Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Analysis, Troubleshooting runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11be/ax/ac/n/g/a/b wireless network adapter. Read more about the 802.11be support here.
11 Common Reasons for Slow WiFi and How to Fix Them
Explore Wi-Fi TROUBLESHOOTING techniques to enhance weak signals, optimize network performance, and fix common connectivity issues. Learn how to resolve slow internet connections and achieve faster speeds for work and everyday use with WiFi troubleshooting tools like NetSpot.
Fortunately, there are ways how to fix slow Wi-Fi, and we explore them in this article.
Why Is My Wi-Fi So Slow?
Internet speed is one of the first things we notice online, and slow Wi-Fi can be frustrating. It disrupts work, streaming, and even simple browsing. Sometimes, even the best internet plan doesn’t guarantee fast speeds.
To understand what makes your Wi-Fi slow and how to fix it, you first need to know what Wi-Fi actually is. It’s a wireless communication technology that connects devices to the internet. A wireless router creates this network, but its performance, range, and efficiency vary.
Common reasons for slow Wi-Fi include:
- Weak signal strength due to walls, floors, or distance.
- Network congestion from too many connected devices.
- Channel interference from overlapping Wi-Fi networks.
- Poor router placement blocking even signal distribution.
- Outdated hardware or firmware limiting performance.
Keep reading to learn how to fix these issues.
The Strenght of Your Wi-Fi Signal Is Too Weak
One of the main culprits behind slow Wi-Fi speeds is a weak signal. Like any wireless transmission, Wi-Fi has a limited range, and several factors influence how far a device can be from a router while maintaining a strong connection. Your router's antenna design, placement, and age all impact its performance.
Older routers or low-end models often have weaker, internal antennas that struggle to provide stable coverage. Newer, high-end routers support MIMO (multiple-input and multiple-output) and MU-MIMO (multi-user MIMO), allowing them to handle multiple simultaneous connections efficiently and reduce signal loss.
Beamforming technology in modern routers directs Wi-Fi signals toward devices instead of broadcasting in all directions, improving coverage and minimizing dead zones. Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E further enhance performance with OFDMA (orthogonal frequency-division multiple access), which optimizes bandwidth distribution among multiple devices, ensuring faster speeds in congested environments.
But even the most state-of-the-art router equipped with all the latest and greatest technologies is limited in terms of its range to a certain degree. Routers are affected by physical obstacles like walls, floors, and large metal appliances. These barriers can significantly reduce signal strength and range, making it essential to identify and address coverage gaps.
Analyze Your Wi-Fi Signal Сoverage
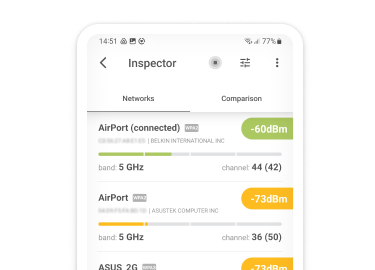
To understand and improve your Wi-Fi coverage, use NetSpot’s Survey Mode to create a detailed heatmap of your Wi-Fi signal strength. It allows you to visualize areas with weak coverage and identify sources of interference.
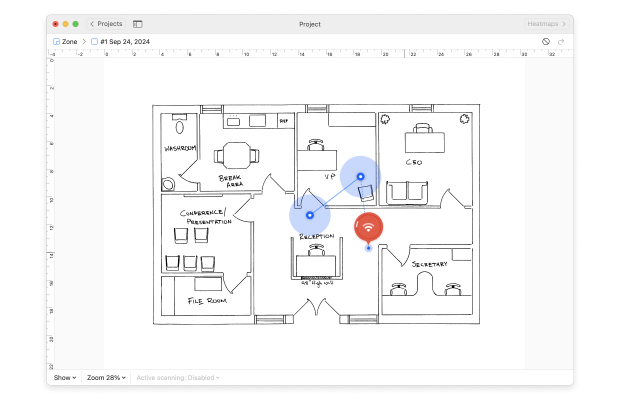
To get started, open NetSpot and click the “Survey” button. Then, upload or create a map of the area you wish to survey. Walk through the space, marking your position on the map, and let NetSpot collect data samples. After completing the survey, you’ll have a clear understanding of your Wi-Fi range and any problem areas that need fixing.
