Use NetSpot to quickly find the least crowded Wi-Fi channels.
How to Get Better Wi-Fi
Discover practical strategies to get better Wi-Fi and boost your network’s speed and coverage quickly.
Craving crystal-clear Teams calls and lightning-fast downloads? Then it’s time to get better Wi-Fi by learning how to boost Wi-Fi signals. With the methods outlined below, you’ll be well on your way to boost Wi-Fi performance like a pro. So, grab your favorite drink — you’re about to master Wi-Fi optimization!
Placement Tips
1. Optimize Router Placement: Banish Physical Barriers
Not all places in your home are equally suitable for your router. Keep your router well away from any metal objects or appliances that produce electromagnetic waves. Metal represents the greatest obstacle to a Wi-Fi signal, and placing it too close to your router often results in a pronounced dead zone.
Other materials, such as glass, wood, plastic, foam, and cardboard, can also disrupt a Wi-Fi signal, but their influence tends to be less severe. Remember that a lot of buildings rely on metal studs rather than standard 2x4 wood behind the particle board, which makes it unwise to position your router nearby.
To ensure more even signal coverage, place your Wi-Fi router roughly in the center of the area you want covered. You can slightly improve your wireless signal by elevating the router above the floor level.
Wi-Fi signals radiate in all directions, not just horizontally. When your router is on the floor, it’s harder for it to emit strong signals. For this reason, people in multi-story homes should position a Wi-Fi router near the ceiling on the first floor, so the second floor also receives a consistent signal.
2. Minimize Interference from Household Devices
Electromagnetic waves emitted by household appliances can significantly disrupt your Wi-Fi signal, leading to slower speeds and unstable connections. While even small devices like fluorescent lightbulbs, circuit breakers, and electric razors emit electromagnetic waves, the most problematic sources of interference are larger appliances.
Microwave ovens, stoves, and dishwashers — commonly found in kitchens — are particularly disruptive because of their strong electromagnetic fields.
Other devices, such as washing machines, tumble dryers, televisions, cordless phones, and radiant heaters, can also weaken your Wi-Fi signal if placed too close to the router. Even seemingly harmless items like baby monitors or wireless speakers can contribute to signal interference, especially in smaller spaces.
To ensure better WiFi performance, keep your router at a safe distance from these devices. Ideally, position it in a room away from major appliances and electronics, and if possible, create a clear space around it to reduce the likelihood of interference. By carefully managing your router’s location, you can significantly improve your network's stability and performance.
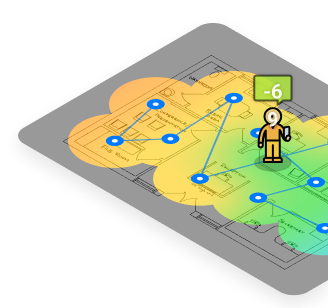
You can learn how much Wi-Fi interference there is in your environment by using NetSpot to perform a Wi-Fi site survey. NetSpot measures the signal-to-noise ratio (SNR), which compares the strength of your Wi-Fi signal against any background noise and interference on the same channel. A higher SNR means a better, more reliable connection.
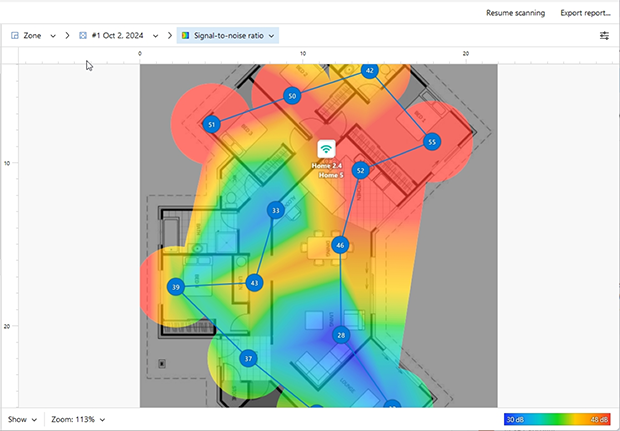
Perform in-depth Wi-Fi site surveys with NetSpot, and create detailed, color-coded heatmaps to analyze your network’s signal strength and identify dead zones. With these insights, you can optimize your router placement and enjoy better Wi-Fi.
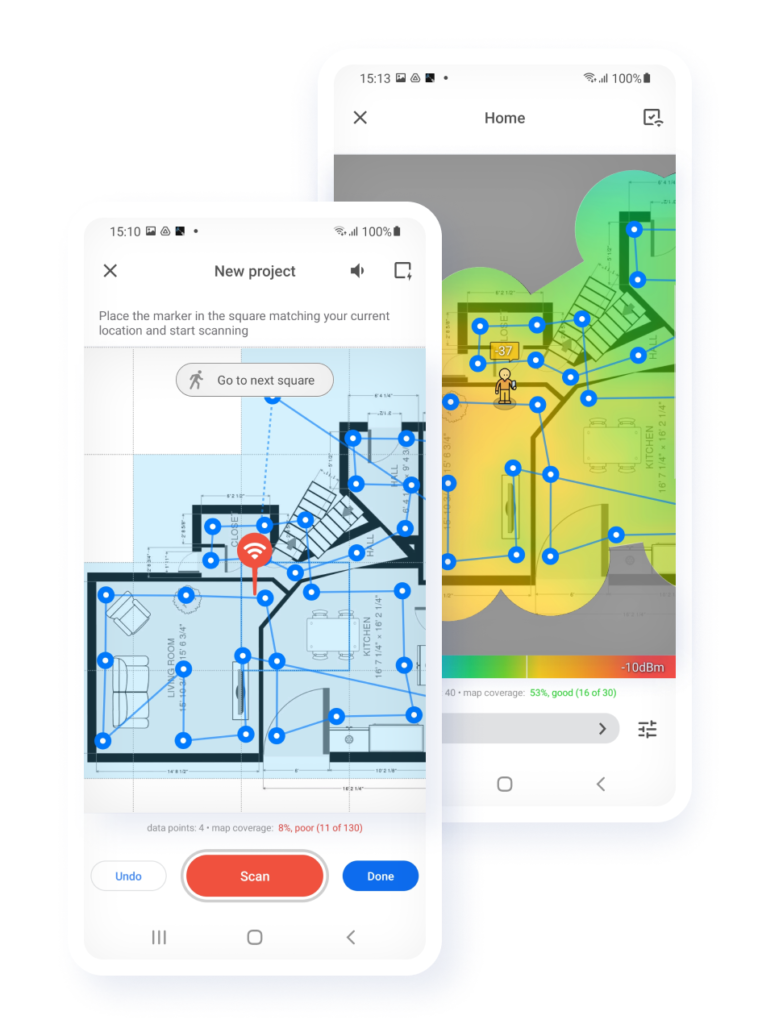
There’s also NetSpot for Android, which offers a great way to troubleshoot Wi-Fi coverage and select the best placement for your router with just a mobile device at hand. You can build Wi-Fi heatmaps directly on your mobile device (in-app purchase required for the heatmaps on device).
Perform WiFi Site Surveys on Android
Optimize Router Settings
3. Choose the Right Frequency and Channel
For better WiFi performance and fewer interference issues, optimizing your router's settings is key. Similar to highway lanes, Wi-Fi offers multiple channels for your router to broadcast on. The exact number can vary depending on the frequency band and local regulations.

