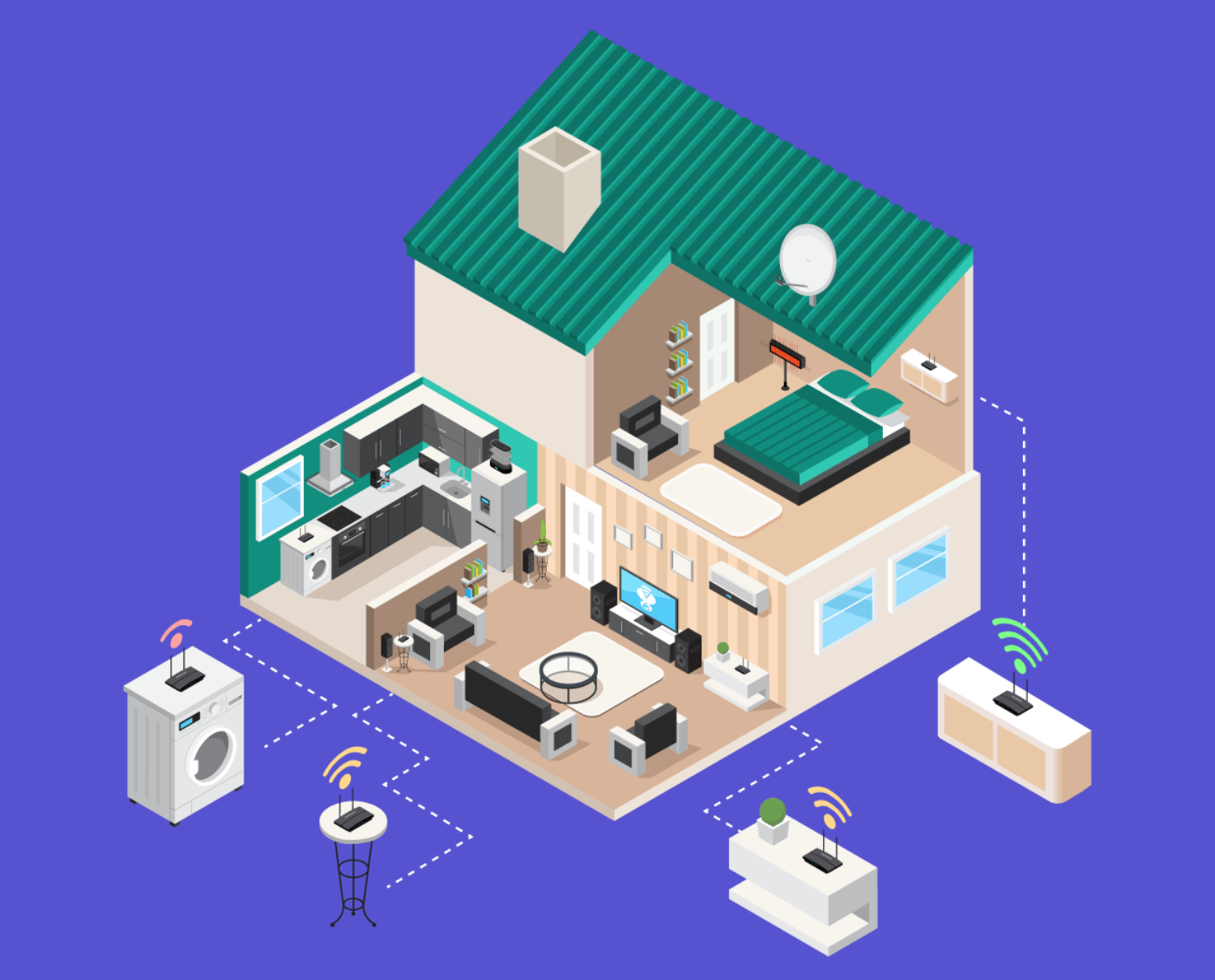
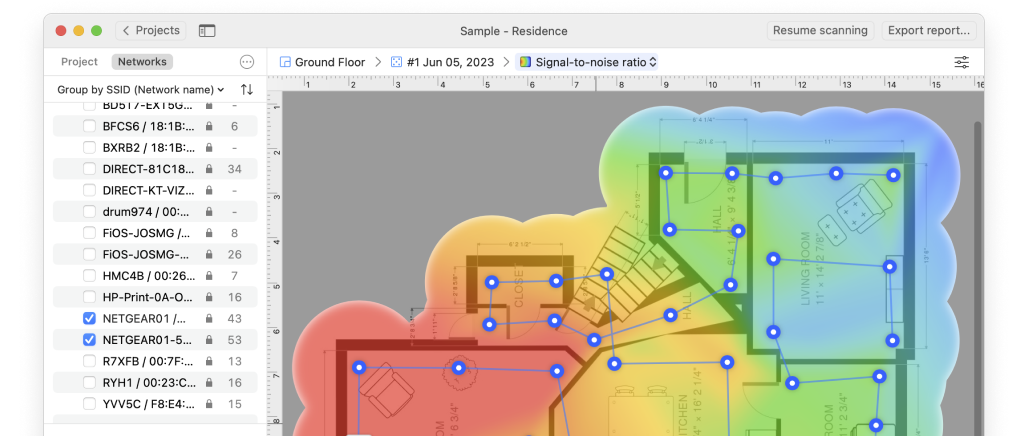
In this article, we explain everything