Analyze Speed and Performance with Active Scanning
NetSpot not only helps visualize signal strength but also enables active scanning, a powerful feature that measures the actual performance of your network. By actively connecting to your Wi-Fi, NetSpot can analyze critical parameters such as upload and download speeds, providing deeper insights into your network’s real-world capabilities.
This is particularly valuable for identifying areas where slow data transfer might hinder your online activities, such as video calls, streaming, or large file uploads.
In addition to signal strength, NetSpot allows you to create Wi-Fi heatmaps of upload speed and Wi-Fi heatmaps of download speed, providing a clear visual representation of your network's performance.
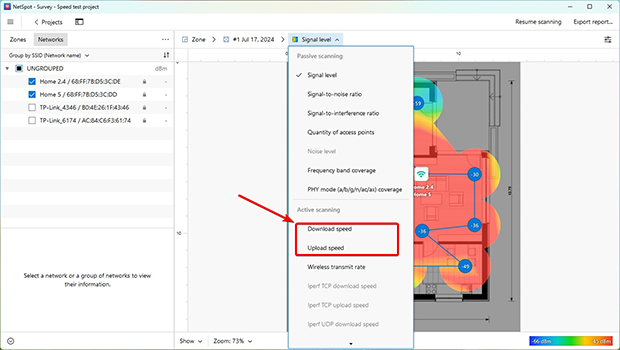
These heatmaps highlight zones with slower data transfer rates, helping you pinpoint areas that may require router repositioning, upgrades, or the addition of access points to improve connectivity.
The Capacity of Your Network Is Exhausted
Another common reason for slow Wi-Fi is network congestion. Think of your WiFi like a highway — when too many cars are on the road at the same time, traffic slows down. Similarly, when multiple devices connect to your network simultaneously, bandwidth gets divided, reducing speeds and performance.
The total capacity of your Wi-Fi network depends on your internet connection type and the technology used in your router. If you use fiber optic internet, you can expect higher speeds and better stability compared to standard broadband services. However, even with a fast connection, poor Wi-Fi management can lead to congestion.
The problem with many Wi-Fi networks is that they compete for bandwidth with other networks. Most routers operate on the 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz bands, which are divided into multiple channels. If too many networks use the same channel, performance drops. When a router is using an overloaded channel, your connection can suffer performance drops because of interference.
In practice, if your wireless router and your neighbor’s router both broadcast on the same frequency and channel, it’s like two overlapping conversations in the same room, making it difficult for either to work efficiently.
Being a professional wireless analysis application, NetSpot can help you discover all nearby Wi-Fi networks and determine which of them might be interfering with your Wi-Fi network.
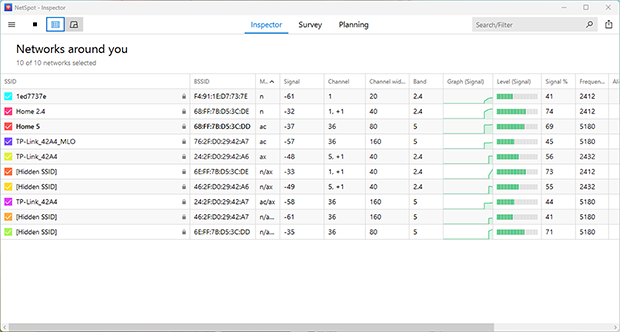
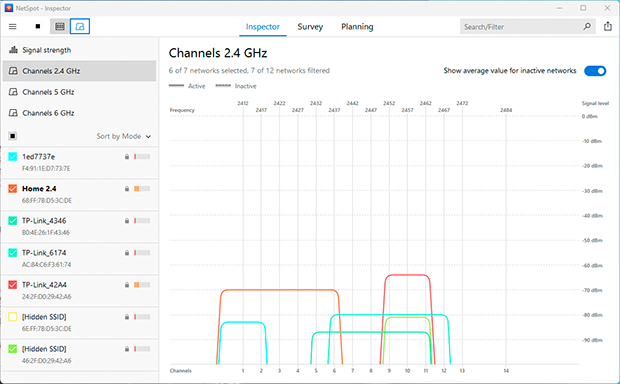

Optimize your WiFi network for maximum performance. Inspect, compare, survey, and analyze WiFi networks with NetSpot.
