WiFi Analyzer — Improving WiFi Performance
A WiFi analyzer is a useful software application that can tell you many things about your wireless network and the networks around you, helping you optimize your WiFi for best performance.
What Is Wi-Fi Analysis?
Wi-Fi analysis is the process of examining and optimizing a wireless network to ensure smooth and efficient performance. It's like a health check-up for your Wi-Fi, and it's performed using a tool known as a Wi-Fi analyzer. In an age where a wireless router is almost as essential as running water, WiFi analysis helps keep the digital traffic flowing.
To understand why WiFi analysis is so important, it's necessary to know how the WiFi spectrum is organized, especially when it comes to the common 2.4 GHz radio band.
This 2.4 GHz radio band is divided into multiple channels, much like the lanes on a highway. In North America, the 2.4 GHz radio band is divided into exactly 11 channels, with channels 1, 6, and 11 being the only channels that don't overlap with other channels.
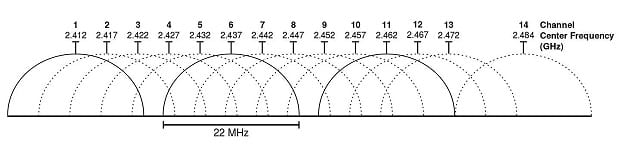
In theory, 11 channels should provide plenty of room for all users, but in reality, many people never change the default configuration of their wireless router, leading to a situation where too many routers transmit data on the same channel.
Imagine a busy road where everyone is trying to drive in the same lane — it's going to lead to congestion, delays, and frustration. The same thing happens with WiFi, and that's where WiFi analysis comes in.
The situation is further complicated by the presence of 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands. While far more immune to signal interference than the 2.4 GHz band, these newer and less used bands have a shorter range and less ability to penetrate walls and solid objects, so they often provide insufficient coverage and speeds.
Utilizing a wireless network analyzer, WiFi analysis can reveal which channels are used the least, allowing you to switch to a less crowded part of the spectrum. You can also create a heatmap of your area to see exactly where your WiFi signal is strong and where it could use some improvement.
What Does a WiFi Analyzer Do?
The purpose of a WiFi analyzer is to gather as much information as possible about available wireless networks to help professionals and home users alike troubleshoot WiFi-related problems, ensure optimal router placement, and more.
In the past, WiFi analyzers were used predominantly by large organizations and enterprises that needed to cover a large area with a strong WiFi signal. These days, WiFi networks are everywhere, and our expectations of them have never been greater.
Without knowing how to use a WiFi analyzer, it’s very difficult for home users, small businesses, and schools to provide reliable coverage and the best data transfer speeds possible. The good news is that WiFi analyzers have become readily available at a variety of price points, and they can be roughly divided into two categories:
- Hardware WiFi signal analyzers: Aimed at professional network administrators and security experts, hardware WiFi signal analyzers are physical devices used for troubleshooting and performance testing. They often have an external directional antenna that lets them discover and analyze remote networks. Some hardware wireless analyzers are self-contained and don’t need to be connected to a computer to function as intended. In virtually all cases, the cost of hardware wireless analyzers starts at hundreds of dollars and goes up to thousands.
- WiFi Analyzer apps: For home users and small businesses, it doesn’t make financial sense to spend money on an expensive hardware wireless analyzer because they can simply download one of the best WiFi analyzer apps and perform WiFi analysis using a laptop, smartphone, or tablet. WiFi analyzer apps are affordable, easy to use, and the information they provide are accurate enough to satisfy the needs of most users.
Of course, not all hardware WiFi signal analyzers and WiFi analyzer apps are created equal, which is why it’s important to know what the best WiFi analyzers are and avoid those that don’t perform well.
What Does High-Performing WiFi Look Like?
Many people who learn how to use a WiFi analyzer are interested in setting up a high-performing WiFi network, but how does such a network look like? Here are a few important characteristics of a high-performing WiFi network:
- Flawless coverage: A high-performing network should cover the intended area without leaving any signal weak spots where common online activities, such as streaming movies, browsing the web, or video chatting, are impossible to perform. A wireless analyzer can be used to create a coverage heatmap that clearly highlights all areas of signal weakness, making it easy to adjust the placement of the router, the position of its antennas, or the arrangement of interference-emitting appliances.
- Sufficient capacity: Sometimes referred to as bandwidth, capacity determines how many people can use the WiFi network at the same time without experiencing a significant degradation in performance. Modern routers that support the latest WiFi standards have far greater capacity than old 802.11g routers, whose capacity is limited to about 22 Mbit/s. In high-usage scenarios, it’s often necessary to deploy multiple access points to provide sufficient capacity, which is where mesh networks come in, making it possible to cover a very large area with a single WiFi network broadcasted by a large number of access points.
- Great speeds: Ideally, you want your WiFi network to deliver the same download and upload speeds as a wired Ethernet connection. If you’re paying for a 100 Mbit/s internet connection, you should be able to reach the maximum speed from any part of your apartment, house, or office. Modern routers use technologies such as MU-MIMO (multi-user multiple-input multiple-output) and beamforming to enhance signal strength and ensure a speedy wireless connection to the internet.
- Uninterrupted connectivity: High-performing WiFi networks should also offer an excellent user experience, and uninterrupted connectivity is an essential part of it. When going from room to room, the last thing you want is for your WiFi connection to drop for a few seconds because you left the range of one WiFi network and entered within the range of another one. Mesh networks solve this problem by wirelessly connecting together multiple routers (called nodes), arranging them in a mesh topology. Modern mesh WiFi systems are so easy to set up that even complete beginners can get them up and running in just a few minutes.
- State-of-the-art security: No WiFi network will maintain its performance unless it’s secured with a strong password and robust encryption. Unsecured networks are a very common target of hackers, who don’t hesitate to take advantage of any opportunity to steal sensitive information and use it for their own personal gain. A WiFi signal analyzer can tell you if your WiFi network is using the latest security standard (WPA3), and you can also use it to determine how secure are other networks in your location.
Common WiFi Performance Issues
Even though the performance of the average WiFi network has improved significantly during the last decade, there are still many WiFi performance issues that plague users every single day:
- Slow connection: There are many factors that can cause WiFi to be slow, including limited bandwidth, poor coverage, insufficient speed provided by the ISP, or signal interference caused by nearby appliances and Bluetooth devices. To fix issues with a slow WiFi connection, you should first determine whether you’re receiving a sufficiently strong signal from your router. You can easily do that with the help of a wireless network analyzer app. The best WiFi analyzer apps can even create a signal heatmap, clearly visualizing where the signal is sufficiently strong, and where it leaves something to be desired.
- No internet connection: Whenever your WiFi connection stops working, you should first check if your WiFi router is operating as it should. If you see an LED indicator light flashing, telling you that the router itself can’t connect to the internet, then your ISP might be to blame. But if the router is working fine and your ISP isn’t experiencing an outage, then you need to fix the problem yourself. First, restart the router and wait a few minutes to see if this solves the problem. If it doesn’t, establish a wired connection and see if you can connect to the internet that way. If you can, log in to the admin interface and check your WiFi settings.
- Unreliable performance: Does your WiFi connection often go from flawless to aggravating? Then you should know that you’re not the only one who’s experiencing issues with unreliable WiFi performance. Such issues are common because they are caused by a number of different factors, including co-channel interference, network overload, and spotty coverage. Many of these issues can be fixed by purchasing a new router, one that supports not just the 2.4 GHz band but also the 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands, as well as various performance-enhancing technologies like MU-MIMO or beamforming. Other issues that can cause unreliable performance require careful troubleshooting using a wireless network analyzer.
