Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Analysis, Troubleshooting runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax wireless network adapter.
5 Powerful Ways to Extend Your WiFi Range
One of the most common WiFi troubleshooting goals is to extend the range of a WiFi network, and we explain several methods on how to do just that in this article.
Unlike a traditional wired network, a wireless network offers flexibility and convenience, allowing devices to stay connected without physical cables. However, this convenience comes with its own challenges, the most common being limited Wi-Fi range and weak signal strength in certain areas.
If your Wi-Fi fails to cover every part of your home or office, or if you frequently experience unstable connections, it’s time to consider ways to extend Wi-Fi coverage and boost signal strength.
Fortunately, there are several effective solutions, ranging from simple adjustments to more advanced upgrades. In this article, we’ll explore the best ways to expand your Wi-Fi range, ensuring a stronger, more reliable connection wherever you need it.
How to Extend WiFi Range
If you’re struggling with weak Wi-Fi signal or limited wireless coverage, there are several practical ways to deal with it. Most Wi-Fi networks face similar common challenges, and luckily, the solutions aren’t overly complicated.
Depending on your particular issue, you can pick something simple or opt for equipment upgrades if needed. Below, we’ll break down the most popular and reliable methods for boosting your Wi-Fi signal and extending your network’s reach.
Method 1. Find a Better Place for Your Router
Even the best WiFi router available won’t be able to provide satisfactory coverage if it’s positioned poorly. As you may know, the WiFi signal is affected by all kinds of interference, including walls, furniture, electronic appliances, and other wireless devices. While it may seem convenient to hide the router inside a cabinet, the strength of your signal will suffer considerably. Different physical obstacles absorb the signal at varying degrees, leading to coverage issues.
How Physical Obstacles Affect WiFi Signal
| Obstacle | Signal Loss (dB) | Impact on WiFi |
| Drywall | 3–5 dB | Minimal impact |
| Wooden doors | 4-6 dB | Slight interference |
| Glass (plain) | 5-8 dB | Moderate signal loss |
| Brick walls | 10-15 dB | Significant interference |
| Concrete walls | 15-25 dB | Major signal degradation |
| Metal surfaces | 20-50 dB | Blocks most of the signal |
| Mirrors | 10-20 dB | Reflects and distorts signal |
As you can see, thick walls, metal surfaces, and even mirrors can severely weaken your WiFi signal. Simply finding a new location for your wireless router can have a dramatic impact on your WiFi signal for a variety of reasons.
💡 Pro Tips for Router Placement
- ✔ Position your router in a central spot to ensure consistent signal coverage throughout your space.
- ✔ Avoid placing it inside cabinets, drawers, or behind thick walls, as these can significantly weaken the signal.
- ✔ Keep the router elevated, such as on a shelf or mounted high on a wall, for better signal distribution.
- ✔ Minimize interference from electronic devices like microwaves, cordless phones, and Bluetooth gadgets.
- ✔ Use a WiFi analyzer to determine the best possible location based on actual signal strength.
You can easily find a better place for your router to extend your WiFi range using a WiFi analyzer and heat mapping tool like NetSpot.
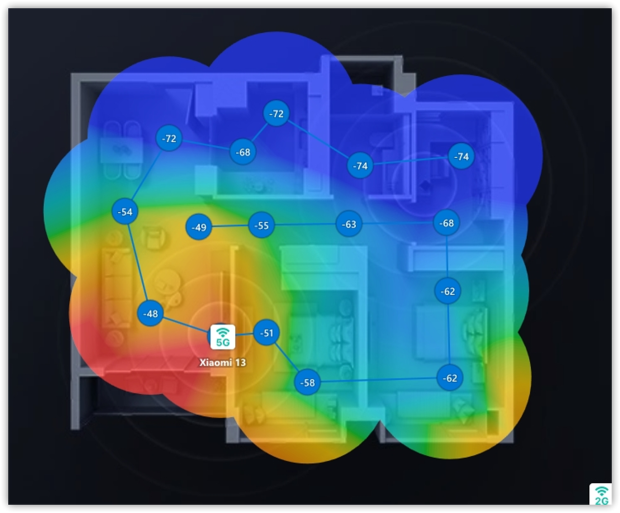
With its WiFi Heatmaps feature, you can visualize your network coverage, pinpoint weak spots, and identify “dead zones” where the signal is lost. This allows you to make data-driven decisions about router placement for optimal performance.
