wireless interference issue.
- Another option is moving the wireless devices.
- If you feel like there is a specific wireless device causing the issue, check if it offers options to switch WiFi channels. Try switching to the robust 5 GHz frequency.

- If it still doesn't really help you can try the updated models with better radio wave noise shielding.
Frequency interference can also be fixed by changing the channel for the WiFi router. The channel can be usually set from 1-11 for the broadcast frequency.

The more expensive and advanced routers can broadcast at 5 Ghz frequency, which is great.
By understanding what causes WiFi interference and how to detect it, you can implement these solutions to ensure your network may no longer be slower or disconnect unexpectedly.
Interference from competing Wi-Fi networks
When multiple Wi-Fi networks in the same area operate on the same frequency channel, they often cause WiFi signal interference by competing for bandwidth. This is a common issue in cities and large apartment buildings, where overlapping networks result in slower speeds, dropped connections, and general instability. In North America, Wi-Fi networks typically use 11 frequency channels, while other regions may have up to 13.
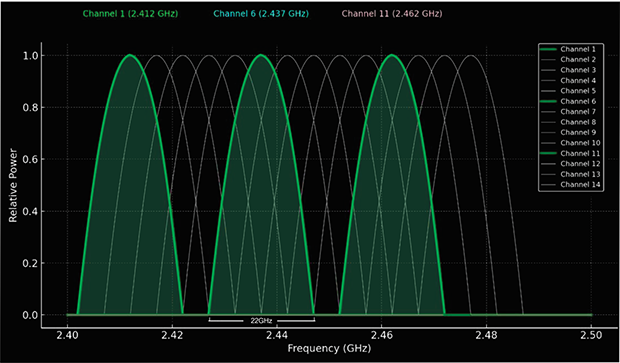
When several networks share the same channel, wireless routers interference occurs, leading to degraded performance.
Types of WiFi Interference
Wi-Fi interference can generally be categorized into three types:
- No Overlap: Networks use completely separate channels, resulting in no interference and optimal performance.
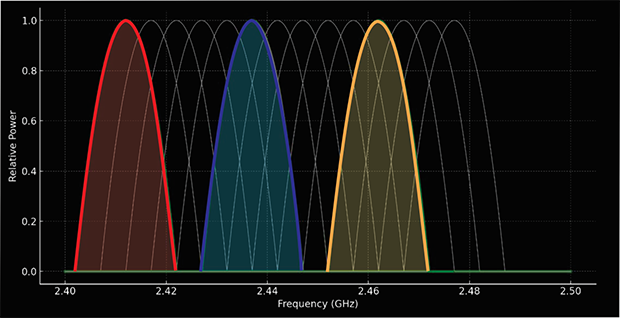
- Full Overlap: Networks use the same channel but can negotiate access due to Wi-Fi's collision avoidance protocols, minimizing interference compared to partial overlap.
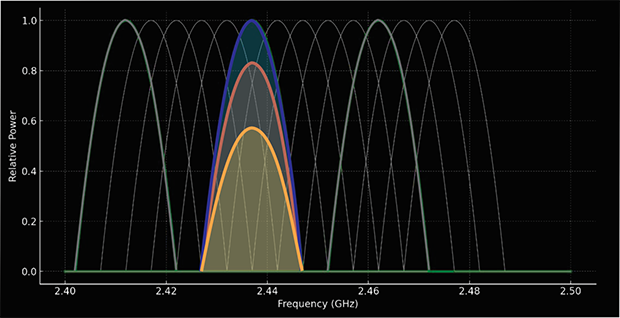
- Partial Overlap: Networks use adjacent channels, which creates significant interference as signals are seen as noise by each other.
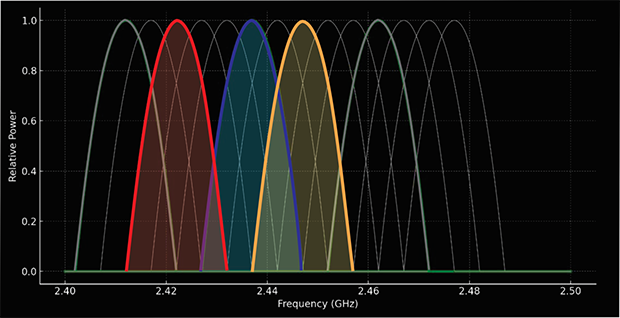
The chart below illustrates how network performance varies based on the type of channel overlap:
| Channel Overlap Type | Impact on Network Performance |
| No Overlap | Maximum performance, no interference. |
| Full Overlap | Moderate performance drop, but better than partial overlap. |
| Partial Overlap | Significant performance drop due to high interference. |
How to troubleshoot
Modern Wi-Fi routers often include features to identify and switch to the least crowded channels automatically. Check your router's user manual to enable this option. If automatic switching doesn't resolve the issue, try setting the channel manually and run speed test to determine which one offers the best performance.