- Signal weak spots: Ideally, you want to see full WiFi signal strength bars on your laptop and mobile devices, whether you're standing right next to your router or in the room that's farthest away from it. Modern mesh WiFi systems can help achieve this because they consists of a main router and several satellite modules, or nodes, that work together to spread the WiFi signal evenly across a larger area. To maximize the efficiency of a mesh WiFi system, you need to know how to use a WiFi analyzer. This tool helps you determine the optimum location for each node, ensuring that the mesh network functions at its peak performance.
- WiFi speeds lagging behind wired internet: If you can achieve the maximum download and upload speeds advertised by your internet service provider when connected to your router using an Ethernet cable but struggle to achieve the same speeds when connected over WiFi, you most likely need to either improve your WiFi coverage or purchase a more capable router that supports the latest wireless networking standards, such as Wi-Fi 6.
- Insufficient bandwidth for multiple users: Not all WiFi networks can support multiple simultaneous users streaming online content, playing video games, or downloading large files from the web at the same time. For starters, you need a sufficiently capable router with enough processing power to serve multiple clients at the same time. The router should support Quality of Service to ensure that one person downloading a movie won’t make it impossible for everyone else to browse the web and send email messages. Technologies like MU-MIMO and beamforming can further enhance everyone’s experience.
What Is the Best WiFi Analyzer App?
A WiFi analyzer can be an invaluable tool for diagnosing problems and optimizing your wireless network. You can use a WiFi analyzer app to improve the speed and reliability of your network. There are many apps from which to choose, so what features should you look for? A good wireless analyzer app should be able to do several things.
To start with, it should quickly detect all nearby wireless networks and gather enough information about them. At the very least, the app should be able to retrieve network names, also known as Service Set Identifiers (SSIDs), security settings, and signal strength data.
Some of the more feature-packed WiFi analyzers also come with heatmapping functionality, which allows you to capture signal strength data on a map to reveal areas of signal weakness and possible high interference.
Best WiFi analyzer apps are not just packed with useful features, but they are also exceptionally easy to use even by people who have little to no previous experience with WiFi analysis.
Features of a WiFi Channel Analyzer
Here are some attributes you will find important in a WiFi analyzer.
Quality data collection — There are many statistics that an analyzer can provide about your network and those located nearby. At a minimum you want your app to display:
- Network name: WiFi networks typically broadcast their names, also known as service set IDs (SSIDs) to identify themselves to wireless devices. SSIDs can be zero to 32 bytes long, and they can contain any non-ISO basic Latin characters. An SSID that is zero bytes long is called a “hidden SSID,” and it’s sometimes used to steers clients to other networks. A good WiFi network analyzer must be able to discover and analyze even hidden SSIDs.
- Band and channel in use: WiFi networks are broadcasted in the unlicensed spectrum, and the IEEE 802.11 standard provides several distinct radio frequency ranges, called bands, in the unlicensed spectrum. The main bands used in WiFi communications are the 2.4 GHz band, 5 GHz band, and more recently, the 6 GHz band. These bands are divided into multiple channels, which are like lanes on the highway, allowing multiple WiFi networks to broadcast their signals without interfering with one another. A WiFi analyzer can reveal when multiple WiFi networks broadcast on the same channel and suggest an alternative channel, aiding in the optimal utilization of these bands and enhancing overall network performance.
- Security settings: To prevent unauthorized access, WiFi networks can be protected with Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP), Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA), WPA2 or the latest WPA3, the third iteration of a security certification standard developed by the Wi-Fi Alliance. Out of these, only the last type of WiFi security provides a sufficient level of security to ensure that no one can connect to your WiFi network without permission and access your personal data during transmit. A WiFi analyzer can tell you useful information about the security settings of your WiFi, helping you determine whether you should change them or not.
- WiFi standard: Technology keeps evolving at a rapid pace, and WiFi standards are no exception. There have been multiple amendments to the original IEEE 802.11 standard, which was released in 1997. Alongside the common WiFi standards such as 802.11g, 802.11n, and 802.11ac, more recent advancements include WiFi 6/6E (802.11ax) and WiFi 7 (802.11be), which allows link rates from 721 to 46120 Mbit/s and functions across the 2.4, 5, and 6 GHz bands, delivering even more efficient and high-speed connections. To analyze as many WiFi networks as possible, it’s important to select a WiFi analyzer that supports older and new WiFi standards alike.
- Signal strength: Everyone knows how painful it can be to use the internet with a WiFi signal strength of just one or two bars. The problem with WiFi strength bars is that they are far from accurate and can even be misleading. A WiFi analyzer displays WiFi signal strength in dBm, which are decibels in relation to a milliwatt (usually -30 to -100), giving you a highly accurate estimate of your signal strength.
- Noise level: Just like it’s difficult to hear another person in a loud room, it’s difficult to receive a strong WiFi signal in an environment with too much wireless noise, which is measured in -dBm format (0 to -100). The closer the measured noise level is to zero, the greater the level of noise is and the more difficult it is to receive a strong WiFi signal.
User interface — The manner in which the network data is presented can impact your ability to use it efficiently. You should be able to quickly find the information you are interested in viewing.
Portability — When it comes to using a WiFi analyzer effectively, portability is key. Taking multiple readings of your network from various locations within the coverage area requires a tool that can go where you go. This is where the convenience of mobile WiFi analyzer apps shines. Whether using a laptop or mobile device, selecting a WiFi analyzer that fits your platform leads to the most productive use of the tool. For example, those who are using Apple devices should explore the best WiFi analyzer iOS apps.
Reporting — You may find that you want to keep records of your WiFi scans and network statistics. Some apps give you the ability to export data to files for later analysis.
The Top 10 Best WiFi Analyzer Apps
For those looking to optimize their WiFi networks, a WiFi analyzer app can be a game-changer, providing insights and solutions that can dramatically enhance performance. Whether you're a tech-savvy professional or just someone looking to boost your home WiFi signal, the right app can make all the difference.
Here are ten WiFi analyzer apps that can help you tune your network for peak performance.
- NetSpot — is the professional app for wireless site surveys, WiFi analysis, and troubleshooting on macOS and Windows.
- Network Performance Monitor — is the web-based tool that designed to be used by enterprise network administrators.
- InSSIDer — one of the oldest and most trusted WiFi analyzer apps.
- WiFi Scanner — both Mac and Windows users will benefit from the advanced features of this tool.
- Real WiFi — a simple WiFi analyzer for Windows with an integrated speed test feature.
- Network Analyzer — includes diagnostic tools and an Internet speed test.
- WiFi Analyzer — is a free WiFi analyzer for Windows.
- Wireshark — is an extremely capable network protocol analyzer used to analyze what’s happening on wireless networks.
- Wi-Fi Scanner (LizardSystems) — is a straightforward analyzer app that targets mainly home users who are interested in learning more information about the wireless activity in their area.
- Vistumbler — is one of the best open source WiFi analyzer apps.

One Wi-Fi analyzer app that meets all of the above-mentioned criteria is NetSpot. This professional app for wireless site surveys, Wi-Fi analysis, and troubleshooting on macOS and Windows is loved by seasoned network administrators and home users alike. More about the NetSpot Windows Wi-Fi analyzer.
NetSpot runs on any Mac computer with macOS 11+ or newer and any Windows computer with Windows 7/8/10/11. Unlike most other Wi-Fi analyzer apps, NetSpot supports three distinct wireless analysis modes: Inspector, Survey and Planning!
-
Inspector Mode
Gives you real-time insights into the WiFi networks around you.
-

Survey Mode
Provides a comprehensive, map-based analysis of your WiFi network's performance.
-

Planning Mode
Enables you to simulate and plan your WiFi network's layout and coverage.
