How to Get The Best WiFi Coverage
Reliable Wi-Fi is necessary for seamless internet access at home or in the office. Whether streaming in the kitchen, hosting video calls in the conference room, or gaming in the living room, strong Wi-Fi coverage ensures fast speeds, minimal interruptions, and maximum productivity.
To get the best WiFi coverage, rely on NetSpot to expand your WiFi to get the widest and fastest coverage possible.
What Is WiFi Coverage?
WiFi coverage refers to the area within which you can connect to a wireless network and access the internet without experiencing issues with slow speeds or connection drops.
Ideally, you want your WiFi coverage to extend across every square inch of your home or office, creating a reliable, uninterrupted online experience. This includes high-traffic areas where you frequently use devices, as well as less frequently used spaces. After all, you never know when you might want to stream a movie from the comfort of your attic or answer emails on the patio.
The problem is that WiFi coverage is almost never perfectly even due to factors like the layout of your space, the type of your WiFi router, and any potential physical obstructions like walls or large furniture. Such obstacles can create dead zones, areas where the WiFi signal is weak or non-existent. That's where the process of WiFi coverage analysis comes in to supply you with the information you need to ensure a strong, reliable signal can reach every corner of your space.
It’s important to remember that Wi-Fi signals are transmitted via radio waves, which means their coverage area largely depends on the frequency used. Higher frequencies, like 5 GHz and 6 GHz, typically offer faster data transfer speeds but cover a smaller area compared to 2.4 GHz. To better understand the differences between these frequency bands, refer to the table below, which provides data on Wi-Fi coverage at various frequencies.
| Frequency | Indoor Coverage Area | Outdoor Coverage Area |
| 2.4 GHz | Up to 2,000 sq. ft. | Up to 3,000 sq. ft. |
| 5 GHz | Up to 800 sq. ft. | Up to 1,500 sq. ft. |
| 6 GHz | Up to 400 sq. ft. | Up to 800 sq. ft. |
Analyze Your WiFi Coverage
The most important part of any endeavor is gathering accurate information and analyzing the existing situation. Before we start a long trip, we need to plan out the roads to use, where the rest stops will be, and places to sleep along the way. Similarly, when it comes to improving WiFi coverage, diving straight into upgrades or changes without proper analysis can be counterproductive.
Planning how to get the best WiFi coverage requires a step-by-step approach. The first step is understanding the current state of your WiFi coverage. You need to identify where the network reaches, evaluate signal strength in different areas, and locate weak spots or dead zones.
A WiFi analyzer is an essential tool for this task. It analyzes every available Wi-Fi network, identifying key factors such as interference from neighboring networks, channel congestion, and overall network performance.
This helps uncover the true causes of issues, which is especially important before making changes like upgrading the router or switching channels. Without such analysis, efforts might be wasted if the root problem, such as interference, remains unresolved. Only by conducting a comprehensive analysis with a WiFi analyzer can you confidently decide what changes will make the most significant difference.
A Wi-Fi analyzer works by taking a poll of each of the Wi-Fi networks it can reach. By transmitting data across the network, it measures how fast the network is, and checks the signal strength of the Wi-Fi radio waves. A good WiFi analyzer isn’t limited to just checking speed.
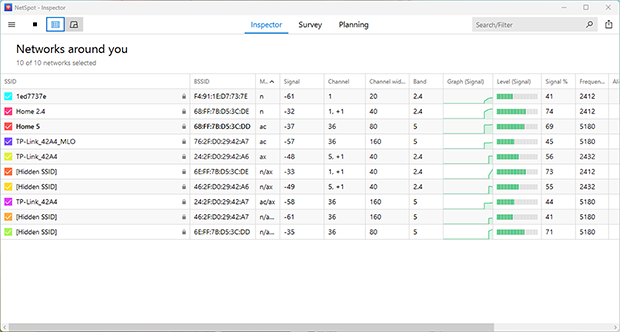
It goes beyond basic checks. Instead of focusing on speed alone, it collects and visualizes in-depth data about channel usage, detects coverage gaps, and identifies interference sources, helping pinpoint and address the root causes of connectivity issues.
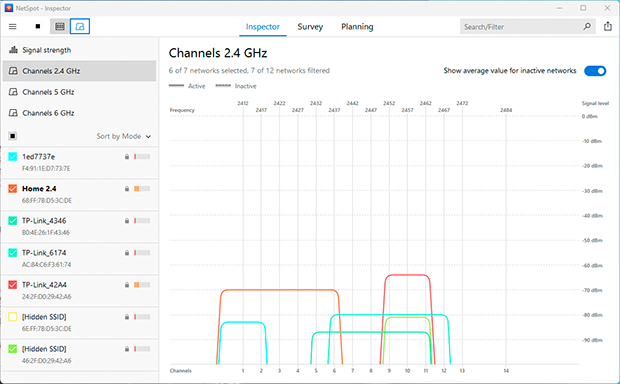
It also reveals the frequency bands in use, highlights overlapping channels, and measures signal-to-noise ratios across multiple networks.