Method 2. Update your router’s firmware
Keeping your device’s firmware current can help you obtain the best WiFi signal that the router can provide. Just like computers and smartphones, routers receive updates from their manufacturers, and it’s important that you install them as soon as possible to keep your router secure and in good working order.
Depending on the manufacturer there are different methods that need to be used to update your firmware. The good news is that most routers make the update process easy, and you should be able to accomplish it directly from the administrator interface.
Some routers even have a companion app for Android and iOS mobile devices, allowing you to take care of firmware updates with a simple tap.
And some routers can be configured to automatically update the firmware. If your router is in that category, it is strongly recommended that you take advantage of the auto updates. Even if the update doesn’t solve your problems with insufficient WiFi range, you can at least be happy, knowing that your router is more secure.
💡 Pro Tips for Updating Firmware
- ✔ Back up your router settings before updating, so you can reinstate them if any problems occur.
- ✔ Use a wired connection (Ethernet) during the update to prevent connectivity issues or interruptions.
- ✔ Restart your router after updating to ensure all changes take effect properly.
- ✔ Review the update changelog — manufacturers often include performance improvements and bug fixes that might enhance your network stability.
Method 3. Use the 5 GHz Band
Dual frequency routers offer you the choice of 5.0GHz and 2.4GHz bands. You might find that switching to the 5.0GHz band improves your WiFi range as it will incur less interference from other electronic devices since the frequency is used less often.

Because of its higher frequency, the 5 GHz band is able to offer superior speeds and, in some situations, better signal strength. Its biggest downside is its shorter range and inferior ability to penetrate solid objects.
However, if you live in a densely populated area, surrounded by WiFi networks broadcasting on 2.4 GHz, the 5 GHz band is an easy choice.
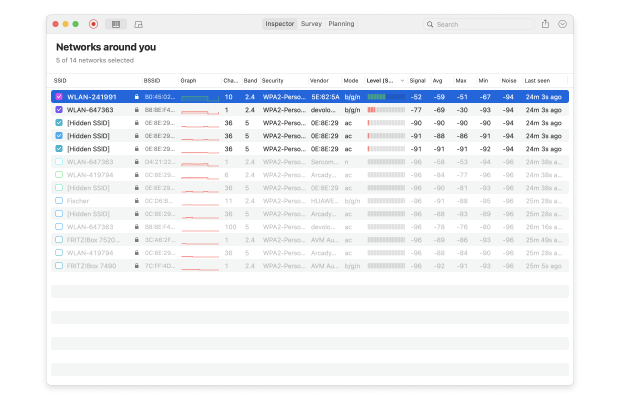
To learn more about nearby WiFi networks and the bands they broadcast on, you can use NetSpot’s Inspector Mode, which quickly gathers a wealth of information about all WiFi networks within reach and presents it in the form of an interactive table.
💡 Pro Tips for Using WiFi Band
- ✔ Use the 5 GHz band for speed, but 2.4 GHz for range. The 5 GHz band is great for streaming and gaming, while 2.4 GHz provides better coverage over longer distances.
- ✔ Upgrade to a tri-band router. Newer tri-band routers feature one 2.4 GHz band and two separate 5 GHz bands, reducing congestion and optimizing performance for multiple devices.
- ✔ Consider Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E. These latest standards improve speed, device handling, and range, while Wi-Fi 6E introduces the 6 GHz band, which offers even lower interference and higher speeds.
- ✔ Check your device compatibility. Some older devices do not support 5 GHz WiFi, so ensure that all your essential devices can connect before switching.
- ✔ Use a WiFi analyzer. Tools like NetSpot help determine the best band for your environment and highlight interference sources that might affect performance.
Method 4. Change Your WiFi Channel
Just like walkie-talkies, all WiFi routers broadcast on a certain channel. In the 2.4 GHz band, there are 11 channels, but only channels 1, 6, and 11 are spaced far enough from one another to not overlap.
The remaining channels can be used, but they are more likely to experience interference resulting in slowdowns, particularly in heavy use, so it’s important to use the least congested non-overlapping channel available in the 2.4 GHz band.
Fortunately, far more channels are available in the 5 GHz (45 channels) and 6 GHz bands (seven 160 MHz, fourteen 80 MHz, twenty-nine 40 MHz, and fifty-nine 20 MHz channels). As a result, issues with their overlapping are much less common.

In any case, a WiFi analyzer such as NetSpot can survey your own network as well as other networks whose signals may overlap with yours and make it easy to determine which channel you should use.