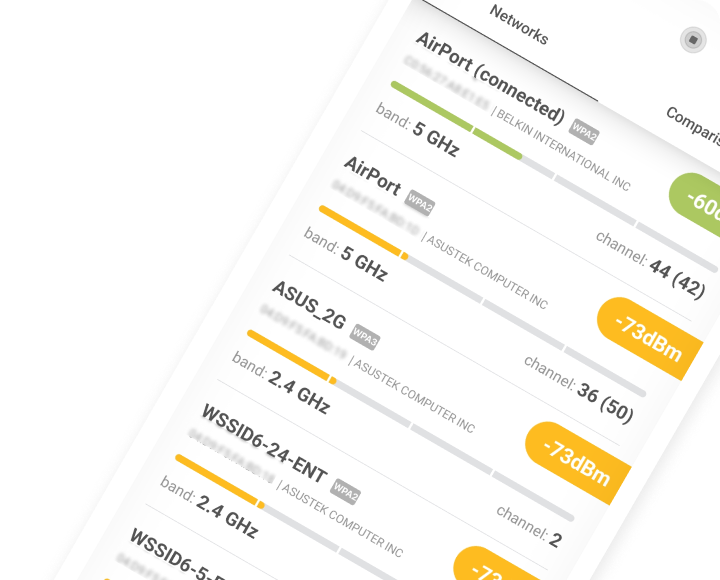
The Speed and Connection Type of Your Internet
Understanding why your Wi-Fi is so slow requires not only a look at your home setup but also the type of internet service you're receiving. Even with a perfect home network, you need to make sure that the internet service your provider is delivering can meet your needs. Unfortunately, this isn't always the case, especially if your internet is delivered via less reliable means such as:
- Satellite: While satellite internet can cover vast distances, it's often slower than other types due to the significant distance the data has to travel.
- Fixed wireless: This type of connection can be affected by various factors, including weather conditions, physical obstructions, and distance from the transmitter.
- 5G: Networks utilize higher frequency bands that don’t travel as far and can be disrupted by barriers like walls or trees. As a result, if there isn’t a direct, unobstructed path to the 5G tower, your connection speeds may fall below what you expect.
Even if you have a more reliable type of internet access, such as fiber optic, your internet plan may still be too limited. This could be in terms of download and upload speed, or your Internet Service Provider (ISP) might be intentionally slowing down your connection, which is typically referred to as throttling and can occur for various reasons, such as exceeding your data cap or during peak usage times.
Some ISPs also throttle bandwidth during peak hours to alleviate network congestion, and they may even prioritize certain types of traffic (web browsing, for example) over others (like video streaming), a practice known as traffic shaping.
What Can You Do?
To ensure your internet plan meets your needs:
- Test your connection speed regularly using tools like NetSpot or speed test platforms to compare actual performance with your plan's advertised speeds.
- Consider upgrading your plan if your current one doesn’t support your household’s usage, especially during peak times.
- Investigate alternative ISPs in your area that may offer faster or more consistent speeds.
You’re Using an Old Wi-Fi Standard
Older wireless routers only support older specifications for implementing wireless local area network (WLAN) computer communication, such as 802.11g, which operates at a maximum transmission speed of 54 Mbit/s and was adopted in the market starting in January 2003.