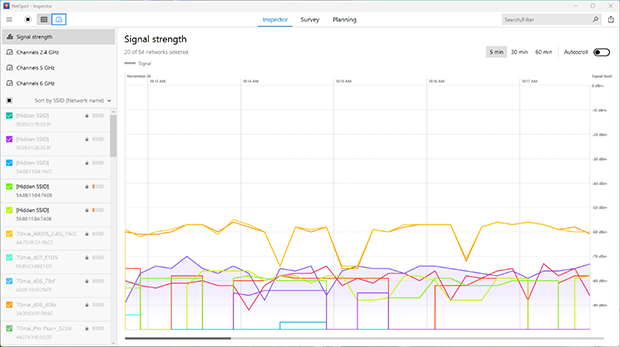
These insights enable you to fine-tune settings and optimize your wireless environment for a more stable and reliable connection.
Good WiFi analyzer can display that information in an easy to understand table format, or if it’s really good by showing off the information on a map. This is why NetSpot works so well. It’s a WiFi analyzer that works with Windows, macOS, and Android devices. NetSpot provides incredible information gathering tools with a simple interface that anyone can understand.
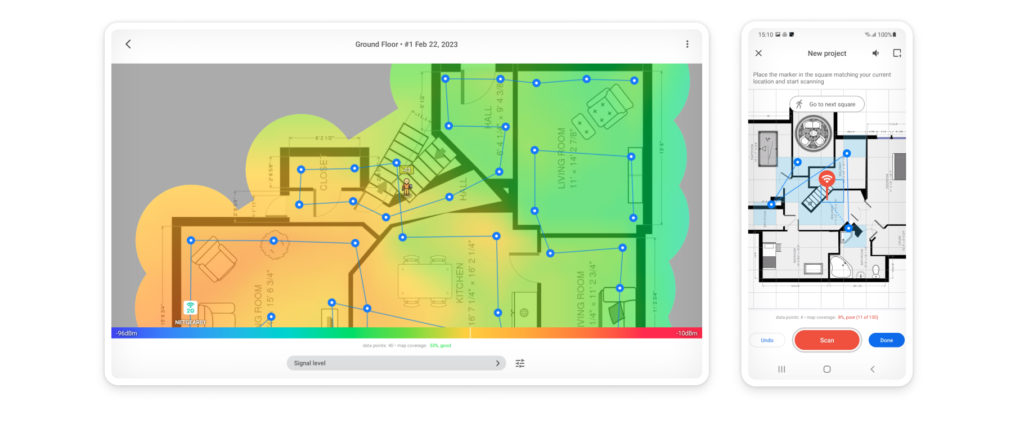
For registered users, NetSpot can use the information to build heat maps.The application is capable of creating around 20 different heatmaps, which allows for a comprehensive overview of network conditions.
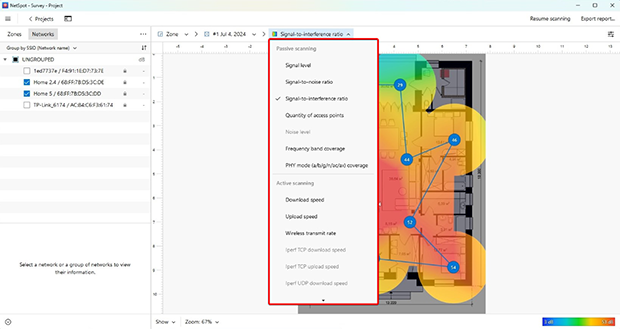
By uploading an image of the floor layout of the space we’re scanning into NetSpot and taking samples of the WiFi in different locations, NetSpot shows how the signal strength looks across the entire location. This lets us know exactly what spots are strong, what are weak, and where we need to increase our coverage.
By using a tablet or cell phone, we can quickly move from place to place in our location and get readings on the WiFi network. With this information we can scan specific spots to get an exact measurement for where we want to know about the strength or weakness of our network, or make multiple readings over time to compare one to another.
Analyze WiFi networks around you, perform wireless surveys, and test Internet speed — all with just a phone or tablet in your hands.