Use a WiFi interference scanner like NetSpot to analyze nearby networks and identify what causes WiFi interference, allowing you to select an optimal channel. For Android users, it provides a powerful tool to analyze Wi-Fi networks, perform surveys, and test internet speed directly from your smartphone or tablet, making it easier to pinpoint what interferes with WiFi in your environment.

Analyze WiFi networks around you, perform wireless surveys, and test Internet speed — all with just a phone or tablet in your hands.
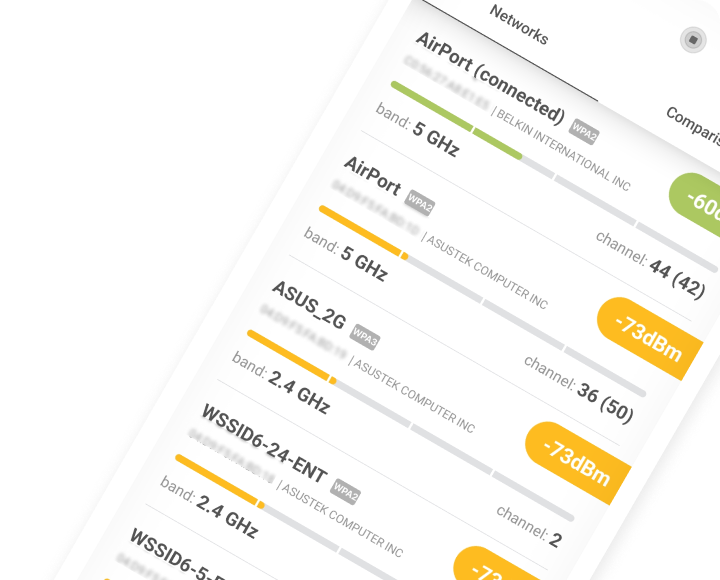
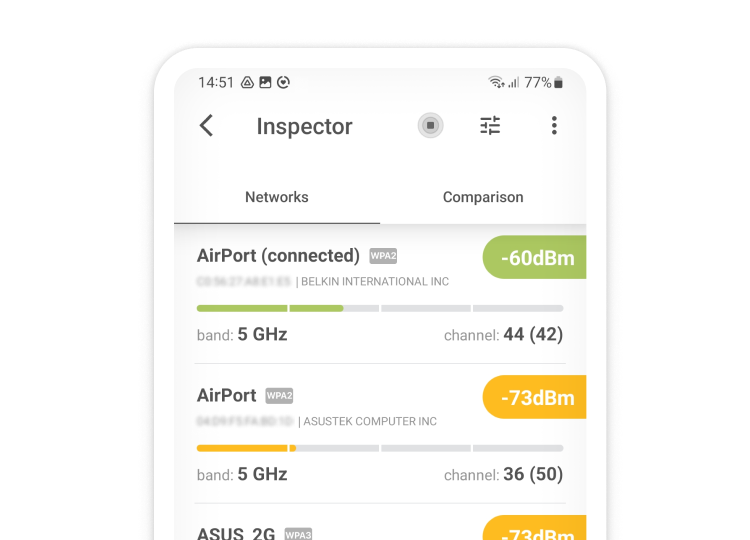
Other Obstacles
Wi-Fi performance can also be influenced by less common obstacles that don’t fit traditional categories but still cause wireless interference:
- Hearing Aids: Devices like hearing aids can cause localized disruptions when placed too close to the Wi-Fi signal source.
- Power Lines and Stations: While not a direct source of interference, these can create electromagnetic noise that impacts your connection.
- Blasting Areas (e.g., Mines): High-intensity operations in such areas can disrupt nearby signals.
- Hand Position: Even the way you hold your phone can block antennas and cause WiFi signal interference. Adjust your grip to improve signal strength.
How to Detect and Eliminate WiFi Interference with NetSpot
When you experience network issues, NetSpot сan help you determine whether wireless interference is the cause. It scans nearby Wi-Fi networks, visualizes channel usage, and provides information that enables you to optimize your router settings for better performance and reducing congestion from overlapping networks.