In the 2.4 GHz band, data traffic often slows to a crawl because most regions only have four non-overlapping channels (1, 6, 11, and 14), each just 20 MHz wide. The problem is made worse by the fact that many routers default to Channel 1 or 6.
As a result, too many data packets pile up on the same channel, causing a Wi-Fi “traffic jam.” The remedy is straightforward: simply find the least crowded channel and switch your router to it.
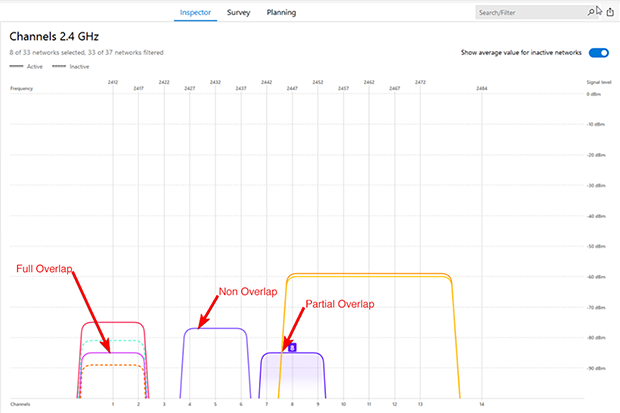
Tools like NetSpot, a professional yet beginner-friendly Wi-Fi analysis solution, allows you to scan nearby networks, identify the busiest channels, and pinpoint the optimal one for better WiFi performance.
With a new channel selected, you need to tell your Wi-Fi router to use it:
Log in to your router as admin.
Go to Settings and look for Wireless Settings.
You should see an option called Channel. The chances are that it will be set to Auto.
Select the desired channel.
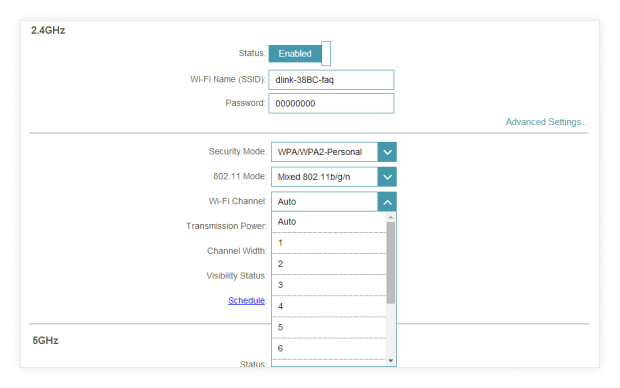
Save the new settings and wait for your router to restart.