Newer wireless routers, however, support advanced standards like:
- 802.11n: Capable of speeds up to 600 Mbit/s on both 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz bands.
- 802.11ac: Offers speeds up to 1 Gbit/s, ideal for high-bandwidth activities.
- 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E): The latest standard, supporting speeds of up to 10 Gbit/s, with enhanced efficiency and reduced latency, especially in environments with many connected devices.
As you can see, it’s unreasonable to expect very high Wi-Fi speeds if you have an ancient wireless router. Similarly, it’s also unreasonable to expect high Wi-Fi speeds with a cutting-edge wireless router but old client devices that don't support the same modern specification for implementing WLAN computer communication.
How to Determine If It’s Time to Upgrade
If you wireless router is outdated, it may be time to upgrade to a newer model. While some performance tips in this article may improve your network slightly, they won’t compensate for the limitations of old hardware. Replacing your router with a model that supports the latest standards ensures a significant performance boost.
To evaluate your router’s current performance, we recommend using NetSpot, a wireless network site survey application for Mac and Windows. Here’s how you can assess your router:
- Open NetSpot.
- Start a new site survey.
- Select the Wi-Fi network broadcasted by your wireless router.
- NetSpot will measure critical metrics such as upload speed, download speed, and wireless transmit rate, giving you an overall picture of your router's performance.
Also, NetSpot conducts detailed speed tests by sending queries to servers and calculating the response times. Using the collected data, including upload speed, download speed, and wireless transmit rate, you can determine whether your router meets your current needs.
In addition to analyzing performance, NetSpot offers a Planning Mode that allows you to simulate the placement of different access points in a virtual environment. This helps you:
- Identify the best location for a new router or access point.
- Compare models and configurations before making a purchase.
By visualizing expected performance, you can ensure your investment provides optimal coverage and speed for your space.
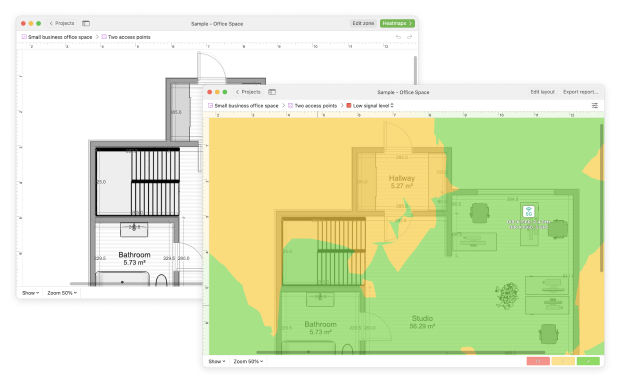
Adjust Quality of Service (QoS) Settings
Most modern routers include Quality of Service (QoS) settings, which allow you to manage your network traffic by prioritizing certain types of activities over others. For instance, you can allocate more bandwidth to video streaming or online gaming, ensuring smooth playback or lag-free gameplay, while limiting bandwidth for less critical tasks like file downloads.
However, if QoS is not properly configured, it can lead to uneven network performance, causing slow speeds for some devices or applications. Accidental misconfiguration by you or someone with access to your router’s settings can be a common culprit.
How to Fix or Optimize QoS Settings:
- Access your router’s settings: Log into your router’s web interface or app.
- Navigate to the QoS configuration section (usually under "Advanced Settings" or "Traffic Management").
- Review and adjust priorities: Ensure essential tasks like video calls or streaming are prioritized over less critical activities.
- Test your network: After making adjustments, monitor your Wi-Fi performance to confirm the changes are effective.
If QoS settings don’t improve performance or create additional issues, you can disable QoS completely to ensure equal bandwidth distribution across all devices.