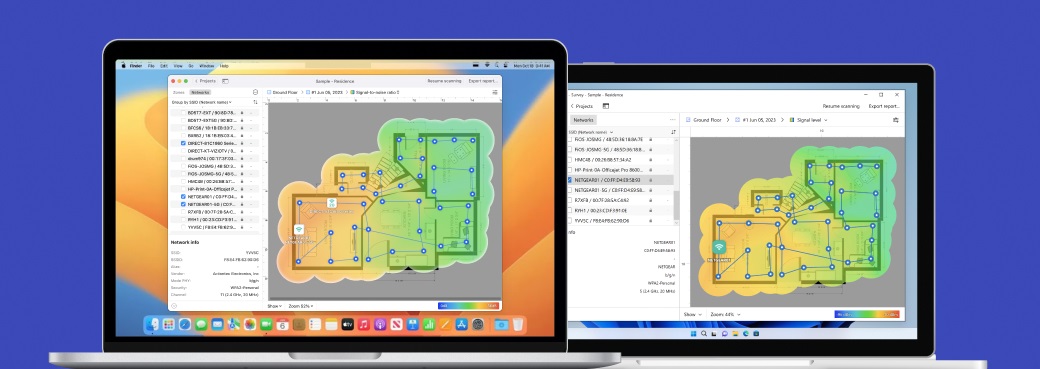
The Inspector Mode is great for taking quick snapshots of nearby wireless networks. When in this mode, NetSpot instantly detects all wireless networks near you, including your own wireless network, and allows you to check their security settings, signal strength, the channel and band they broadcast on, and much more.
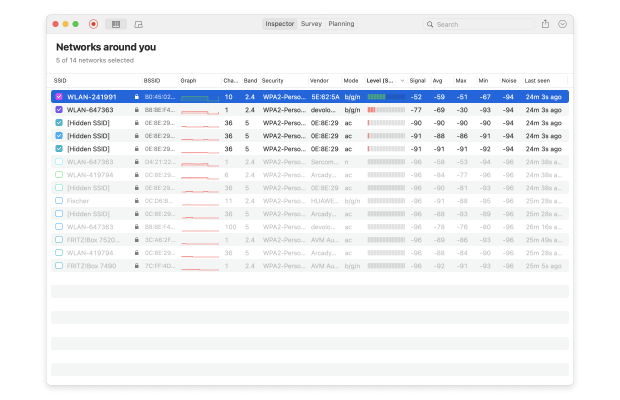
When in the Survey Mode, NetSpot allows you to outline your real-life wireless network data on a map, clearly showing where your signal is the weakest and where it is the strongest.
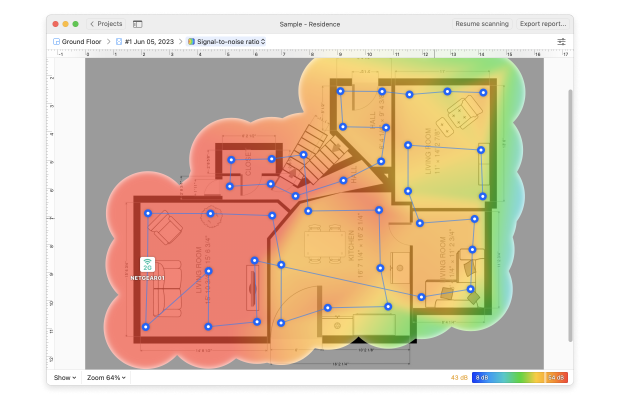
NetSpot’s heatmapping functionality supports multi-level projects with different areas, floors, and so on, and it even makes it possible to create any number of snapshots within each zone to quickly compare various wireless configurations with one another.
Finally, there’s the Planning Mode, which can be used to perform a predictive site survey. This feature is especially beneficial for those who are in the process of setting up a new WiFi network or looking to expand an existing network's coverage. It enables users to input a virtual map of the area and simulate how the network would perform in various configurations.
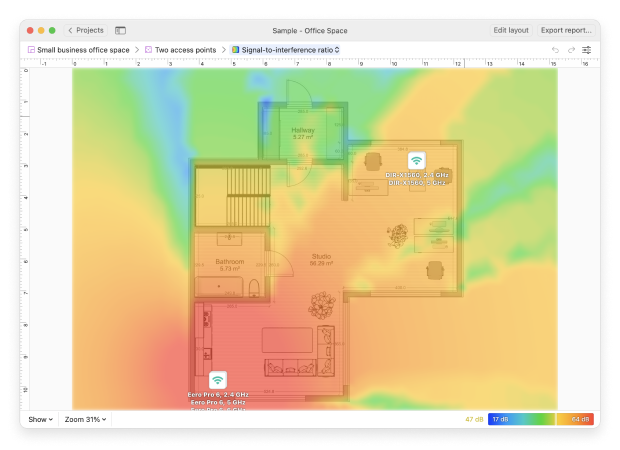
By adjusting the placement of access points, users can effectively predict signal coverage, identify potential dead zones, and optimize the overall network layout before any physical installation begins.
-
Works on Windows, macOS, and Android
-
Easy to use yet delivers professional results
-
Two wireless analysis modes
-
Heatmapping functionality
-
Multiple WiFi signal visualizations
-
None
- Summary recommendation: Get NetSpot
This web-based tool is designed to be used by enterprise network administrators and is powered by cutting-edge technology and advanced monitoring features.
Network Performance Monitor is designed to function as an automatic network analyzer, providing administrators with the information they need to maintain internal wireless network performance and spot potential issues before they affect employee productivity.
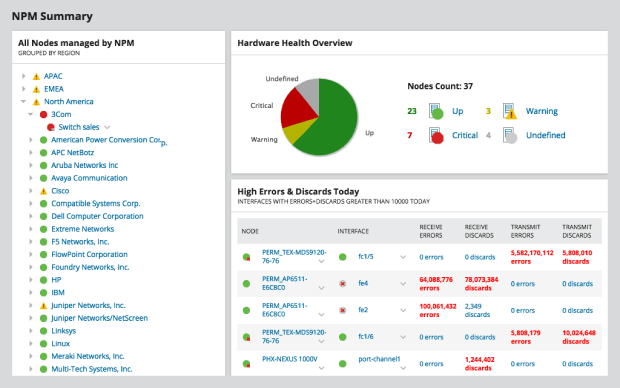
All important performance metrics are displayed on a customizable dashboard, including device downtime, average response time, and interface availability. Administrators can gain additional visibility into their networks thanks to a library of custom WiFi heatmaps within the Network Performance Monitor dashboard.
Even though Network Performance is an expensive enterprise-grade WiFi analyzer, anyone can test its features for up to 30 days for free.
Pros and Cons
-
Enterprise-grade WiFi analyzer
-
Customizable dashboard
-
Advanced WiFi visualizations
-
Free version available
-
Very expensive
-
Not suitable for home users
inSSIDer has been around since 2007, making WiFi analysis a breeze. The tool conveniently displays all essential information you need to see how your network performs in relation to other neighboring networks, including WiFi channel details, signal strength, and security settings.
Strong emphasis is placed on making the gathered data easily understandable, which is great if you're new to WiFi analysis or looking to pinpoint specific issues without getting lost in technical jargon. inSSIDer even scans your Local Area Network (LAN), showing you the devices connected, their types, and even their names when possible. All this without having to dig through complicated menus.