you need to know to determine the best placement for a WiFi router in an apartment, office, or multi-story building.
The Best Place for Your Router
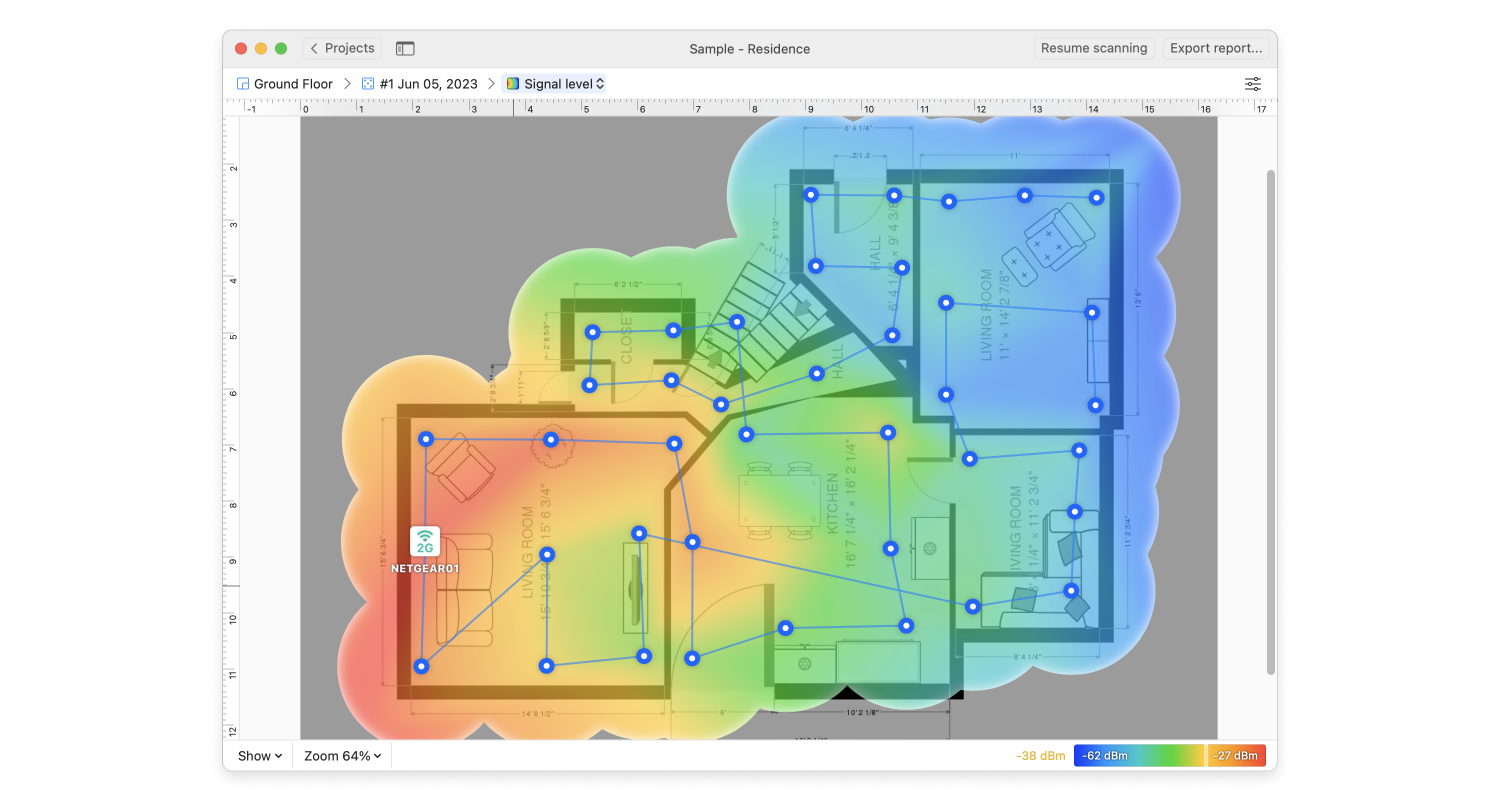
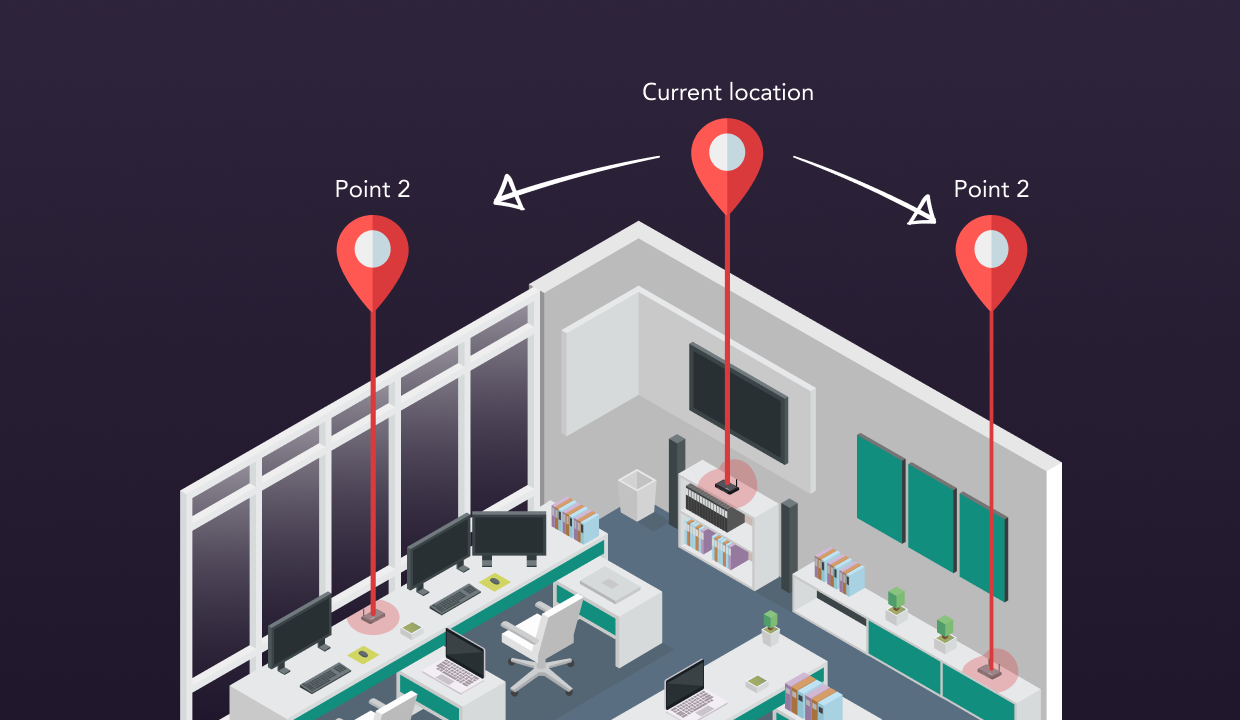