11 Effective Steps to Fix a Slow Wi-Fi Network
Now that we’ve explored the possible causes of poor internet performance, let’s discuss exactly how to fix slow Wi-Fi using these 11 effective steps. Dealing with sluggish, laggy, or unstable Wi-Fi signals can be incredibly frustrating, but there are many straightforward ways to boost your network’s performance at home or in the office.
If you’re searching for how to fix slow Wi-Fi speeds or need a comprehensive guide to troubleshoot poor Wi-Fi performance, the following list will help you address each potential issue methodically — starting with the easiest and least expensive solutions first.
We recommend following these steps in the order they appear, ensuring you save the most costly or time-consuming options for last.
Diagnose the cause of the slowdown
Before you go any further, you should determine if the slowdown is caused by a local problem or your internet service provider. You can do that by running an internet speed test app like NetSpot on your Android and iOS device and comparing the results with the speeds advertised by your provider.
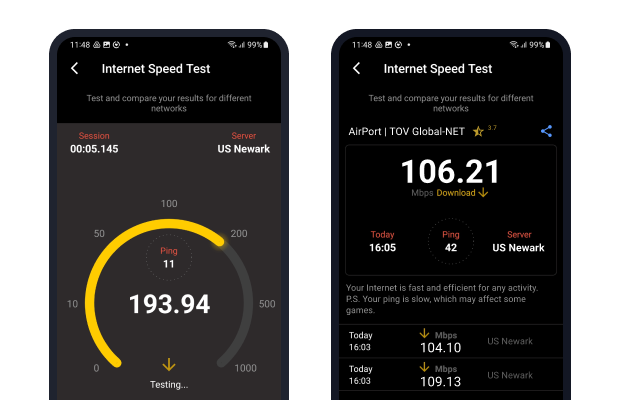
Restart Your Router
Modern routers are basically small computers with fairly complex operating systems that are guaranteed to contain more or less serious bugs capable of causing all kinds of performance problems. Unplug your router for 30 seconds before reconnecting it to ensure a full reset. A simple router restart is often enough to leave the buggy state and resume normal operation.
Choose the best Wi-Fi channel
Use tools like NetSpot’s Inspector Mode to identify crowded channels in your area. Select a non-overlapping Wi-Fi channel to reduce interference and improve speed. If no ideal channel is available, choose the least crowded one.

Optimize router placement
You can not expect your Wi-Fi network to perform great if your router is tucked away in some corner, far away from your devices. If you’re not sure where to place it, create a Wi-Fi signal heatmap first to gain better understanding of Wi-Fi coverage in your area.
Manage Bandwidth Usage
Bandwidth-intensive devices or malware can slow your connection. Use a strong password to prevent unauthorized access, and install antivirus software to protect against malware. Enable Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router to prioritize critical activities like streaming or gaming.
Keep Your System Clean and Secure
Outdated software and malware can severely impact your internet speed.
- Update your drivers: Ensure your network adapter drivers are up to date. Windows users can do this via Device Manager, while macOS handles driver updates automatically during system updates.
- Run antivirus scans: Regularly scan your computer for malware or viruses that could be consuming bandwidth in the background. Use trusted antivirus programs to eliminate threats and maintain optimal performance.
Limit the number of connected devices
Some routers are not powerful enough to support a large number of simultaneous connections. To ensure that all users can achieve reasonably fast speeds, you can limit the number of devices that can connect to the router at the same time. Consider upgrading to a router with multi-user MIMO (MU-MIMO) for better simultaneous device performance.
Find a reliable VPN
A VPN can speed up your connection if there’s some kind of obstruction on the path your data packets would normally travel. Essentially, it provides an alternative route that may come in handy if the route provided by your ISP suddenly start to take up too much time. However, ensure your VPN provider offers high-speed servers to avoid adding latency.
Upgrade your router
Sometimes, it’s simply not worth troubleshooting an old router that uses outdated wireless technologies and has very limited transmission power. Instead, buy a new one and instantly enjoy improved signal strength and faster download and upload speeds.
