WiFi speed test app runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11be/ax/ac/n/g/a/b wireless network adapter. Read more about the 802.11be support here.
WiFi Speed Test with NetSpot
Learn how to test Wi-Fi speed the right way and actually raise it. Learn how to run a Wi-Fi speed test, read heatmaps, and boost coverage using NetSpot for macOS and Windows — fast, accurate, repeatable.
Paying for a high-speed wireless internet access and not getting the advertised speeds is infuriating. With NetSpot, you can test real Wi-Fi performance, find weak signal and interference, and determine if your ISP or your network is to blame.
How to Test Wi-Fi Speed with NetSpot
NetSpot lets you do both quick “on-the-spot” speed checks and deeper, heatmaps-based testing.
On mobile, Android gives you a fast Internet Speed Test with Download and Ping; on iPhone/iPad, NetSpot measures Download, Upload, and Ping right where you stand and saves historical results.
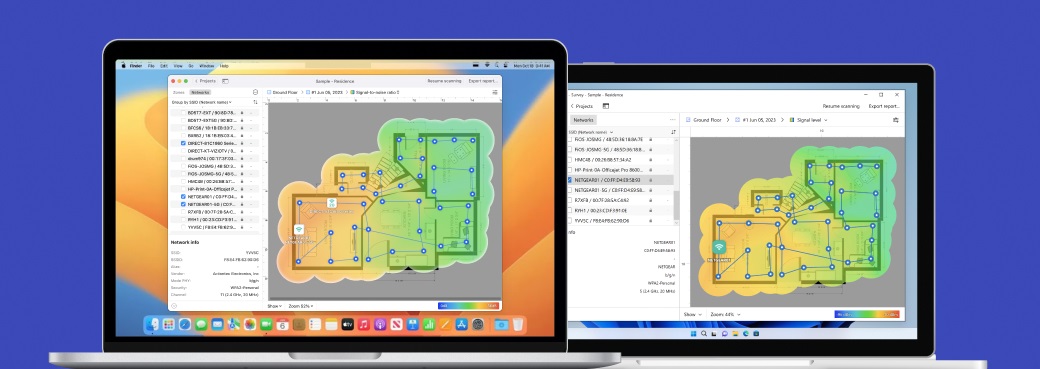
In desktop versions, Active Scanning feature lets you test WiFi speed in an instant. Active Scanning tests upload rate, download rate, and wireless transmit rate via HTTP, TCP, or UDP.
As such, you can either perform a quick speed test or an in-depth wireless speed measurement. Create a new Survey project, load or draw your floor plan and calibrate it. Enable Active Scanning, select the connected network you want to test, then walk the space to collect measurement points. When you’re done, click the Heatmaps button.
-
Full coverage
Get the most efficient and full-bodied WiFi coverage throughout the planned space.
-

Cross-platform
Available for any MacBook or any laptop with Windows 7/8/10/11 on board.
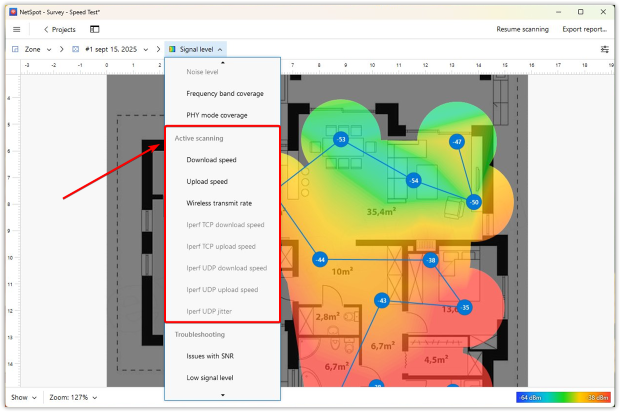
During Active Scanning, NetSpot measures speed at each sampled point and builds separate heatmaps:
- Download speed heatmap shows how quickly your device can receive data from the network — ideal for spotting areas where streaming or browsing will feel slow.
- Upload speed heatmap highlights how fast you can send data back, which matters for video calls, cloud backups, or file sharing.
- Wireless transmit rate map reflects the raw data rate negotiated between your device and the access point, helping you understand the real channel capacity versus actual internet throughput.