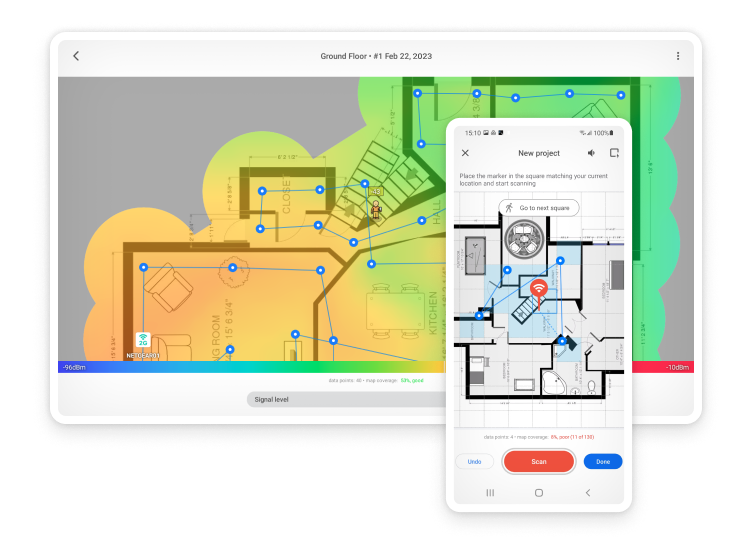
What Troubles/Issues Can You Face And How To Fix Them
WiFi networks sometimes don’t work the way we want. We have a device that won’t connect, or a laptop that seems as slow as a phone modem when we communicate with the Internet. We need to combine troubleshooting techniques with a WiFi analyzer to let us know if our results are doing any good.
Here’s a few things we can do to troubleshoot WiFi issues:
- Update device drivers. Make sure the latest device drivers have been installed so the computer or laptop can work the best with the WiFi hardware. Computers aren’t made perfect from the start, and developers learn from their mistakes to make the software that runs them a little better.

- New drivers can help improve WiFi networks by helping the connection between the hardware and the operating system be more efficient and effective.
- Replace the WiFi hardware. For a USB WiFi adapter, sometimes the contacts are not making a good connection, or the USB port itself is flawed. At times moving the USB device from one port to another can make a difference.

- Other times it’s the device itself we’re using that’s deficient in some way. The best way to troubleshoot hardware issues is to replace the device in question, then test the network and see how the WiFi network operates.
- Signal to noise ratio. The more WiFi networks in a location, the more signals our computers and devices have to parse out.
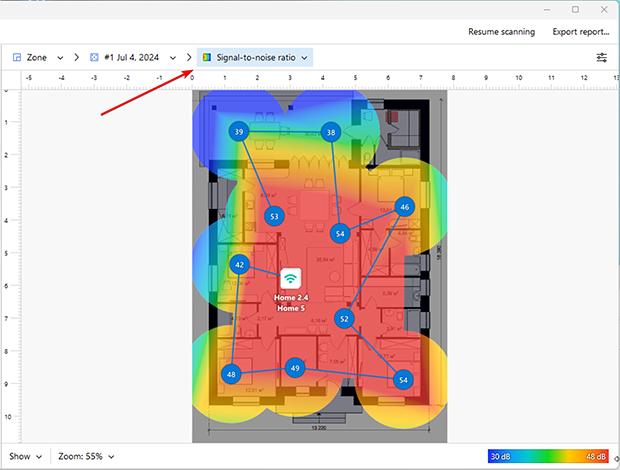
- WiFi signals work on channels, and if all of the networks are in one channel, it can be like trying to hear a friend in a room full of noisy people. Setting the WiFi network to a different channel can help reduce the amount of noise our devices have to get through.
- Device conflict. Some Bluetooth devices can interfere with the frequency of a WiFi network. For example, connecting a Playstation 4 controller via Bluetooth to a computer that only works on the 2.4 Ghz network can disconnect the computer from the WiFi network.
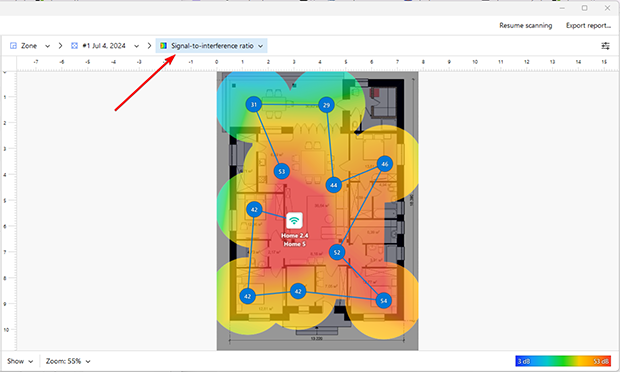
To check on issues such as Signal to interference (SIR), channel settings, and other statistics, use NetSpot to learn what the WiFi network is doing, and troubleshoot the WiFi issues you’re having. It can help narrow down where the problem is to help you fix what’s wrong.