You can now verify that your router is broadcasting on the new channel using a Wi-Fi network analyzer like NetSpot.
If your equipment allows, consider switching to the 5 GHz or 6 GHz bands. Fortunately, wireless traffic jams occur far less often in the 5 GHz and 6 GHz bands. These bands offer significantly more channels and greater bandwidth options.

When your equipment supports 5 GHz or 6 GHz, switching to these frequencies can provide an instant speed boost for short-range connections.
Here’s how to enable them:
Log in to your router as admin.

Access your router’s settings and navigate to the Wireless Settings section.

For 5 GHz, switch the 802.11 mode to 802.11n or newer, and for 6 GHz, select 802.11ax or newer.
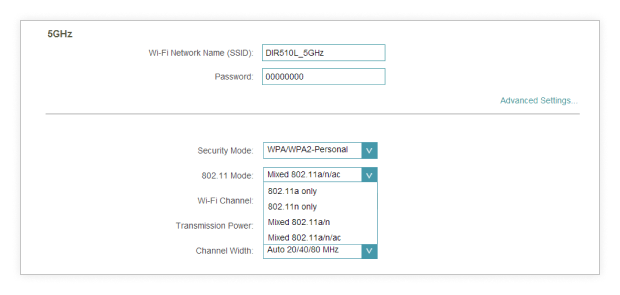
Click Apply to save your changes.

Restart your router to finalize the updated settings.
Note: All routers are different, and the steps you need to follow enabled 5 GHz or 6 GHz Wi-Fi on your router may be completely different from those described above.
One downside of the 5 GHz and 6 GHz wireless frequencies is that they don’t penetrate solid objects nearly as well as the 2.4 GHz wireless frequency. This can be a problem in office buildings and residential areas, so it’s advisable to always use 5 GHz and 6 GHz in conjunction with 2.4 GHz. That way, you can get the best of both worlds.
4. Control Bandwidth-Hungry Applications and Clients
One data-hungry app or device can slow down the entire Wi-Fi network for everyone else. Fortunately, many modern routers include a QoS (Quality of Service) feature that lets you prioritize critical applications or devices. This delivers a smoother online experience and helps you get better WiFi performance for gaming, video calls, or streaming.