Together, these visualizations reveal not just whether your WiFi is “fast” in general, but where bottlenecks appear and what type of activity they affect.
NetSpot doesn’t just measure speed — it lets you dig deeper into WiFi performance by giving you control over how tests are run. In the Preferences menu, you can fine-tune test parameters: choose between HTTP, TCP, or UDP, and set how much data should be transferred. This flexibility is useful because each protocol highlights different aspects of network performance:
- HTTP simulates everyday web traffic such as browsing and streaming.
- TCP shows how reliable transfers like downloads or file sync behave, including the impact of retransmissions and acknowledgments.
- UDP strips away reliability mechanisms to measure raw packet flow, revealing latency and jitter issues that are critical for VoIP, gaming, or real-time apps.
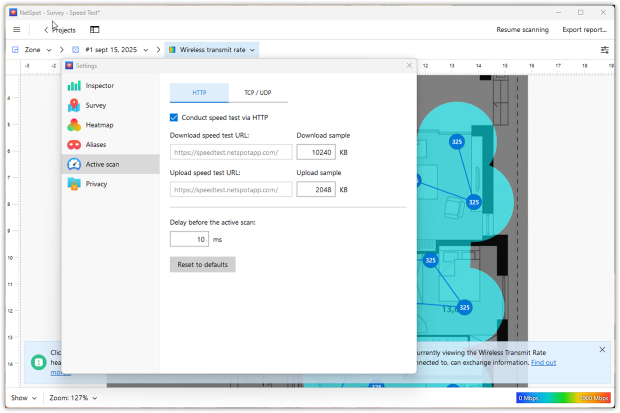
By adjusting these parameters, you can run either quick lightweight scans or detailed stress tests that mimic real conditions on your network. This flexibility helps you detect issues a typical online speed test might miss.
For more information, see this guide.
For advanced users, NetSpot supports integration with iperf3, a utility that performs in-depth throughput testing across your local network.
You can measure TCP and UDP bandwidth, latency, and jitter — making it easier to detect LAN-related issues that a typical internet speed test might miss.
NetSpot visualizes iperf results in Survey mode as separate heatmaps:
- Iperf TCP download speed — shows how fast your device can reliably pull data over TCP, reflecting real-world download and streaming capacity.
- Iperf TCP upload speed — measures how quickly your device can push data upstream via TCP, useful for file uploads, backups, and video conferencing stability.
- Iperf UDP download speed — illustrates raw packet reception without retransmissions, giving insight into how your network handles latency-sensitive traffic.
- Iperf UDP upload speed — highlights how efficiently UDP packets can be sent out, critical for gaming, VoIP, and streaming scenarios.
- Iperf UDP jitter — measures the variation in packet delivery times. High jitter indicates instability, which can cause stutter in video streams or distorted audio in calls.
Unlike standard download and upload speed heatmaps, these visualizations represent the pure performance between two endpoints inside your LAN, independent of your internet connection. This makes them especially valuable in enterprise setups, mesh deployments, or any situation where you need to validate throughput before going live.
NetSpot gives you tools for every level of testing. On the one hand, you can run quick speed checks or generate clear heatmaps for download, upload, and transmit rate to spot weak zones right away. On the other, if you need to go deeper, NetSpot integrates with iperf3 to deliver professional-grade throughput testing inside your LAN.
How to Increase Wi-Fi Speed
Knowing how fast your WiFi is just half of the battle. The other half of the battle is knowing how to increase WiFi speed. Randomly moving your different router between rooms or trying to adjust the angle of the antennas can yield impressive results, but you need to have actual data to support what you’re doing. Use NetSpot heatmaps to make targeted changes instead of guessing.
When you review the heatmaps, areas with the weakest signal will appear in blue and places with the strongest signal marked red. These color-coded visualizations help you instantly spot performance bottlenecks. Various heatmaps, such as the Signal-to-Noise Ratio heatmap, can help you identify sources of signal noise. These often include home appliances, electrical wires, fluorescent lights, and smartphones.