Once you know which channel is the most suitable, you can sign in to your router’s administrator interface and configure it to use it. Your router will then restart to apply the new settings.
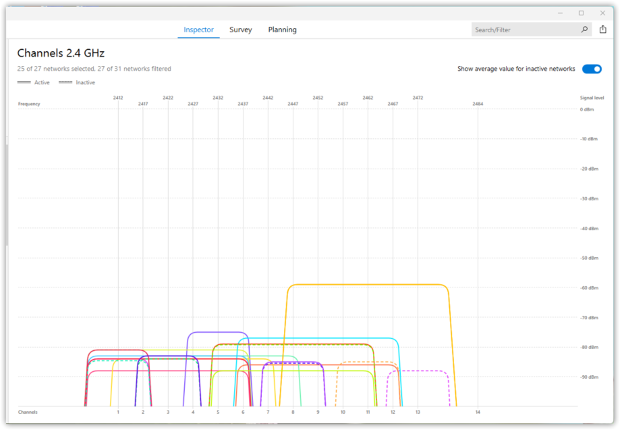
💡 Pro Tips for Choosing the Best WiFi Channel
- ✔ For 2.4 GHz networks, always prefer channels 1, 6, or 11, as they don’t overlap and provide the best stability.
- ✔ Check for congestion — If a non-overlapping channel is crowded, choose the least occupied one for better performance.
- ✔ For 5 GHz networks, choose higher-numbered channels (36 and above) to avoid Dynamic Frequency Selection (DFS) restrictions that may cause temporary disconnections.
- ✔ For 6 GHz networks, prioritize 160 MHz channels when possible, as they offer the highest speeds with minimal interference.
- ✔ If no non-overlapping channels are available, choose a channel with full overlap rather than partial overlap. Fully overlapping networks can “negotiate” and share the spectrum more efficiently, while partial overlap causes more interference and packet loss.
Method 5. Enhance Your Equipment
Upgrading your equipment — whether it’s a better antenna, a WiFi extender, a new router, a mesh network, or powerline adapters — can significantly boost your coverage and improve connectivity. In this section, we’ll help you choose the best option for your needs.
Get a Better Antenna
If you have a router with a replaceable external antenna, you can easily improve its performance by getting a better one. The gain of WiFi antennas is indicated in dBi (antenna gain in dB above an isotropic radiator). Many budget routers come with a small antenna with just 2 dBi, and replacing such antenna with a high-gain alternative is guaranteed to provide a significant boost in WiFi range.
To reinforce a particular area of signal weakness, you can point a directional antenna toward it, but you need to keep in mind that other directions may suffer. That said, most router antennas tend to be omnidirectional.
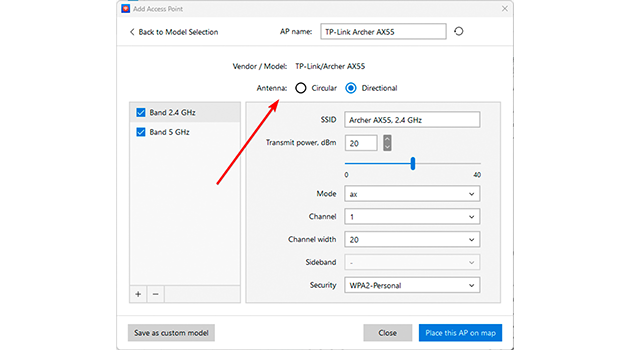
NetSpot’s Planning Mode allows you to virtually test different antenna configurations, helping you optimize your Wi-Fi setup before making physical changes.
Using a WiFi extender
A WiFi extender or booster takes the original signal and repeats it to extend its reach. WiFi extenders are also available without any ingress protection for use indoors. Such WiFi extenders are usually considerably less expensive than their outdoor counterparts, and they’re just as easy to install.
They come in a variety of styles including extenders that simply plug into a nearby electrical wall outlet and can solve the problems of an inadequate WiFi range. Regardless of which type you select, make sure to use NetSpot to determine the optimal placement for your WiFi extender so that it extends your WiFi range as much as possible.
Upgrade Your Router
Upgrading your router can significantly enhance the performance and range of your Wi-Fi network, especially if your current router is several years old. Newer routers support advanced technologies, including Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 6E, and Wi-Fi 7, offering significantly improved speeds, reduced latency, and better efficiency for multiple connected devices.
- Wi-Fi 6 (802.11ax): Delivers better efficiency and supports more devices simultaneously with features like OFDMA and Target Wake Time (TWT).