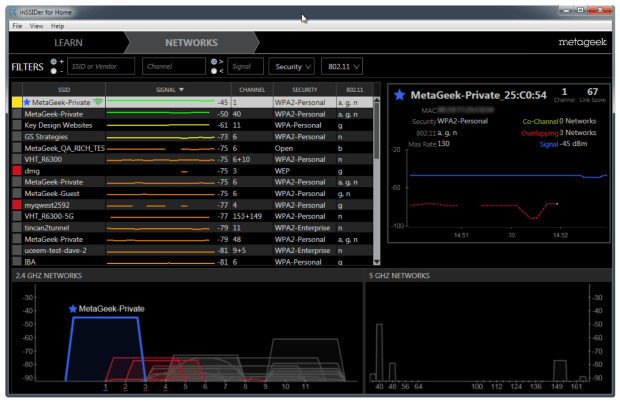
Because inSSIDer is developed primarily for Windows, Mac compatibility is restricted to a few specific (and outdated) versions. What's more, a MetaGeek account is mandatory to use the tool. This requirement may deter those users who don't wish to share their personal information with yet another company.
Pros and Cons
-
One of the oldest and most trusted WiFi analyzer apps
-
Simplifies complex data into plain English
-
Shows devices on your Local Area Network (LAN)
-
MetaGeek account required to use the tool
Both Mac and Windows users will benefit from the advanced features of this tool, including the ability to graphically display the network’s signal strength.
This multiplatform WiFi analyzer app works with all 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac access points and provides full support for both 2.4 and 5 GHz networks and all channel bandwidths. Its most noteworthy features include the ability to connect to any detected network, wireless connection statistics in the form of graphs and tables, summary reports in HTML format, automatic speed tests, and fast IP scanning that detects unknown devices connected to your WiFi network.
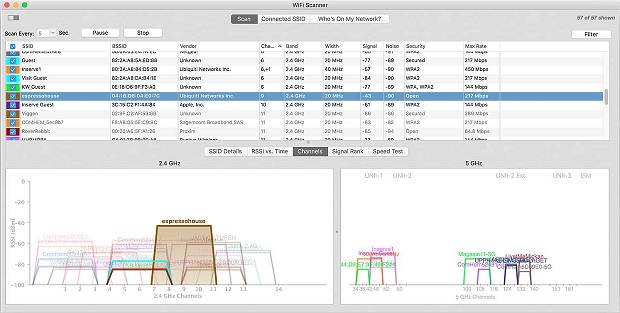
WiFi Scanner is a paid app that costs $14.99 for the Windows version and $19.99 for the Mac version. A free trial is available for those who would like to test its features before buying.
Pros and Cons
-
Available for both Windows and Mac
-
Support for 802.11 a/b/g/n/ac
-
Offers a lot of features
-
The Mac version is more expensive than the Windows version
Real WiFi, available directly from the Microsoft Store, is designed to make your life easier when it comes to optimizing your wireless network. You can use it to identify interference from neighboring networks so that you know how to adjust your settings for faster internet speed without purchasing a new router.
One stand out feature offered by Real WiFi is its integrated internet speed test. With it, you can quickly and easily gauge the actual performance of your connection in real-time. We also appreciate the ability to detect devices connected to your network. This Device Scan feature can be a real eye-opener, especially if you suspect unauthorized devices are accessing your network.
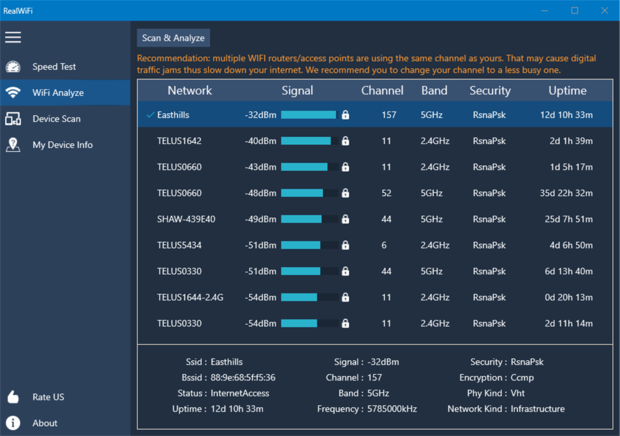
However, while it's packed with handy features for the everyday user, Real WiFi might not be suitable for those seeking highly specialized or advanced analysis. The app makes WiFi analysis accessible for the average user but may fall short for networking professionals or enthusiasts looking for a more robust wireless analyzer tool.
Pros and Cons
-
Easily accessible through the Microsoft Store
-
Provides essential tools like Internet Speed Test, WiFi Analyzer, and Devices Scan
-
Ideal for personal use and basic troubleshooting
-
Lacks advanced features that might be needed by professionals or tech-savvy users
Users wishing to run their analyzer on an iOS device will love the features of this tool which include diagnostic tools and an Internet speed test. With Network Analyzer by Techet, you can diagnose various WiFi problems with ease and with nothing but your iPhone.
It takes just a few taps to detect all devices connected to your network and see their IP addresses. When troubleshooting a large network, you can narrow down the number of scanned devices by specifying an exact IP range. Scan results can be further filtered by multiple parameters.
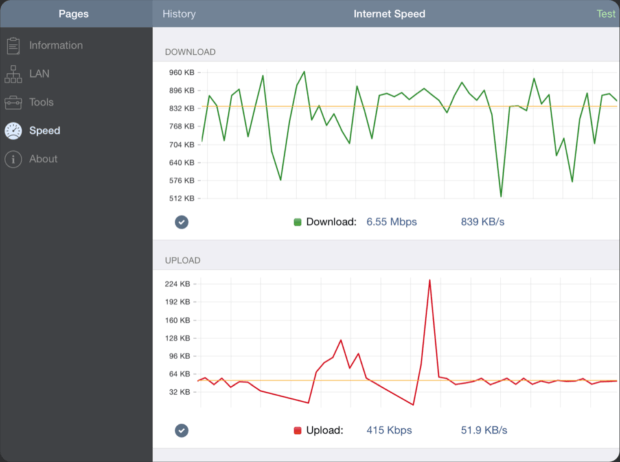
Network Analyzer can scan most common ports or user-specified port ranges to help you discover potential points of intrusion and close them before malicious hackers can take advantage of them. Being a modern WiFi analyzer app, Network Analyzer supports both IPv4 and IPv6, and it makes selecting between the two versions of the Internet Protocol a matter of a simple configuration option.
Pros and Cons
-
Compatible with all recent versions of iOS
-
Integrated internet speed test
-
Plenty of features
-
Support for IPv4 and IPv6
-
Outdated user interface
-
Not great for amateurs
Here is a free WiFi analyzer for Windows which can be used on your laptop to monitor signal strength, find open channels, and test your network’s speed. You can download WiFi Analyzer directly from the Microsoft Store and instantly turn your PC or laptop into a network analyzer.
With the free version of WiFi Analyzer, you can discover nearby WiFi networks and learn all essential information about them, such as their names and channels. The free version doesn’t contain any ads, and you can use it without any limitations.
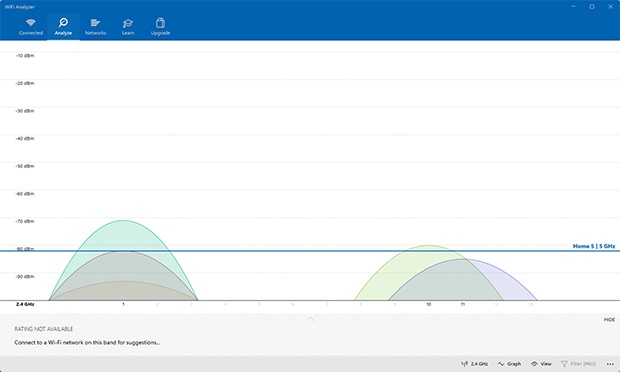
If you would like to unlock additional features, you can upgrade to the PRO version of WiFi Analyzer via an in-app purchase. The PRO version offers live-tile support, beeper for signal strength, the ability to connect to WiFi networks straight from the app, filters, and more.