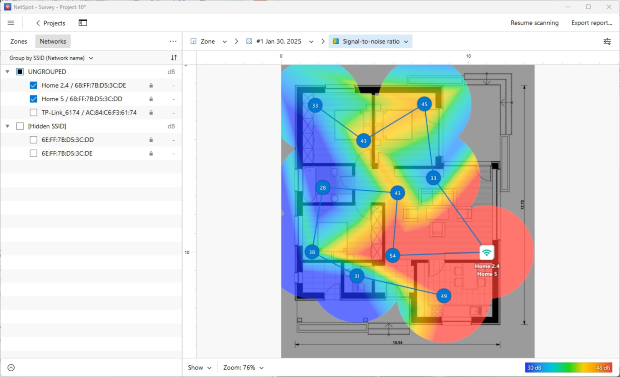
If the Signal-to-noise ratio or Signal level visualizations show large blue areas, it's a clear sign to focus on coverage and noise before changing anything else.
If you discover that noise isn’t really an issue, you may simply need a router with a better range or a wireless repeater. Better yet, consider a modern mesh Wi-Fi system instead of single-band repeaters: extenders often halve throughput because they receive and retransmit on the same channel, while mesh nodes coordinate and can use dedicated backhaul.
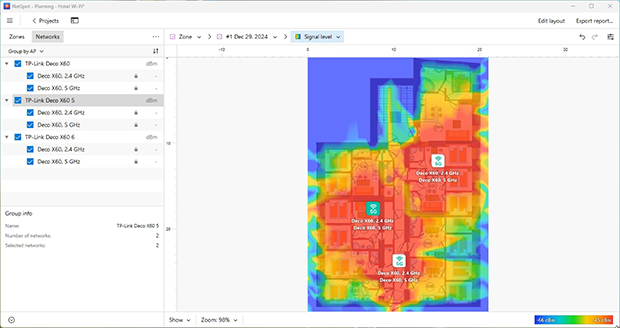
You can also use NetSpot's Planning Mode to simulate different AP placements and hardware upgrades before spending a dime.
The built-in predictive engine helps you choose the best locations for wireless access points, test different antenna types — omnidirectional or directional (and even adjust antenna power and tilt to reflect real-world behavior) — and compare router models from a wide selection of popular manufacturers.
This level of simulation makes NetSpot’s Planning Mode especially useful when designing a new network or upgrading an existing one.
Besides detailed area mapping and planning, NetSpot is also great for quick wireless network signal assessments. The Inspector Mode instantly takes a snapshot of all wireless networks in your surrounding area, allowing you to see how many of them are on the same channel as you, what security they’re using, and a host of other useful information.
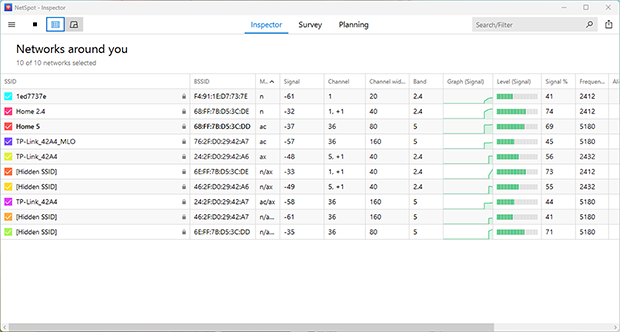
You can zoom in on individual networks to display more details or export the data as a spreadsheet.
When interference is the culprit, switch bands (prefer 5 GHz or 6 GHz where supported) and choose cleaner channels. On 2.4 GHz stick to 1/6/11; if a clean channel isn’t available, full overlap on one of these is usually better than partial overlap.
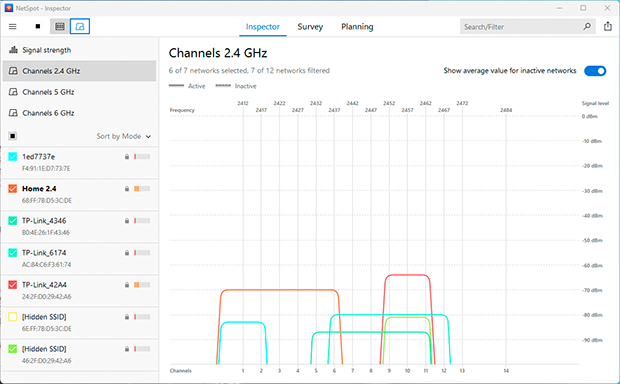
Use NetSpot’s “Channels” graph in Inspector Mode to track how busy each channel is in real time — it helps you avoid congested frequencies and make informed decisions when reconfiguring your router.