- Wi-Fi 6E: Extends Wi-Fi 6 into the 6 GHz band, reducing congestion and allowing ultra-fast speeds.
- Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be): Future-proofing your network with even lower latency, increased bandwidth, and improved channel allocation.
Older routers may not efficiently manage the bandwidth demands of today’s high-definition streaming, online gaming, and smart home devices. They often operate on overcrowded frequencies, leading to interference and reduced performance.
In contrast, newer routers can operate on multiple frequency bands (dual-band or tri-band), offering dedicated channels for different types of devices, reducing interference, and ensuring smoother connectivity.
Additionally, contemporary routers come with advanced features such as beamforming and MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output). Beamforming enables the router to focus signals directly towards individual devices, avoiding the scattergun approach of broadcasting signals indiscriminately in every direction, thereby improving signal strength and range. MU-MIMO allows the router to simultaneously interact with several devices at once, significantly boosting network efficiency and capacity.
The physical design of newer routers often includes more or high-gain antennas, which can further extend the Wi-Fi coverage area. Furthermore, the latest routers come with enhanced security protocols, providing better protection against unauthorized access and cyber threats.
Investing in a new router can be a straightforward and effective way to extend your Wi-Fi range, especially if you’re experiencing connectivity issues, slow speeds, or have a growing number of Wi-Fi-enabled devices in your home. It represents a critical step towards building a more reliable and faster home network capable of handling today’s digital demands.
Employing a mesh network
If your budget allows it, then we recommend you extend the WiFi in your house by replacing your existing router with a mesh system to create a so-called mesh network.
A mesh network is made up of two or more WiFi access points, typically called nodes, which together blanket a large area with seamless WiFi coverage. By setting up a mesh network in your house, you can gain the ability to roam with your devices from room to room uninterrupted by connection drops and slowdowns.
WiFi Extender or Mesh Network? 🤔
If you’re unsure which solution suits you best, consider your home’s size and network needs. WiFi extenders are best for fixing isolated dead zones, but they degrade signal strength with each hop. In contrast, mesh networks create a unified system where each node delivers full-speed WiFi without drops.
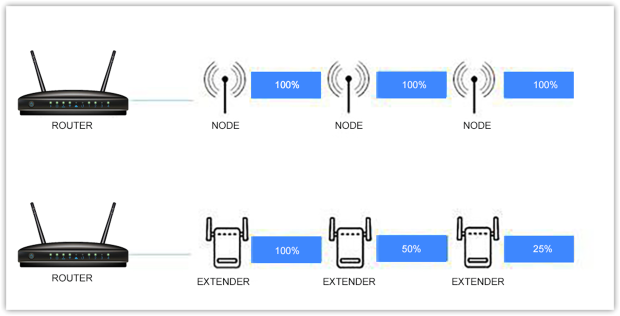
For small coverage issues, an extender might suffice. But if you want seamless connectivity across a large home, a mesh system is the superior choice. Setting up a mesh network is simple:
- Buy a mesh system that can cover your entire house.

- Connect the main mesh node to your existing router or modem using an Ethernet cable.
- Evenly place additional nodes around your and connect them to AC wall outlets.
- Use a companion smartphone app or a web interface to set up the mesh system.

- Use NetSpot to create a signal heat map and optimize the placement of individual nodes based on it.
That’s how easy it is to set up a mesh system!
Using Powerline Adapters
Powerline adapters use your home’s electrical wiring to extend network connectivity to distant rooms. They are particularly useful when running Ethernet cables is impractical, such as in multi-story homes, buildings with thick walls, or areas with poor Wi-Fi coverage.
Pros: More stable than Wi-Fi extenders, less interference, works well in homes with thick walls or multiple floors, and provides lower latency than wireless solutions.
Cons: Speed depends on the quality and age of the electrical wiring, may not function well in homes with separate electrical circuits or older wiring.
Some Powerline adapters come with built-in Wi-Fi access points, allowing them to create a secondary wireless network in areas with poor coverage. This can be particularly useful for garages, basements, and outdoor spaces where running an Ethernet cable would be impractical.
💡 Pro Tips for Enhancing Wi-Fi Equipment
- ✔ Choose antennas with higher dBi ratings (at least 5 dBi for better range, 9+ dBi for long-distance signals) and position them vertically for optimal performance.
- ✔ Position Wi-Fi extenders strategically — place them halfway between your router and the weak signal area for the best results.