Pros and Cons
-
Easy to use
-
Free with in-app purchases
-
Good enough for most home users
-
Lacks heatmapping capabilities
-
Too limited for professional use
First released in 1998, Wireshark is an extremely capable network protocol analyzer used to analyze what’s happening on wireless networks. It runs on Windows, Linux, macOS, Solaris, FreeBSD, NetBSD, and many other operating systems and can be downloaded and used for free without any limitations thanks to its open source license.
Wireshark can capture data packets both from wireless networks and Ethernet, and the captured data can be browsed via its graphical user interface or the terminal. The graphical user interface makes deep packet analysis easier by color-coding network packets based on their type. However, this alone doesn’t make Wireshark accessible to inexperienced users.
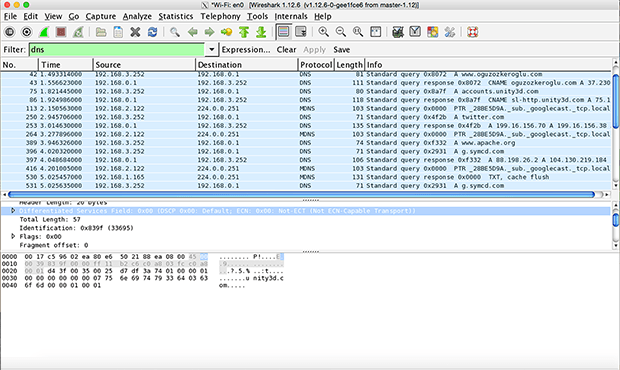
Fortunately, there are many online resources, including beginner-friendly videos, that explain how to use Wireshark for network protocol analysis, and they do a great job of supplementing the official documentation.
Pros and Cons
-
Free and open source
-
Extremely capable network protocol analyzer
-
Multi-platform
-
Live capture and offline analysis
-
Confusing for new users
Wi-Fi Scanner by LizardSystems is a straightforward analyzer app that targets mainly home users who are interested in learning more information about the wireless activity in their area. It can also be used by professionals who are unable to justify paying extra for a professional data recovery tool, whose numerous features would greatly exceed their needs.
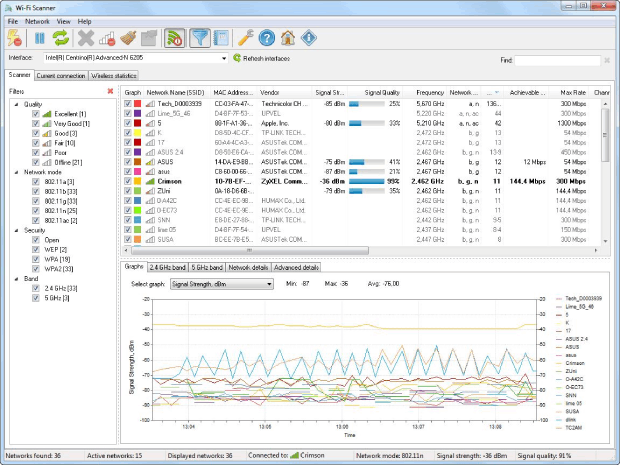
Home users can download and use Wi-Fi Scanner for free, but businesses are required to purchase a perpetual business license for $99.95. Regardless of whether you stay with the free version or purchase a license, you get to enjoy support for 2.4 and 5 GHz frequency bands, 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax, as well as WPS 1.0 and WPS 2.0.
Performing a WiFi scan with Wi-Fi Scanner by LizardSystems is easy enough, but the available graphs could be more visually appealing. We appreciate the ability to quickly apply various filter to narrow down the number of displayed WiFi networks, and we also like the option to instantly switch between different network interfaces.
Pros and Cons
-
Free personal license
-
Support for 2.4 and 5 GHz frequency bands
-
Clean user interface
-
Actively developed
-
Visually unappealing graphs
-
No heatmapping functionality
-
Windows only
Vistumbler is one of the best open source WiFi analyzer apps. It’s used mainly for large-scale access point visualization based on collected wireless and GPS data. The most recent version is optimized for Windows 10, but it also works with older versions of the operating system.
All data collected by Vistumbler can be exported into a number of file format, and that includes the GPS locations of discovered access points, which can be exported into a Google Earth KLM file or GPX (GPS eXchange format).
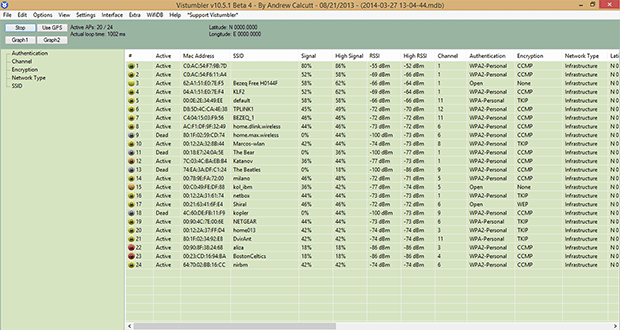
Don’t let the outdated user interface of Vistumbler discourage you from giving it a try. While it’s certainly true that Vistumbler developers prefer function over form, the user interface is fairly easy to get used to.
Pros and Cons
-
Open source
-
Runs only on Windows
-
Outdated user interface
-
Not great visualizations
One of these WiFi apps should be able to help you improve your network’s performance. Download one to the platform of your choice and scan your network. It might point out a simple way to fix to issues that negatively impact your network and its users.
How to Perform Wi-Fi Analysis Using a Wi-Fi Analyzer App?
Wi-Fi analysis may sound very technical and daunting, but it’s anything but that — as long as you use a simple yet capable Wi-Fi analyzer app like NetSpot. In addition to NetSpot, you’ll also need a laptop with a WiFi card so you can detect nearby Wi-Fi networks.
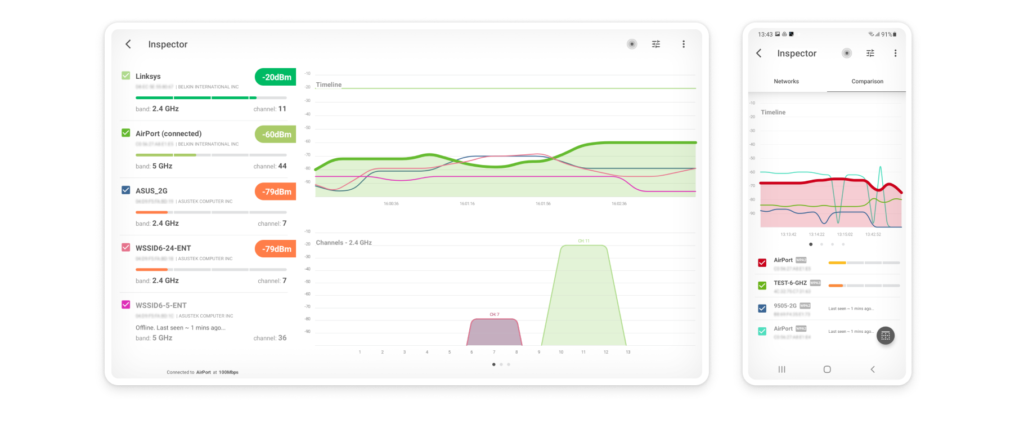
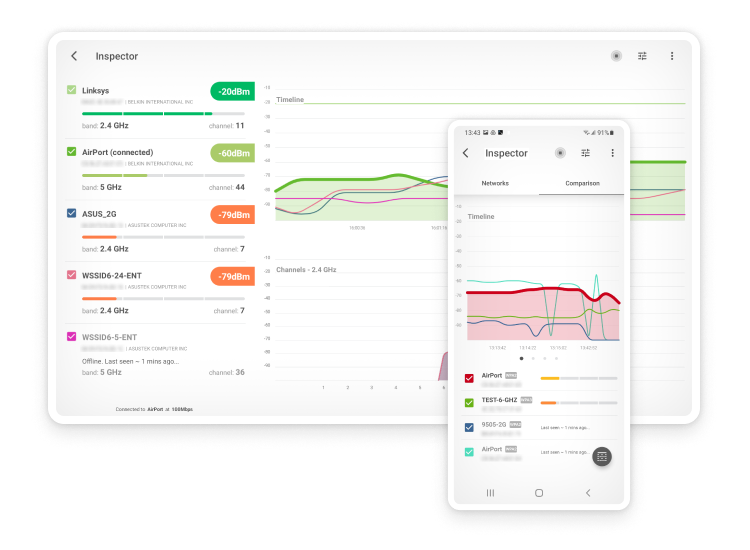
With NetSpot, you can choose between three distinct WiFi analysis methods. The first method, called Inspector Mode, is all about quick and easy WiFi network discovery, instantly listing all WiFi networks available in your area, along with all important information about them, including network name, band and channel, security settings, WiFi standard, signal strength, and noise level.