Switching on QoS (Quality of Service) prevents your gaming session or crucial Zoom call from getting bogged down by someone else’s 4K streaming. It’s a handy way to keep Wi-Fi running smoothly, particularly if you share your network with many users and devices.
To change your router’s QoS settings and improve your network performance:
Log in to your router as admin.

Open your router’s settings menu and head to the Wireless Settings section.
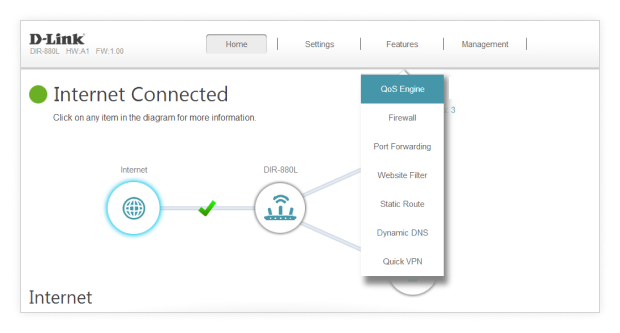
Locate the QoS Settings.
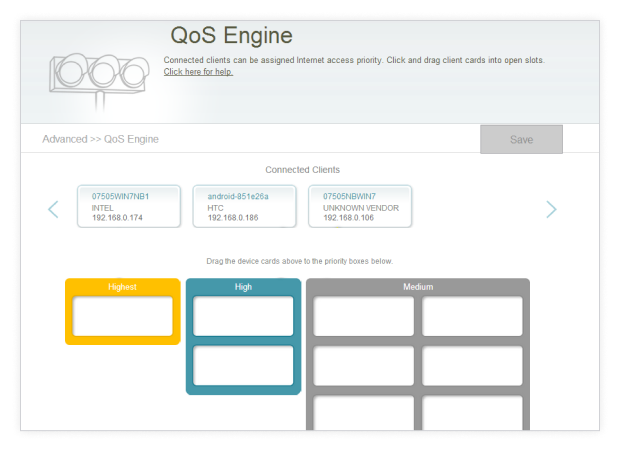
Configure your QoS rules.
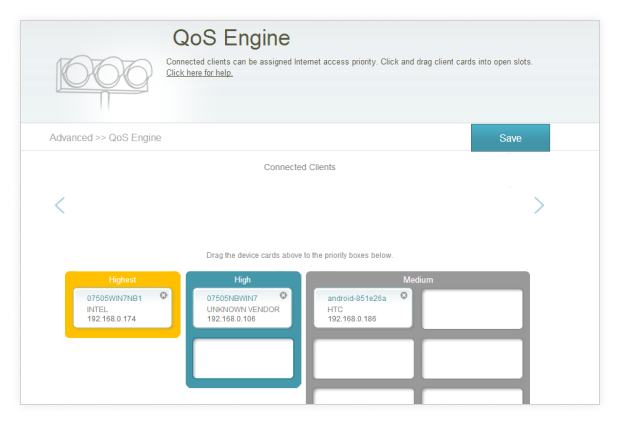
Confirm the changes, then let your router reboot fully.

Some routers make configuring QoS settings straightforward with user-friendly interfaces, while others may require a bit more effort. If you’re uncertain, consult your user manual or check the manufacturer’s website for detailed instructions.
Taking advantage of QoS is a simple yet powerful way to get better WiFi and ensure bandwidth is distributed effectively, giving priority to the tasks that matter most.
5. Change Your DNS Address
The Domain Name System, often called DNS, translates website addresses like www.google.com into numeric IP addresses such as 64.233.160.0. By default, your modem is most likely configured to use your internet service provider’s DNS server, whose performance may not be the best.
Switching to a faster DNS server can improve your internet speed and help you get better WiFi performance. Popular public DNS servers include Google’s DNS (8.8.8.8) and Cloudflare’s DNS (1.1.1.1), both known for their speed and reliability.