Expand coverage with a Wi-Fi extender or mesh system
Besides replacing your existing router with a newer model, you can also fix slow Wi-Fi speeds by adding a Wi-Fi repeater or mesh system to your network. A Wi-Fi repeater can extend coverage in one direction, while a mesh system offers seamless connectivity across multiple zones. Mesh systems are ideal for large homes or offices with multiple dead zones.
Switch to a different ISP
If you’re constantly dealing with a slow Wi-Fi network, your internet service provider might be to blame. To verify that it really is, you want to perform an internet speed test using a wired connection and compare the result with the speed you’re paying for.
Get a perfect WiFi speed with NetSpot
Don’t settle for a decent Internet connection, NetSpot ensures a consistent WiFi speed.Conclusion
Wi-Fi slowdowns are among the most annoying problems internet users deal with on a regular basis. The good news is that learning how to fix slow Wi-Fi is seldom difficult, especially if you're familiar with the methods described in this article and equipped with a wireless network analyzer like NetSpot.
How To Fix Slow Wi-Fi — FAQs
There are many different things you can do to make your Wi-Fi faster, including:
- Turn your router off and back on again.
- Use a more suitable Wi-Fi channel.
- Find a better place for your router.
- Protect your Wi-Fi network with a password.
- Eliminate signal interference.
- Upgrade to a high-end Wi-Fi router.
- Limit the number of connected devices.
- Switch to a more reliable ISP.
Your Wi-Fi speed can be affected by interference from neighboring networks, outdated router technology, poor placement, or too many connected devices. Use NetSpot to analyze your network and optimize settings.
Run a speed test with and without a VPN. If speeds improve when using a VPN, your ISP might be throttling your connection.
To fix slow Wi-Fi at home, you first need to figure out what causes it to perform so poorly. We recommend you use a Wi-Fi analyzer like NetSpot to determine your network’s configuration and coverage. Then, use the information provided by NetSpot and combine it with the tips from this article.
Differences in device hardware, software, and Wi-Fi standards can cause varying internet speeds. To address this:
- Update drivers: Ensure your laptop's network drivers are current.
- Check Wi-Fi standards: Verify that your laptop supports the same Wi-Fi standards as your router.
- Scan for malware: Use antivirus software to detect and remove any malware that might be affecting performance.
If your Wi-Fi network has suddenly become very slow, you might be dealing with the so-called bandwidth hog, a user or application that uses substantially more bandwidth than other users and applications on the same network. There’s also a chance that your ISP is experiencing issues, so take your time to analyze the problem and don’t jump to any conclusions.
You should start by determining why your Wi-Fi is performing poorly. For example, it's possible that your router is tucked away in a distant corner, or perhaps there's too much wireless interference in your area caused by other networks using the same Wi-Fi band and channel. Once you know the cause of your Wi-Fi issues, it's time to take the right steps to fix them, which could be as simple as moving your router to a better location or switching to a different channel.
If your Wi-Fi speed is considerably slower than the speed advertised by your internet service provider, then you can do the following to speed it up:
- Kick out all Wi-Fi leeches by changing your password.
- Find a better place for your router.
- Analyze your Wi-Fi environment and optimize your router settings accordingly.
- Buy a more powerful router.
There are many causes of Wi-Fi slowdowns, including:
- The router is positioned too far away from its clients.
- Too many people sharing the same Wi-Fi.
- High-bandwidth tasks such as torrenting and video streaming.
- Wireless signal interference created by other Wi-Fi networks.
Yes, when multiple devices share the same network, it can lead to bandwidth congestion. Disconnect unused devices to reduce load and ensure smooth performance. Configuring Quality of Service (QoS) settings on your router allows you to prioritize essential applications and devices. If the issue persists, upgrading to a router with MU-MIMO technology can better handle simultaneous connections.

Tools like NetSpot help visualize Wi-Fi coverage, detect interference, and optimize router placement for a faster, more stable connection.