The second WiFi analysis mode is called Survey Mode, and it allows you to perform a WiFi site survey and create a WiFi heatmap so you can see exactly where your WiFi signal is strong and where it could use some improvement.
The third and last mode supported by the WiFi spectrum analyzer, called Planning Mode, focuses on the future planning and optimization of your WiFi network. In this mode, users can virtually map out their environment and simulate how different network setups will perform. This includes the ability to place virtual access points on the map to see how their location affects signal coverage and strength throughout the area.
By combining these three WiFi analysis methods, you can get a very accurate idea about the performance of your WiFi network and understand exactly what you need to do to improve it or deploy it. For example, it takes just one click to see which WiFi channels nearby WiFi networks broadcast on, which makes it straightforward to solve channel interference issues.
Performing WiFi Analysis Using Inspector Mode
NetSpot’s Inspector Mode is so easy to use that it doesn’t need any explanation. Simply activate it using the toggle located in the top bar and watch as NetSpot creates a snapshot of all WiFi activity around you. NetSpot will then continue to analyze surrounding areas in real-time.
If you would like to pause the real-time analysis, you can do so using the Pause button in the top-left corner. Close to the Pause button is the Signal level and noise graphs button, which lets you see easy-to-understand graphs that represent the — you’ve guessed it — signal strength and noise levels of selected networks.
The information collected by Inspector Mode include:
- SSID: The Service Set Identifier is what’s commonly referred to as the network name. Wireless networks broadcast this string of letters, numbers, and possibly even special symbols to differentiate themselves from one another and make it easy for clients to establish a connection.
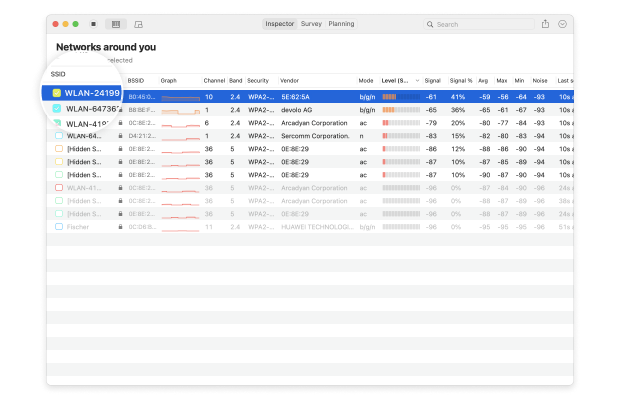
- BSSID: Similar to the Service Set Identifier, the Basic Service Set Identifier is used to uniquely identify an access point or router broadcasting a wireless network.
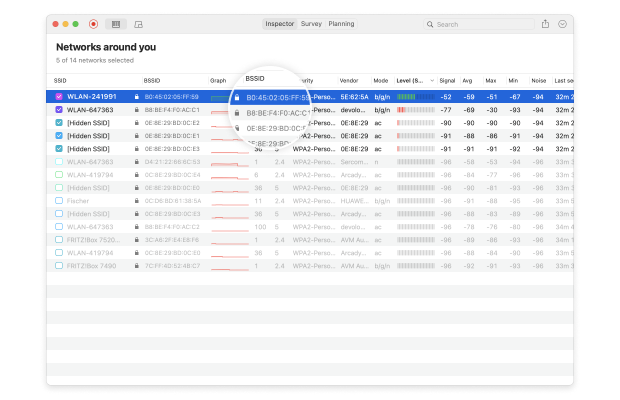
- Signal strength: Measured in dBm (decibel milliwatts) and expressed only as negative values, the signal strength of a wireless network directly influences data transfer speeds, latency, and connection reliability.
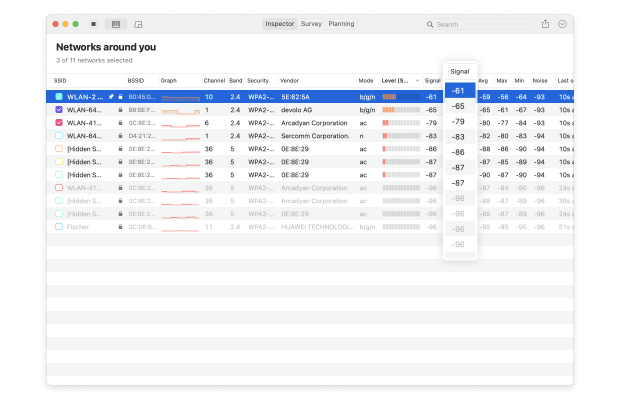
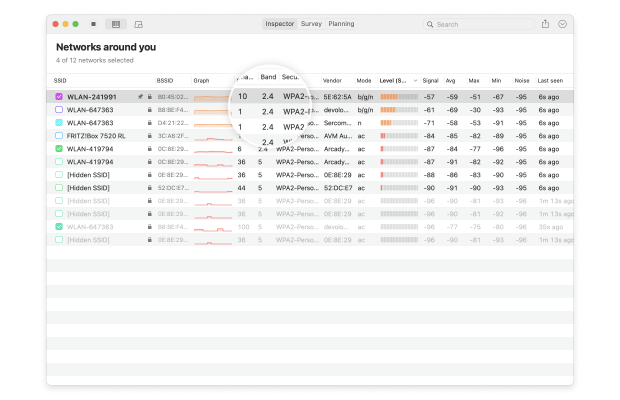
- Channel number: To reduce signal interference, the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands are divided into multiple channels, some of which may be more crowded than others, especially in densely populated urban areas.
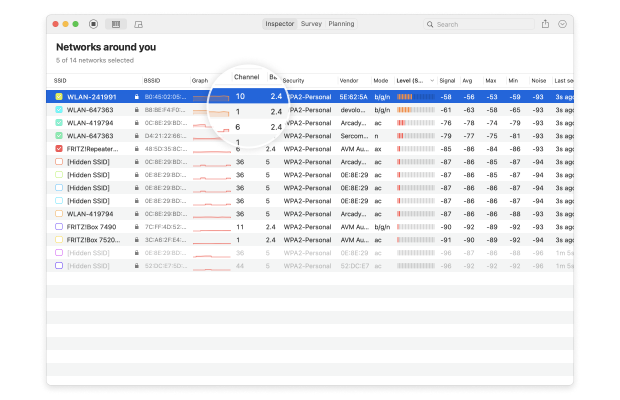
- Band: The 802.11 standard provides several radio frequency bands. Most modern WiFi routers support the 2.4 and 5 GHz bands, and so does NetSpot.