- ✔ Upgrade to a dual-band or tri-band router to reduce congestion and provide faster speeds for multiple devices.
- ✔ Activate the QoS (Quality of Service) feature on your router to give priority to critical tasks such as video conferencing and gaming, ensuring they run smoothly even when background downloads are in progress.
- ✔ Use a wired backhaul for mesh networks when possible — connecting nodes via Ethernet greatly improves performance and reduces latency.
How to Extend WiFi Range with Another Router?
If you have exhausted the free methods of extending your WiFi range to no avail it might be time to consider purchasing some additional equipment in order to improve your WiFi coverage. There are a number of different ways you can do this.
Before you purchase another router and set it up, we highly recommend you check your WiFi coverage using NetSpot so that you have reliable data that you can use to determine whether the change you made produced a desirable result.
Method 1. How to Extend WiFi Range with Another Router with Cable?
If your current router has a free Ethernet port, you can simply connect another router to it with an Ethernet cable and place the new router anywhere you want. Since the maximum recommended length for Cat5e cable is around 100 meters, you can position the new router pretty much anywhere you want.
Because your existing router is almost guaranteed to support and use DHCP, a network management protocol that dynamically assigns an IP address and other network configuration parameters to each device on a network, you can simply connect the new router to it and use it as an access point — no additional configuration required.
Basically, you are using the second router to catch the WiFi signal and push it to previously unreachable parts of your home or office.
Method 2. How to Extend WiFi Range with Another Router without Cable?
Connecting two routers with an Ethernet cable can be a lot of work — not to mention that high-quality Ethernet cables are not exactly cheap. At the cost of some performance, you can extend WiFi range with another router without a cable by setting up the new router as a wireless repeater.
The job of a wireless repeater is simple: rebroadcast the signal from your main router. Unfortunately, not all WiFi routers can work as repeaters, so do your research and select one that can. Alternatively, you can replace the stock firmware with DD-WRT, an alternative router firmware with plenty of useful features.
How to Extend Wi-Fi Range Outside?
Extending WiFi range outside is relatively easy, provided you have the right equipment for the job. Because a regular WiFi router wouldn’t be able to survive the exposure to the elements, you need a device that’s meant to be left outside regardless of whether its freezing or raining. We recommend an outdoor WiFi extender, sometimes called a WiFi repeater or access point.

Your outdoor WiFi extender of choice must have a sufficiently high ingress protection (IP) rating, and the temperature range it can withstand must cover even extreme temperatures in your area. When it comes to setting up an outdoor WiFi extender, you simply connect it to power and position it within the range of your indoor WiFi router.
There is no reason that you need to suffer from the plague of a weak WiFi signal. One of the remedies we have covered should help you get that signal to each and every device in your home or office.
How To Extend WiFi Range — FAQs
There are several ways how you can extend the range of your WiFi for free, including:
- Move your router to a more suitable place
- Install the latest version of your router's firmware
- Take advantage of the 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands
- Optimize WiFi channel settings
To increase the range of your WiFi router, you can download a wireless network analyzer like NetSpot and use it to determine the best location and settings possible.
Yes, you can extend the range of your WiFi with another router, either by connecting the two routers together using an Ethernet cable or by setting up the new router to function as a wireless extender.
You can purchase a WiFi extender or replace your existing router with a mesh WiFi system to create a seamless wireless network extending from your home to your detached garage.
That depends on which router you own, where it is installed, and how it is configured. Sometimes, the best way to extend your WiFi is to move your router somewhere else, but you may also need to replace it with a better model, and anything in between.
WiFi signals struggle to penetrate floors and ceilings. To improve connectivity in your basement or attic:
- Use a WiFi extender placed midway between the router and the basement/attic.
- Consider a powerline adapter, which can transmit the network signal through electrical wiring.
- Install a dedicated access point wired to your main router for the best performance.
If your WiFi connection weakens or drops at a specific time daily, it could be due to:
- Electronic interference: Devices such as microwaves, baby monitors, or Bluetooth speakers might be in use at the same time.
- ISP congestion: Some internet providers throttle bandwidth during peak hours.
- Router settings: Check if your router has scheduled tasks like automatic reboots or updates during that time.
If your WiFi extender isn't improving signal strength:
- Ensure it’s placed correctly — midway between your router and the weak signal area.
- Check for firmware updates on your extender.
- Use NetSpot to analyze your signal and find a better placement.
- If interference is an issue, consider switching to a mesh WiFi system instead.
