Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Analysis, Troubleshooting runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax wireless network adapter.
Why’s My WiFi Not Working: 2025 Troubleshooting Guide
Need help with WiFi troubleshooting? Discover how to diagnose and fix weak signals, slow internet, and noisy networks using NetSpot.
Wi-Fi always seems to give out when you need it most — right before a meeting, in the middle of a large download, or just as you’re settling in to watch something online. The good news? A lot of these problems are easier to fix than they seem. With a little time and the right approach, you can often sort things out on your own.
This guide breaks down the most common Wi-Fi issues and the steps you can take to sort them out. We’ll also look at how specialized apps, including tools like NetSpot, can help you get a clearer picture of what’s going on with your network.
Before You Start: A Quick WiFi Troubleshooting Checklist
Before diving into more advanced ways to fix your WiFi connection, take a moment to double-check the basics. Many wireless network issues come from something simple that’s easy to overlook.
- Is your WiFi router plugged in and powered on?
- Have you verified that you're connected to the right Wi-Fi network (SSID)?
- Is your router’s firmware up to date?
- Is the Wi-Fi not working on just one device, or is the problem across multiple devices?
Running through this quick WiFi troubleshooting checklist can save you time. If everything above looks good and your WiFi connection is still slow or dropping out, it’s time to dig into deeper fixes.
Common WiFi Problems and How to Fix Them
Before diving into detailed fixes, let’s start with the one solution that surprisingly works in a lot of cases — even when your WiFi just refuses to cooperate.

Here’s the quick 3-step reset that solves more wireless issues than you’d think:
Plug it back in and give it a minute or two to reboot.
Why does this work? Your router, like many electronics, has capacitors — tiny components that hold on to power even after you unplug the device. Waiting a full half-minute helps ensure everything fully shuts down. This simple reset clears out any temporary glitches in the router’s memory or CPU, giving it a clean slate to start from.
It’s a small step, but if your WiFi is not working at all, this method is often enough to bring everything back online.
Still not fixed? No problem — let’s take a closer look at some of the most common WiFi issues and what you can do to handle them.
WiFi Doesn’t Work in One Room
Problem:
Wi-Fi connectivity issues in certain rooms often stem from physical obstructions, distance from the router, and interference from other electronic devices. Thick walls, floors, and large furniture can block or weaken Wi-Fi signals, especially if the materials are dense like concrete or metal.
The further a room is from the router, the weaker the signal, leading to poor connectivity. The layout of the house and the positioning of the router also play significant roles.
Solution:
Start with the basics: try moving your router to a more central and elevated location — away from large metal objects, thick concrete walls, and electronics that might cause interference. A simple repositioning often helps more than people expect.
If that doesn’t cut it, you may need to extend your wireless coverage. A mesh WiFi system or an extra Wi-Fi access point can help distribute the signal more evenly throughout the space. Mesh systems are especially useful for multi-room apartments or houses with unusual layouts.
Expert Tip:
Before spending money on new gear, it’s smart to run a WiFi analysis. Tools like NetSpot, WiFi Analyzer, or similar apps can help you create a WiFi heatmap — a visual map showing how strong your signal is in different parts of your home or office. This can pinpoint exactly where the dead zones are, so you know where improvements are needed.
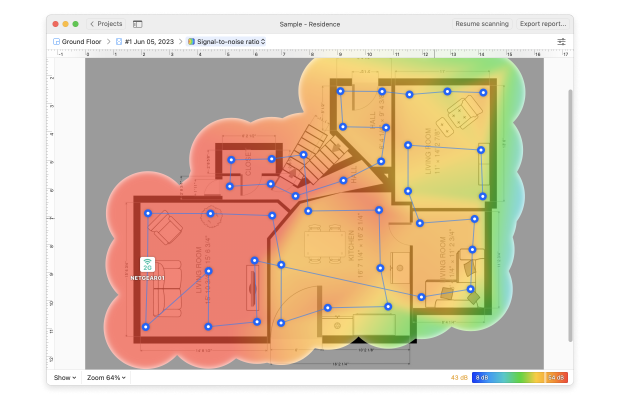
Slow Internet Over WiFi
Problem:
Your internet feels sluggish, video streams buffer endlessly, and file downloads crawl at a snail’s pace — especially during peak hours. One common reason for slow WiFi is that too many nearby networks are operating on the same WiFi channel. This leads to channel congestion, signal interference, and reduced performance, particularly in the 2.4 GHz band, which only has a few non-overlapping channels.