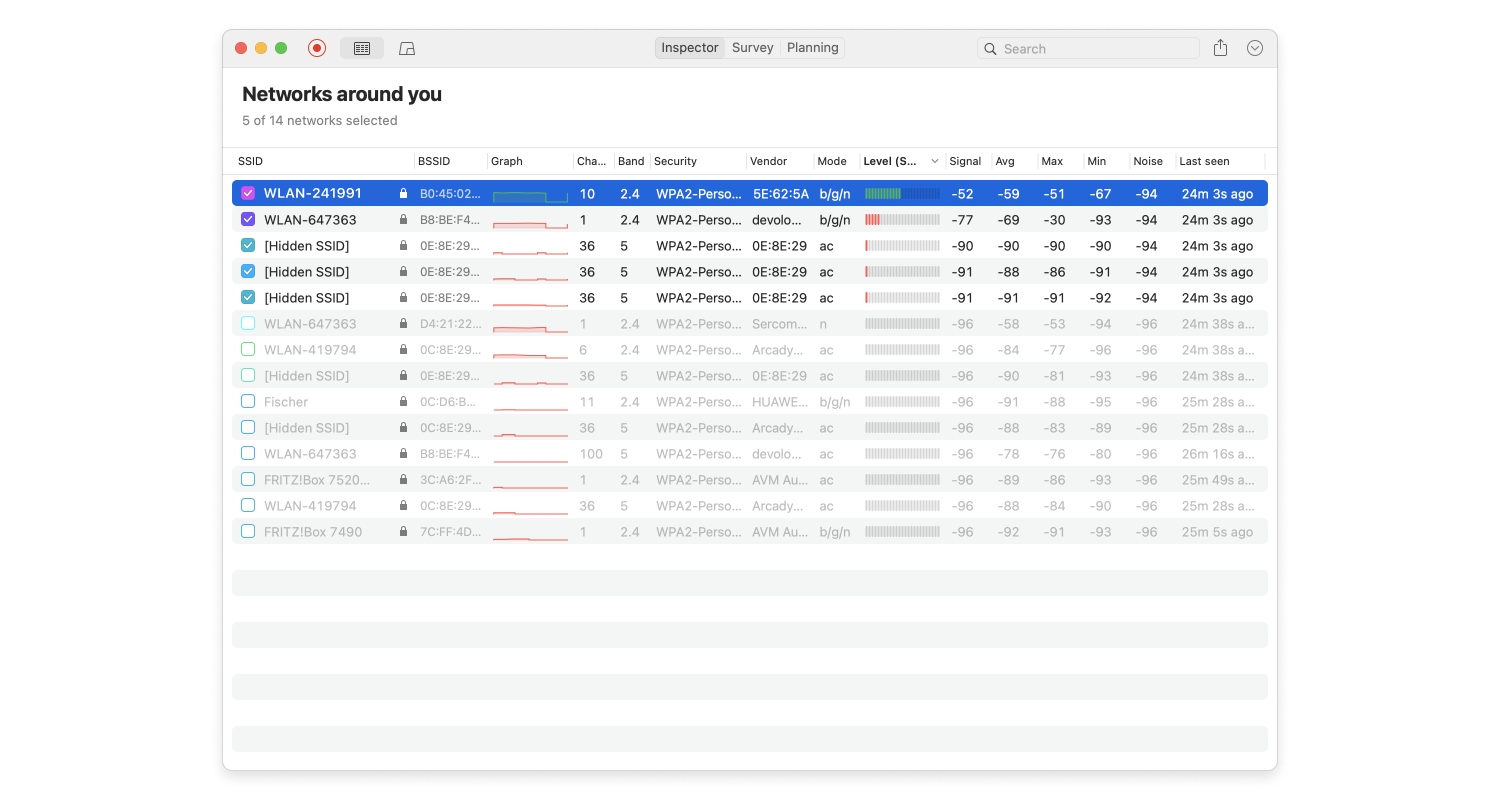
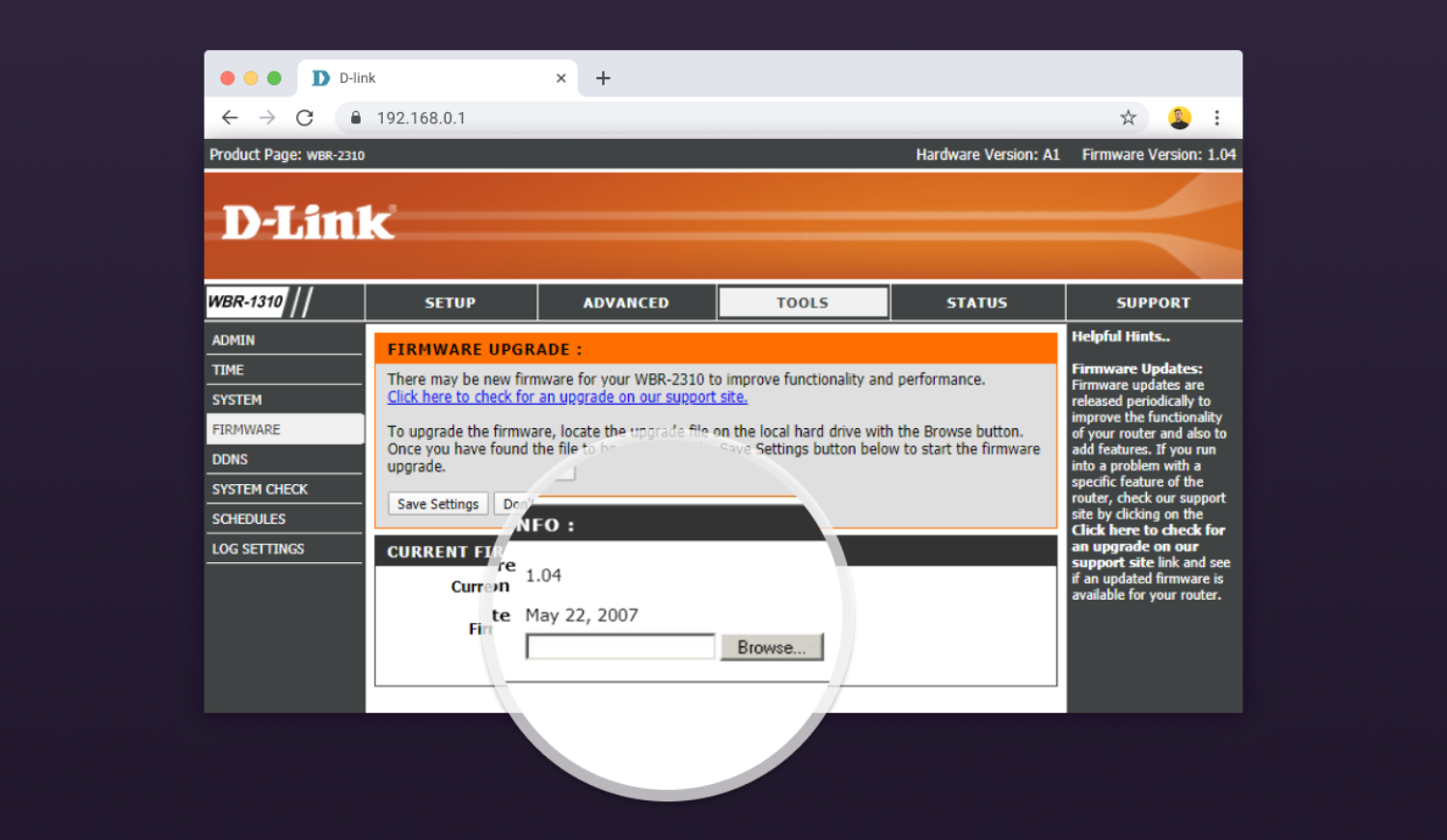
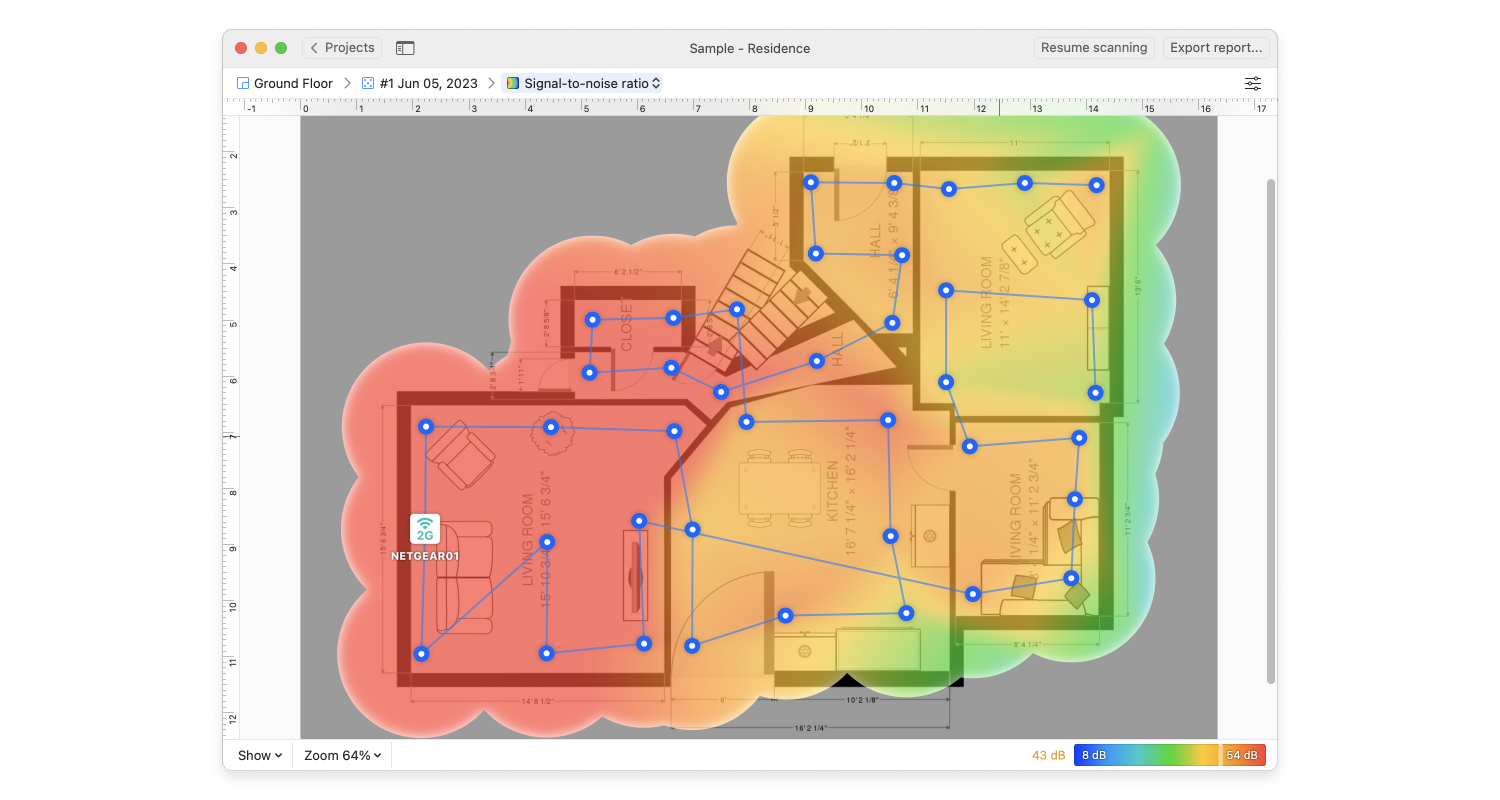
You’ve finally decided to splurge on a new WiFi router, installed it, and discovered that your wireless coverage is still far from ideal. Most likely, your new WiFi router isn’t to blame at all — the problem is its placement.