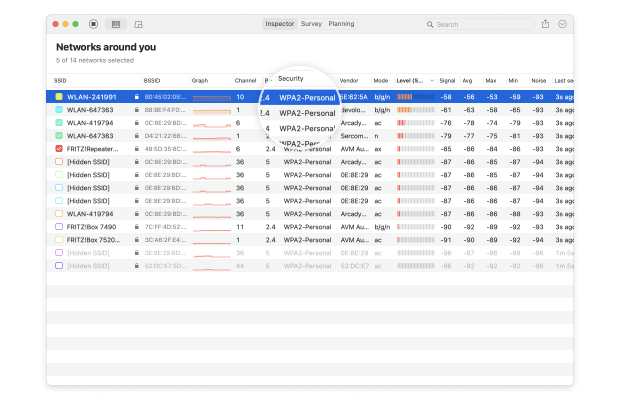
- Security: WEP, WPA, WPA2, and WPA3 are four security standards designed to secure personal, enterprise, and IoT wireless networks. Out of these, only WPA3 can resist modern cyber-attacks and protect sensitive information from snooping.
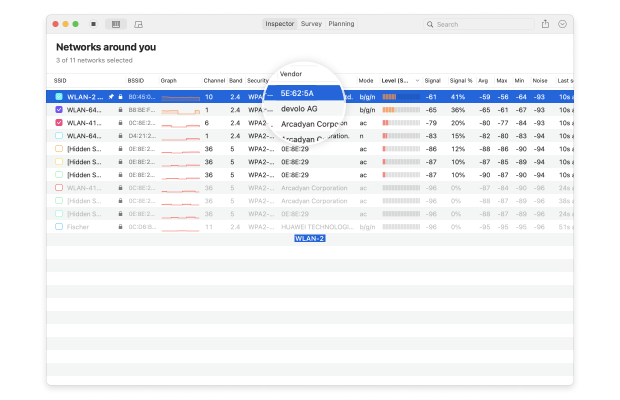
- Vendor: There are many router manufacturers, and not all are respected by cybersecurity professionals.
- Mode: WiFi standards are constantly evolving to meet our growing needs. NetSpot can analyze any 802.11 network, including 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax.
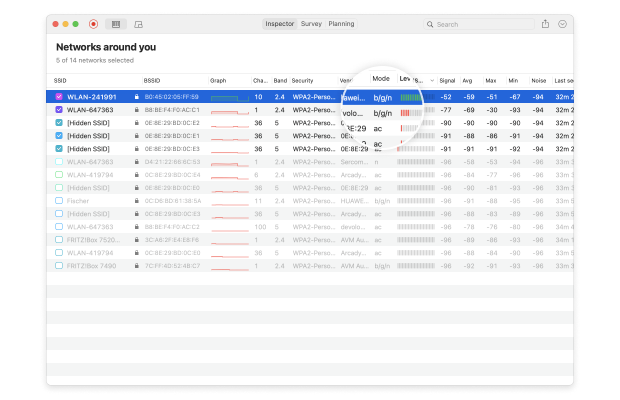
- Noise: Wireless signals can clash with radio frequency interference emitted by microwave ovens, Bluetooth headphones, baby monitors, wireless security cameras, and many other electronic devices, and NetSpot can detect the amount of this background noise in your area.
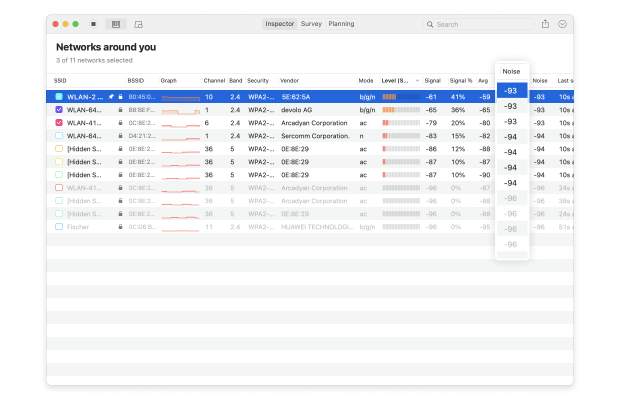
As you can see, NetSpot can provide a wealth of information about wireless networks in your area, and it also lets you perform an in-depth analysis of the network you’re connected to thanks to Survey Mode.
Performing WiFi Analysis Using Survey Mode
The Inspector Mode gives you all the information you need to avoid problems with interference and channel overload. But if you would also like to optimize the placement of your home router, you should switch to the Survey Mode and create a signal heatmap of your area.
This is how to create a new survey:
Start by downloading and opening NetSpot on your device. Then click on the Survey button to begin.
Click on Create New… to start a new project. Name your project and add a description if needed.
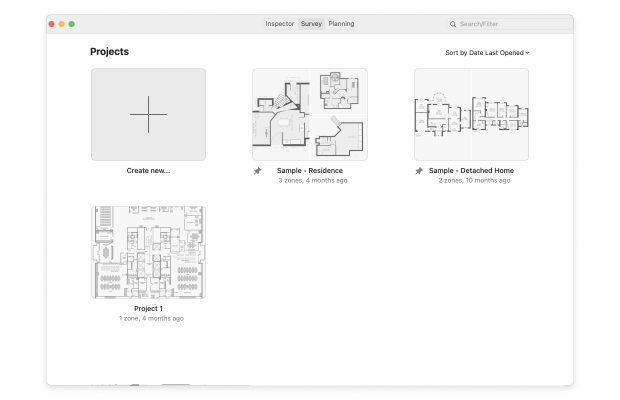
Either upload a map file (like a blueprint, sketch, or a Google Maps screenshot) or draw a new plan directly in NetSpot. If drawing a new plan, you can specify the area dimensions in feet or meters.
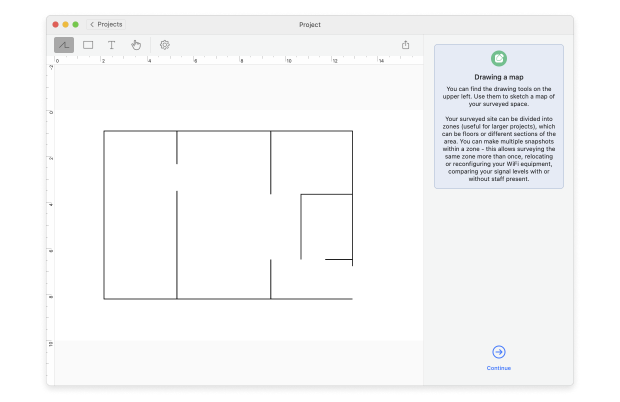
For a new drawing, use the tools provided below the canvas to sketch your surveyed space. If your area is large or has multiple zones, consider creating separate maps for each. Click Continue when the map is ready.
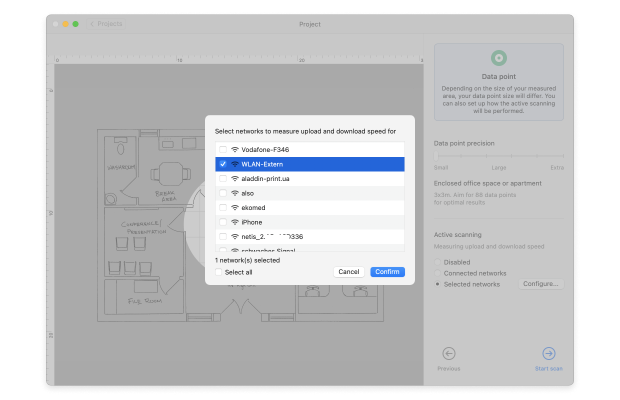
Decide on the density of data points based on the size and complexity of your space. Consider whether you’ll perform Active scanning and select the networks for scanning. Click Start Scan to begin collecting data.