To find the fastest DNS server for your location, we recommend using Domain Name Speed Benchmark, a free tool for Windows:
- Download and start Domain Name Speed Benchmark.
- Switch to the Nameservers tab.
- Click the Run Benchmark button.
After the test completes, check the Conclusions tab to identify the best DNS server in your area.
If you prefer not to use a benchmarking tool, you can manually test popular DNS servers like Google, Cloudflare, or OpenDNS and see which one works best for you.
Once you’ve chosen the best DNS server:
- Log in to your modem or router’s admin panel.
- Locate the DNS Settings option (typically under Network or Internet settings).
- Replace the default DNS addresses with the primary and secondary addresses of your chosen server.
- Save your settings and restart your modem.
Changing your DNS address is a quick and effective way to optimize your internet speed and enjoy a better WiFi experience.
Hardware Upgrades
6. Get a Stronger Antenna
Many Wi-Fi routers ship with relatively small, weak antennas. While it’s not necessarily because manufacturers want to cut costs, higher-gain antennas do tend to be quite large. For reference, a standard router antenna might stand just a few inches tall and provide around 4 dB of gain, whereas a 10 dB antenna can measure anywhere from 10 to 15 inches in height.
If you don’t mind the extra size, installing a high-gain Wi-Fi antenna is an excellent way to strengthen your home or office network without having to replace the router entirely.
If you’re aiming to get better WiFi without purchasing a brand-new router, upgrading to a more powerful antenna is a great solution.
However, selecting the right antenna can be tricky. That’s where NetSpot shines. Using its Planning mode, you can test different antenna options (directional or circular) in a virtual Wi-Fi setup before making a purchase, making sure your chosen hardware truly improves your network’s performance.
Although Wi-Fi antennas come in different varieties, the most common one is the so-called “rubber duck” antenna, a compact monopole made of a coiled wire housed in rubber or plastic for protection.
Most antennas of this type share the same RP-SMA connector, and there are plenty of models to choose from online. Some even come with an extension cable, so you can position the antenna away from your router and optimize signal coverage. With NetSpot’s Planning mode to guide your decision — and the right high-gain antenna — you’ll be well on your way to achieving better WiFi coverage.
7. Buy a Wi-Fi Repeater/Booster/Extender
Even though they are referred to by many names, Wi-Fi boosters, repeaters, and extenders serve a similar purpose: extending or enhancing your existing network.
Wi-Fi repeaters work by picking up your router’s signal and sending it out again, effectively generating a second network.
Wi-Fi boosters and extenders are very similar, they also amplify the signal before rebroadcasting it. Since boosters typically have a longer reach than repeaters, they’re especially useful if your original Wi-Fi signal is quite weak.
You can usually find a decent booster or repeater for under $100, and the setup process is often as simple as pressing the WPS button. To help you choose the right Wi-Fi booster for your needs, we've compiled a list of the top Wi-Fi boosters on the market. Here are our top picks:
- TP-Link RE550 AC1900 WiFi Range Booster
- Linksys RE7000 Max-Stream AC1900+ Wi-Fi Range Booster
- Netgear Nighthawk X4 AC2200 WiFi Range Booster
- Netgear Nighthawk X6S EX8000 Tri-band WiFi Booster
- D-Link DAP-1610 AC1200 WiFi Booster
To achieve the best performance when using a Wi-Fi repeater or booster, consider using a Wi-Fi booster app like NetSpot. It will help you analyze your existing signal and determine how best to extend the existing Wi-Fi network.
Using NetSpot’s “Planning” mode, you can evaluate Wi-Fi boosters and repeaters before making a purchase. You can select a device from a preloaded list or manually input its parameters to simulate network performance.
This helps you find the most effective solution for your needs.
8. Set Up a Mesh Wi-Fi System
Occasionally, a single router — no matter how capable — can’t reliably cover the entire living space with a strong Wi-Fi signal. Dead zones, weak connections, or unstable speeds can make even the most advanced router insufficient for large or multi-story homes.
Sometimes, a mesh Wi-Fi setup is the ideal solution. These systems feature a main router along with one or more satellite units working together to blanket your home with continuous coverage.
Beyond improved reach, mesh networks also simplify management through dedicated apps, giving you the ability to prioritize devices and automatically optimize performance. Many models even come with Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E compatibility, ready to handle higher speeds and increased numbers of connected devices.
If you’re thinking of buying a mesh network, you’ll find plenty of reliable options on the market. Here are some of our top recommendations:
One of the best things about this approach is the ability to expand over time: you can start with a single router and one satellite, then add more units later if your Wi-Fi still isn’t meeting your needs. For more information and recommendations, check out our article on the best Wi-Fi mesh network systems.
Regular Maintenance
9. Keep Your Router Updated
If you keep up with current events, you’ve no doubt heard about the rising tide of large-scale malware attacks that are draining billions of dollars from businesses and individuals every year. The majority of these incidents would be far less feasible if routers stayed current with firmware updates.
Once malware infiltrates a router, it can hijack bandwidth and quickly move on to infect other devices on the network. Even in the absence of dangerous malware, routers running outdated firmware deliver poorer performance compared to those that are regularly updated.
To check if your router is up to date:
Connect to your router’s network and open a web browser.