WiFi Boosters/Extenders
To boost our WiFi signal, we can use a WiFi extender, also known as a booster to expand the reach of our network.
A typical WiFi booster can come in different types, but usually they take two main forms:
- Repeaters. Repeaters work by taking the signal from the WiFi network, and passing it back and forth between the main WiFi router and the device. It’s like a post office that takes your message, forwards it onto your friend, and then takes their letter back and returns it to you.
- Mesh. With a mesh network, multiple devices work together to pass messages back and forth between them. In this case we’re not relying on just one friend to pass along a letter back and forth, but a whole range of people who take our letters and pass them around until they reach their destination. As we move through our building in a mesh network, the mesh device that has the strongest signal with it can connect and pass along the data to the main router device. This is a method to boost WiFi networks that Google uses in their WiFi devices.
The problem is where to put the WiFi booster to get the best coverage for the network. We could just guess. Or use the power of NetSpot to map out the WiFi signal across our location. By sampling the strength of the WiFi network in different locations, NetSpot can help us find the weak areas. By knowing where the signals are weakest or have the most noise to signal ratio, we can figure out how to boost our WiFi to extend its reach.
How To Boost WiFi
Once we’ve identified all of the weak spots, then it’s time to boost our WiFi signal. The most important tips are in the link provided below, but NetSpot is essential for making sure we get the position right. It’s not enough just to put in our WiFi mesh network or repeaters and hope for the best. We need information to understand how adding in devices affect the network.
By using NetSpot, we can test the before and after effects of our changes.
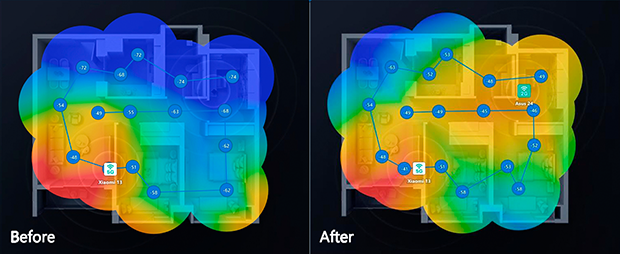
We can add repeaters or mesh network devices to the location, and once they’re connected to the router, there is a new WiFi network configuration.
Each time we add a new repeater, update the device drivers, or find a new position for our router, scan the location again with NetSpot so we can see how the changes affected the network. With this information, we can improve the WiFi network to get the maximum range and throughput. Information is power — and with NetSpot, you’ll have all of the information and power you need to make the WiFi network work to its best ability.
How to Get The Best WiFi Coverage — FAQs
The best way to analyze Wi-Fi coverage is by using a Wi-Fi analyzer app like NetSpot. It allows you to visualize your network's signal strength, identify weak spots, and create detailed heatmaps. By uploading your floor plan into NetSpot and taking measurements, you can determine where your network performs well and where it needs improvement.
Yes, there are several apps that can measure WiFi coverage. NetSpot, for example, is a popular option that runs on Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS. It provides comprehensive information about signal strength, frequency type, signal-to-noise ratio, and other useful statistics in an easy-to-understand format.
Extended WiFi coverage refers to a coverage area created using a WiFi extender, a device that takes the signal from your primary router and retransmits it to areas where the signal is typically weak or non-existent.
Yes, here’s how:
- Place your router near a window facing the outdoor area.
- Use an outdoor WiFi extender to amplify the signal.
- Install a mesh system with nodes specifically designed for outdoor use. NetSpot can help you map your WiFi signal to ensure even outdoor coverage.
Wi-Fi dead zones can be identified using a Wi-Fi analyzer like NetSpot. It shows you areas with poor or no signal on a Wi-Fi heatmap. Once identified, you can fix dead zones by repositioning your router, adding a Wi-Fi extender, or upgrading to a mesh system for better coverage.
Wi-Fi boosters, or extenders, take the existing signal from your router and retransmit it to cover weak areas. Mesh systems, on the other hand, use multiple nodes to create a single seamless network, offering better performance and coverage for larger spaces or complex layouts.
Yes, a Wi-Fi analyzer like NetSpot can significantly improve your network performance by identifying issues such as dead zones, interference, or poor channel selection. It provides actionable data that helps optimize your network setup for better speed and coverage.