How do Wi-Fi Speed Tests Work
Online WiFi speed tests usually measure latency, download speed, and upload speed. Each of these test components affects the performance of your internet connection.
Latency, or ping, is the time it takes a server to respond to a request sent by your web browser, a music streaming app, or operating system. Latency is measured in milliseconds, and anything over 40-70ms is usually considered too high. If you’re just watching online videos on YouTube, you aren’t likely to notice high latencies because your web browser automatically pre-loads a portion of the video to deliver a smooth viewing experience. But if you’re playing an online game, even a few extra milliseconds of delay can cause you to lose a match because your opponents will literally have more time to respond than you.
Download and upload speeds are self-explanatory measures that seldom tell the full story. When you check WiFi speed using WiFi speed tests, your client (usually a web browser) establishes multiple connections and either begins to send or receive chunks of data. Using the real-time transfer speed, the actual download and upload speeds are calculated.
The problem is that the accuracy of these tests can be influenced by several factors:
- Network activity — As you may know, trying to stream a 2160p video on YouTube while downloading a large Linux distribution is no fun. Even without going to such extremes, it’s easy to influence the accuracy of online WiFi speed tests. A background system process may trigger and cause your operating system to send usage reports over the internet, a friend may message you on Skype or Telegram, an automatic update may start.
- Signal strength — It goes without saying that the closer you are to your router, the faster WiFi speeds you can expect. But even when you stay in the same place, you’ll inevitably see your WiFi signal strength fluctuate. This can be caused by changes in weather, doors and windows opening and closing, and interference caused by other WiFi networks in your area, among other things.
- Usage peaks — If you use a WiFi speed test service with servers in your time zone, prepare to see different results at 3 a.m. than at 2 p.m. You’re not the only person using these tests, and the servers that host them also have limited capacity.
Conclusion
NetSpot is a versatile, professional WiFi analysis and troubleshooting tool for experience users and total beginners alike. Its modern user interface is self-explanatory, making it effortless to use the software to its fullest potential.
WiFi Speed Test — FAQs
Run a quick wired baseline first (laptop → router via Ethernet). Then walk the same path in NetSpot with Active Scanning. If both wired and Wi-Fi speeds cap well below your plan everywhere, that points to the ISP. If wired hits your plan but Wi-Fi drops in certain rooms, you’re looking at coverage, interference, or placement — not the provider.
The accuracy of online WiFi speed tests can be influenced by a few factors:
- Network activity during the test — a background update of an app, streaming a movie, or talking to a friend on Skype can easily affect the results of a WiFi speed test.
- Signal strength — this value depends on how far you are from a wireless signal source, as well as on the physical obstacles in the way of the signal and current radio interference at the moment.
- Usage peaks — depending on when network users are the most active, the speed test may give you dramatically different results.
With NetSpot’s Active Scanning feature you can quickly and easily test the upload and download speeds, as well as wireless transmit rate via HTTP, TCP, or UDP. Unlike online WiFi speed tests, NetSpot lets you decide which size of data packets to download or upload to perform the tests. This gives you the flexibility of either performing a quick speed test or a deeper analysis.
To perform a WiFi speed test with NetSpot, click the Test Connection button, verify your WiFi settings and start a new WiFi area survey project. Load or create your map, select “Enable active scanning of the connected network,” and begin the scan.
Poor SNR or SIR almost always shows up as lower throughput. If signal looks strong but speeds sag, interference is likely. If signal is weak and speeds are low, it’s a coverage/placement problem. Read throughput heatmaps side by side with SNR/SIR to pinpoint the cause.
Yes. Pause backups, big downloads, and updates, and temporarily disable VPN before testing. That keeps results stable and repeatable.
Browser tests measure a single moment to a nearby server and are sensitive to background traffic. Active Scanning logs download, upload, and wireless transmit rate along your floor plan, so you see exactly where speeds drop and whether it’s signal, interference, or congestion.
Do at least two passes: one near the router to get the ceiling, and one in your “slow” spot to see the floor. Repeat later in the day to catch peak-time slowdowns. Consistent method, same device, and no background downloads make results comparable.