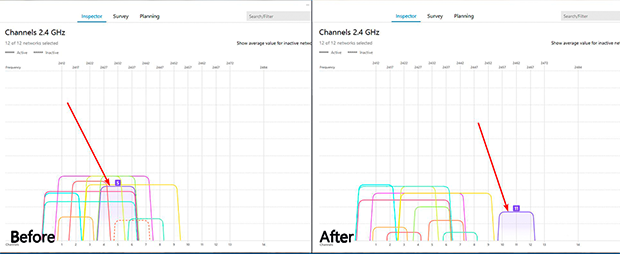
By performing site surveys, you can pinpoint weak signal areas and, if physical obstacles are causing problems, identify the ideal router placement to ensure maximum coverage.
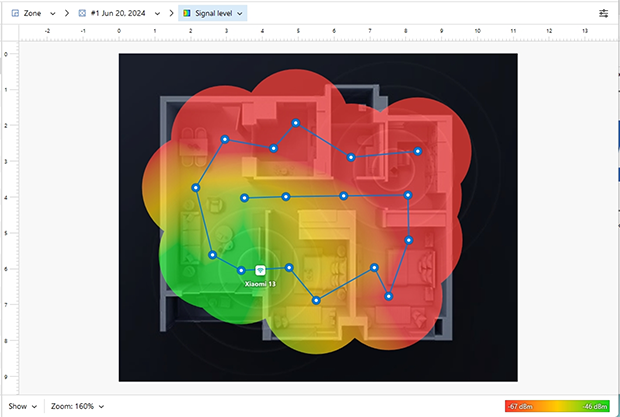
In areas with severe interference, consider upgrading to a dual-band 802.11ac or 802.11ax router, which offers better performance and the ability to use the less crowded 5 GHz band. For multi-level buildings, setting up additional routers in bridge mode can eliminate coverage gaps and reduce WiFi interference causes related to overlapping networks.
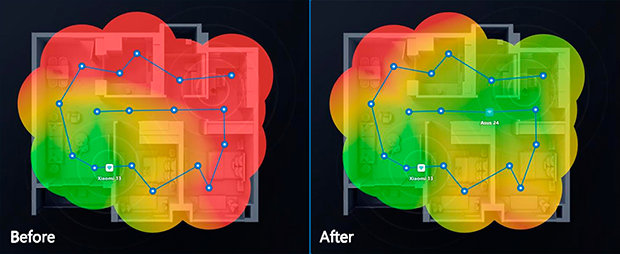
By understanding how to detect WiFi interference and using tools like NetSpot, you can tackle even the most challenging network problems, ensuring fast, reliable, and interference-free connections.
WiFi Interference — FAQs
To stop WiFi interference, start by repositioning your wireless router to a central, elevated location, away from walls, mirrors, and metal objects. Use a WiFi interference scanner like NetSpot to identify overlapping networks and choose the least crowded channel. If physical barriers are a problem, consider using Wi-Fi extenders or Powerline adapters to improve coverage in weak areas.
If there is physical interference with your WiFi signal, you can troubleshoot it by performing the following:
- Estimate the very middle of your wirelessly covered area and put your router in it. See how that affects the signal.
- Try setting up the router antenna vertically.
- Put the router on an elevated surface, e.g. a desk.
Dense materials such as concrete, metal, and brick are the strongest blockers of Wi-Fi signals. Mirrors also create high levels of WiFi signal interference by reflecting and scattering radio waves. Positioning your router away from these materials can improve signal strength.
Every building has walls and furniture and other possible obstacles in the way of a wireless signal. See if you can mend the poor WiFi signal by:
- Moving the wireless device to a different spot. Even a couple of feet can make a huge difference in WiFi signal strength. Even readjusting the antenna might help.
- Adding a WiFi extender to your network.
- Getting a Powerline adapter. These adapters are very efficient for larger spaces with thick walls.
Wireless interference occurs when external factors disrupt the radio waves used by Wi-Fi to communicate. This can result in slow speeds, dropped connections, and weak signals. Common sources include physical barriers, overlapping networks, and devices operating on similar frequencies.
Start with enabling channel auto-switching on your WiFi router. Look into its user manual if you are not sure how to do it. If the speed is still slow, try setting up a channel manually and perform a speed test. Try NetSpot — it is a great WiFi Channel Scanner.
With the help of NetSpot you can see which wireless channels other networks are using, and what channel might be a better solution for your WiFi network.