Log in with the admin username and password (also likely on the router sticker).

Locate “Firmware Update” or “Router Update” in your router’s settings.
Wait for the update to finish — don’t power off the router or interrupt the process.

Some modern routers offer an automatic update feature, which can be enabled in the settings. If you’re unsure how to enable this or can’t find the firmware update section, visit the manufacturer’s website for instructions.
By keeping your router firmware up-to-date, you reduce the risk of malware attacks, close security holes, and enjoy better WiFi performance overall.
10. Don’t Forget to Reboot
The classic IT tip, “Turn it off and back on again,” works just as well for Wi-Fi routers. Restarting your router can often boost your Wi-Fi speeds by clearing its memory and enabling any pending updates to take effect.
To reboot your router, either press the restart button located on the back (you may need a pointy object like a pen to get to it because many router manufacturers use recessed restart buttons) or simply disconnect the router from power and turn it on again.
If your router really starts installing an update during the reboot, be patient and don’t interrupt the update process by turning off your router. Depending on your router’s performance, the update process may take more than 10 minutes.
Advanced Optimization
11. Cut Off Wi-Fi Leeches
In today’s world, having Wi-Fi that’s both encrypted and secured with a strong password is non-negotiable. With so many people depending on wireless connections, the demand for open, fast networks is huge. Don’t assume your neighbors won’t hop on your network just because they have their own — they often will if yours isn’t protected.
That’s why it’s crucial to encrypt your Wi-Fi. To protect your network:
Enable strong encryption: Use WPA3 if your router supports it, or WPA2 as a minimum.
Use a password that’s difficult to guess. A solid password should:
- Combine uppercase and lowercase letters, symbols, and numbers.
- Steer clear of commonly used passwords like “123456” or “qwerty.” You can check out a list of the most frequent passwords here.
- Be at least eight characters long, as shorter passwords are more vulnerable to brute-force attacks.
- Exclude personal information such as your name, your pet’s name, or phone number.
- Be unique, and avoid writing it down. If necessary, use a password manager.