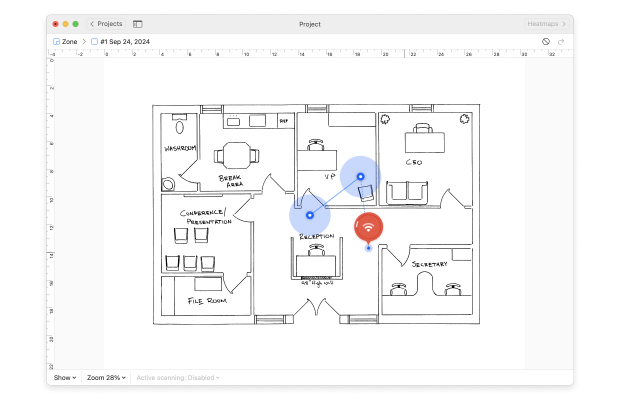
Move to a corner of your space and mark it on the map where you are standing. Stay still while the app takes its first measurement. You’ll know it’s finished when the progress indicator changes and you hear an audio alert. Walk through your space, taking measurements at intervals that ensure slight overlap between the blue circles on your map, covering the area you intend to scan.
Click Heatmaps to view the wireless network coverage and various parameters affecting it.
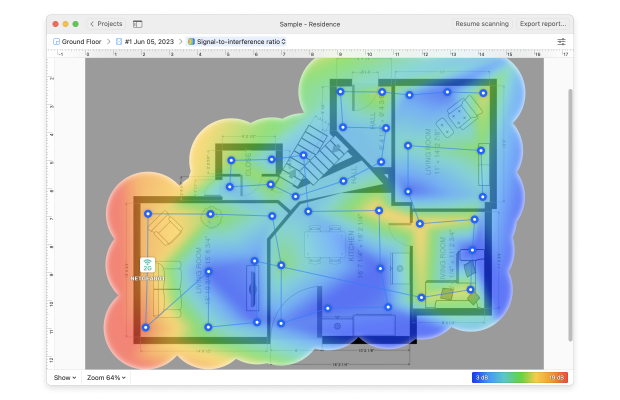
Choose from different heatmap types to analyze various aspects of your wireless network's performance.
- Signal-to-noise ratio: highlights your signal level as compared to your noise level.
- Signal level: highlights your signal level, allowing you to easily see areas of signal weakness.
- Quantity of access points: highlights the number of access points available from each measurement point.
- Noise level: highlights the amount of background noise measured from each measurement point.
- Signal-to-interference ratio: highlights co-channel interference caused by other wireless networks.
- Download speed: highlights internet download speeds recorded during an active scan.
- Upload speed: highlights internet upload speeds recorded during an active scan.
- Wireless transmit rate: highlights the internet wireless transmit rate recorded during an active scan.
- Troubleshooting issues with SNR: this heatmap visualization makes it easier to identify and troubleshoot weak areas of signal-to-noise ratio coverage (macOS only).
- Troubleshooting low signal level: this heatmap visualization makes it easier to identify and troubleshoot areas of weak signal level.
- Troubleshooting high noise level: this heatmap visualization makes it easier to identify and troubleshoot areas of high noise level (macOS only).
- Troubleshooting overlapping channels (SIR): this heatmap visualization makes it easier to identify and troubleshoot areas of high co-channel interference.
- Troubleshooting low download rate: this heatmap visualization makes it easier to identify and troubleshoot areas of low download speeds.
- Troubleshooting low upload rate: this heatmap visualization makes it easier to identify and troubleshoot areas of low upload speeds.
Keep in mind that some of these visualizations are available only in the Pro version of NetSpot.
To obtain the most accurate results possible, it’s a good idea to repeat the survey process several times, at different times of the day. Why? Because the results may be influenced by temporary usage spikes, intermittent interference, and other difficult-to-predict factors whose influence becomes obvious only with additional measurements.
Learn More About WiFi Analysis with NetSpot
If there’s something that’s not completely clear to you, we encourage you to visit NetSpot’s help page, where you can learn more about using this professional wireless analyzer to perform WiFi analysis. If you perform WiFi analysis on a regular basis, NetSpot PRO can save you a lot of time, energy, and even money.
As you can see, WiFi analysis isn’t nearly as daunting as it would be if it wasn’t for modern WiFi analyzer apps such as NetSpot. With them, WiFi analysis is a piece of cake and something that every owner of a wireless router should do to avoid slowdowns and connection drops.
About WiFi Analyzer — FAQs
The purpose of a WiFi analyzer is to gather detailed information about all wireless networks within range and display them in an easy-to-understand format to help everyone from regular home users to professionals troubleshoot WiFi-related problems and optimize performance.
There are many different WiFi analyzers users can choose from, each offering a slightly different set of features and capabilities. The best WiFi analyzers support the latest WiFi technologies, are easy to use, and cost a reasonable amount of money. NetSpot is a great example of a WiFi analyzer that meets all these criteria and stands out from the competition when it comes to usability and performance. See the list of the best wifi analyzer windows apps.
Even though free WiFi analyzers seldom offer the same number of features as their paid counterparts, many are more than capable enough to satisfy the needs of regular home users and even some professionals. The best free WiFi analyzer apps mentioned in this article include NetSpot (Inspector mode), inSSIDer, Real WiFi, WiFi Analyzer, Wireshark, and Vistumber.
Modern WiFi analyzers tend to be intuitive and easy to use, so using them to gather detailed information about available wireless networks is usually quite straightforward. In most cases, all you need to do is install your WiFi analyzer of choice on a laptop and launch it to initiate an automatic scan of WiFi networks.
To check WiFi interference, you need a WiFi analyzer app that supports the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and the newer 6 GHz bands. You then need to analyze nearby wireless networks to see which frequency bands and channels they’re using and avoid the most used parts of the radio frequency spectrum.
That depends on which WiFi analyzer you choose. The Best WiFi analyzer apps, such as NetSpot, Network Performance Monitor, or inSSIDer are all perfectly safe, and you can rest assured, knowing they won’t harm your computer.
Just like cell phones, televisions, and radios, WiFi networks use radio waves to transmit data over the air. This means that the signals they send can be blocked walls, common household objects, and even other electronic devices broadcasting on the same frequencies.
The best WiFi analyzer apps can tell you everything you need to know about nearby WiFi networks, provide you with detailed information about a network’s coverage, reveal areas of channel interference, and more, making them indispensable when it comes to troubleshooting and optimization.
A WiFi analyzer is a useful tool whose purpose is to provide a wealth of information about wireless networks, including their signal strength, coverage, names, and security configuration. This information can be used to troubleshoot WiFi-related issues, plan network deployments, and more.
Modern WiFi analyzers like NetSpot are easy to read because they present all gathered information in the form of interactive tables, graphs, charts, and heatmaps. In most cases, you can spot issues with coverage, signal strength, or security settings at a glance and quickly determine what you need to do to solve them.
To analyze a WiFi signal, you need a computer with a WiFi card and a WiFi signal analyzer like NetSpot. You can then simply start the WiFi signal analyzer, wait for it to gather information about the signal, and see if you can spot anything unusual.
To check WiFi signal strength, you don’t need any special equipment. All you need is one of the best WiFi analyzer apps described in this article.
There are many WiFi analyzer apps for Android that make it possible to quickly and easily scan your and surrounding wireless networks and observe the changes in data charts in real-time. One of them is the Android WiFi analyzer from NetSpot, and you can download it for free directly from the Google Play Store. Check our article about the best WiFi analyzer apps for Android.
Due to Apple’s restrictions, there are not many WiFi analyzers for iPhone (check our list of the best wifi analyzers for iPhone).
Read how to choose the best WiFi analyzer for mac, if you are looking for one.