If you often have visitors, consider setting up a dedicate guest network. You can limit its signal range or give it a different password, and don’t forget to update that password regularly.
12. Use the Latest Wi-Fi Technologies
The latest wireless standards, like IEEE 802.11ac (Wi-Fi 5) and 802.11ax (Wi-Fi 6 and Wi-Fi 6E), provide faster upload and download speeds along with better coverage than older versions such as IEEE 802.11b and g. Upgrading to these technologies is a must if you want to get better WiFi and improve your network’s speed and stability.
To fully benefit from improved Wi-Fi offered by the latest technologies, make sure your router and devices like smartphones, laptops, and smart TVs are compatible with these standards. Upgrading older equipment is essential for the best performance.
When selecting a new Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E Wi-Fi router avoid overly cheap models that lack key features.Unless your budget is very strict, it’s always worth spending extra to purchase a router with an excellent range and modern features such as MU-MIMO, Quality of Service, guest networks, gigabit Ethernet ports, and replaceable external antennas. These features will help you get better WiFi performance and ensure future compatibility.
Most routers are built to last about five years, a period that often coincides with significant updates in Wi-Fi technology. The latest innovation, Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be), has already arrived, and devices that support it are now available. This cutting-edge standard promises to bring wireless speeds closer to those of wired connections, offering an exceptional way to get better Wi-Fi and handle high-demand tasks effortlessly.
13. Measure Wired Internet Performance
If you’ve tried tips to get better WiFi and still haven’t seen any improvement, it’s a good idea to shift your focus from your wireless connection and test your wired speeds. Follow these instructions using an Ethernet cable along with a laptop or desktop that has an Ethernet port:
- Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to your modem.
- Connect the other end to your laptop or desktop computer.
- Go to https://www.speedtest.net/ in your browser.
- Click the GO button to measure your wired internet performance.
- Compare the results with the speeds advertised by your internet service provider.
We recommend running this wired test several times, preferably at different times of the day, to get a more accurate average speed compare the test results with your wireless internet performance, which you can easily measure using an app like NetSpot for Android and NetSpot for iOS.
If both your wired and wireless speeds fall below expected levels, the issue likely lies with your internet service provider. Share the results of your speed tests with them and request a resolution.
Should your provider be unable or unwilling to address the problem, it might be time to consider switching to a new provider, as even the best strategies for improving Wi-Fi signal won’t fix a poor internet connection.
By confirming your wired speed first, you’ll know whether to blame your ISP or focus on optimizing your home network to get better WiFi.

14. Purchase a Better Internet Plan
Many people don’t realize how numerous Wi-Fi-connected devices have become. From desktops and smartphones to smart home devices and appliances, these gadgets use up a lot of bandwidth, and not every internet plan is capable of keeping up with the demand.

If you’ve been paying for the same internet plan for the last 10 years, then you should look at what other options are available consider upgrading to get better wifi. A newer plan often provides faster speeds and more bandwidth, helping you achieve better wifi performance at home or in the office. You could potentially save money as the cost of high-speed internet plans has dropped significantly over the past few years.
15. Contact Your Internet Service Provider
When your Wi-Fi isn’t performing well, getting in touch with your internet service provider (ISP) could help you address the issue effectively. A customer-focused ISP will often help diagnose your issues remotely or may even send a technician to evaluate your Wi-Fi signal and suggest ways to improve it.
Here are some practical tips on how to contact your ISP:
- Phone number: Most internet providers have a hotline you can call to connect with a representative. You’ll typically find the number on your bill, the ISP’s website, or through a quick internet search.
- Email: If written communication is more your style, most ISPs provide the option to contact them via email. You can typically find the email address on the ISP's website or in your account information. Just know that email responses can be slow to process, so this method is best for non-urgent issues where you don't need immediate assistance.
- Support portal: Many ISPs have an online portal where you can submit support tickets. This system often lets you monitor the progress of your request and includes a knowledge base to help you troubleshoot common problems on your own.
- Live chat: Some ISPs offer live chat for instant communication with a support agent. This option is particularly useful if you have a quick question or want to avoid waiting on hold.
- Mobile app: A number of ISPs provide mobile apps that let you manage your account, track your usage, and get in touch with customer support. Downloading the app can make it much easier to access help when needed.
When contacting your ISP, be sure to have your account information and a clear description of the issue you're experiencing. This will help the representative better assist you and resolve your issue more quickly. Additionally, be patient and polite, as customer service representatives are more likely to go above and beyond for customers who are respectful and understanding.
Conclusion
With these placement tips, hardware upgrades, and router optimizations, you should have no problem boosting your wireless network without buying a new router. Make sure to have NetSpot at hand to check whether our tips helped each time you try one.
How to Get Better Wi-Fi — FAQs
To get better WiFi, optimize your router placement, minimize interference from household devices, use tools like NetSpot to find the least crowded channels, and think about switching to a higher-speed internet plan or installing a mesh Wi-Fi system.
If you’re looking for ways to enhance your Wi-Fi signal strength, here’s some good news: there are quite a few things that you can do to boost your WiFi without spending a single dollar. For example, you can use a WiFi signal analyzer to determine a more suitable place for your router, or you can switch to the 5 GHz band for an instant boost in performance, especially if you live in a densely populated urban area.
Use tools like NetSpot to scan nearby networks and identify the least crowded channels. Switch your router to the optimal channel for reduced interference and improved performance.
Wi-Fi extenders can be effective, but their performance heavily relies on proper placement. If positioned incorrectly, an extender may not work as efficiently and could even disrupt your network by introducing extra signal interference. To ensure optimal performance, plan the placement of your Wi-Fi extender with the help of a Wi-Fi analyzer tool like NetSpot.
It can. Switching to a faster DNS server (e.g., Google’s 8.8.8.8 or Cloudflare’s 1.1.1.1) often reduces response times and enhances overall network performance.
Wi-Fi boosters are an excellent way to expand signal coverage by amplifying your current Wi-Fi and rebroadcasting it as a separate network. They’re a great option for anyone looking to improve Wi-Fi signal strength without investing in a new router.
To give you a quick answer — that is how you get a great WiFi coverage.
Getting into some detail, not every spot will do for your WiFi router. Positioning your router close to metal objects or devices that produce electromagnetic waves, such as dishwashers, microwaves, or electric stoves, can greatly reduce its efficiency. Even non-metal materials can weaken your Wi-Fi signal to some extent. For optimal coverage, position your router on an elevated surface to allow for better signal distribution.
Regularly updating your Wi-Fi router is essential for protecting against hacker attacks. Cybercriminals are constantly creating new malware designed to steal bandwidth and infect other devices on your network.Getting new security firmware versions on your router consistently will keep your network secure.
WiFi repeaters, boosters and extenders help you get your WiFi signal to farther rooms and levels of your home or office space. Choose what will work best for you according to the size of your space, compatibility with your router and your budget. A good repeater or a booster can cost less than $100.
Wi-Fi routers can transmit on various wireless channels, but the 2.4 GHz band only has three non-overlapping options. In contrast, the 5 GHz band provides 24 non-overlapping channels. Most routers are set to default to channels like 1 or 6 right out of the box.
Because many owners leave their routers with the factory settings, those channels get overloaded. Find the least occupied channel in your area with the help of such software as NetSpot and switch your router to it.
What do Mac Wi-Fi Signal Strength Numbers Mean?
WiFi signal strength is commonly expressed using a value referred to as RSSI, which stands for received signal strength indicator.
This value is a measurement of the power present in a received radio signal, and it basically tells you how much signal strength has been lost from the time the signal left your WiFi router and until the signal reached your Mac.
Since you want to lose as much signal strength as possible, you also want to see small RSSI values (closer to zero, the better). Here are basic RSSI guidelines:
- -20 dBm: This is as good as it gets in the real world. Achieving a better signal strength would require laboratory conditions.
- -50 dBm: This is a good WiFi signal strength for most users, and achieving it should be difficult even in less than ideal conditions.
- -70 dBm: This is the lowest acceptable signal strength value. Anything lower than -70 dBm, and your online experience is guaranteed to be miserable.
Of course, knowing what is a good WiFi signal strength is only one half of the battle. You also need to know how to improve WiFi signal, and we explain just that in the next chapter of this article.
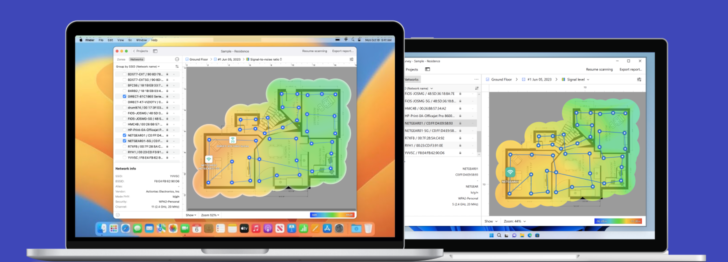

For better WiFi, use NetSpot to analyze your current coverage, locate weak spots, and determine the optimal placement for your booster or repeater.