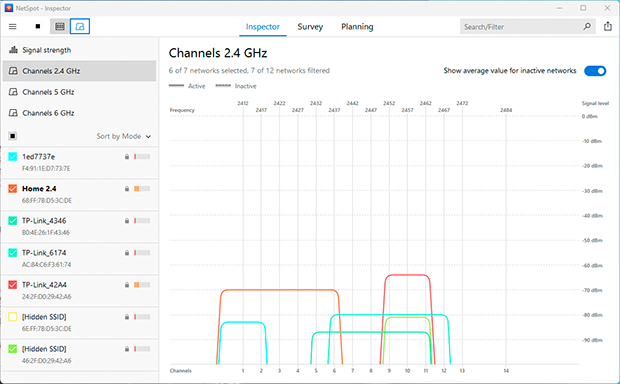
WiFi Keeps Disconnecting Randomly
Problem:
Few things are more frustrating than when your WiFi keeps disconnecting for no reason. This may be caused by a variety of underlying factors — most commonly an overheating router, outdated firmware, or even unstable power supply to the device.
Solution:
Start by checking the physical condition and placement of your router. If it's tucked away in a tight, dusty cabinet or surrounded by other electronics, it may be overheating. Move it to a well-ventilated spot with some space around it. If the vents are dusty or blocked, gently clean them.
Next, check your router’s settings. An outdated firmware can cause random disconnects or slowdowns, especially if there have been security patches or performance updates released by the manufacturer. Log in to your router’s admin panel and check for any available firmware updates.
Also, consider the age of your equipment. If your router is more than 4–5 years old, it may simply be struggling to keep up with modern devices and network demands. Upgrading to a newer model with support for Wi-Fi 6 or Wi-Fi 6E can help eliminate these random dropouts.
Expert Tip:
Make it a habit to review your router’s firmware status once a month. Many newer routers support automatic reboots on a schedule — doing this once a week can improve stability and reduce background glitches.
Can’t Access Certain Websites
Problem:
You’re online — WiFi’s connected, apps work, maybe even streaming is fine. But some websites just won’t load, giving you “DNS not found” errors or endless loading wheels. This often happens when your DNS cache gets corrupted, either on your device or your router, making it hard for your system to translate domain names into actual IP addresses.
Solution:
The first step is to flush the DNS cache, which forces your device to request fresh address info from the network:
- On Windows, open Command Prompt and run:
ipconfig /flushdns - On macOS, open Terminal and type:
sudo dscacheutil -flushcache; sudo killall -HUP mDNSResponder
After that, do the classic move — restart your router. Turn it off, pause for half a minute, and power it back on. It sounds simple, but it’s one of the most effective ways to fix stubborn WiFi issues like this.
Expert Tip:
Try this: open your terminal or command prompt and type
ping 8.8.8.8
If you get a response, it means your internet connection is alive — the issue is most likely DNS-related, not a full outage.
Download/Upload Speeds Are Too Low
Problem:
Your WiFi connection looks stable, but your downloads crawl and uploads feel stuck. This kind of slowdown often points to hidden issues like network congestion, inefficient router placement, or interference from nearby electronics.
Solution:
Start by running an Active Scan using a Wi-Fi analyzer like NetSpot. One of the most useful features here is the ability to generate download and upload speed WiFi heatmaps. These visual maps show you exactly which parts of your home or office suffer from weak transfer speeds — even when the signal itself looks strong. You might find, for example, that your living room has great signal bars but sluggish uploads due to interference or poor router positioning.
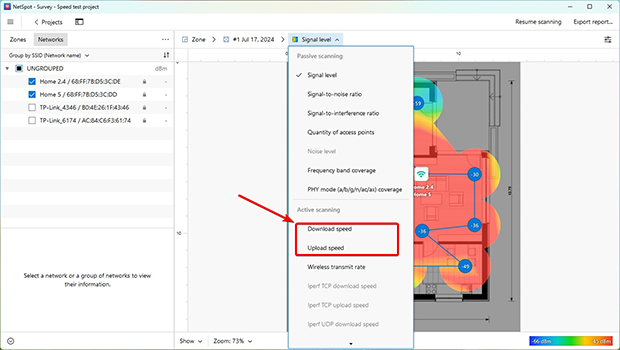
Wireless Network Troubleshooter Tips with NetSpot’s Heatmaps
NetSpot goes beyond simple WiFi scanning — it's a full-fledged diagnostic toolkit available for Windows, macOS, Android, and iOS. Whether you’re dealing with weak signal, interference, or inconsistent speeds, the app helps you visualize what’s really going on across your network.
With features like real-time signal analysis, download/upload speed testing, and most importantly, the ability to build detailed heatmaps, NetSpot gives you a clear view of problem areas — no guesswork needed.
For users with PRO or Enterprise licenses, NetSpot unlocks a set of automated troubleshooting visualizations. These are designed to identify and isolate network issues, showing you exactly where your Wi-Fi is underperforming and why. Below, we’ll walk through the key heatmap types and explain how to interpret them to improve your network.
Tip 1. Issues with SNR
The Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) heatmap, which is available in the macOS version of the software only, will show you where your signal strength is not strong enough to overcome the existing environmental noise from other electronic devices.
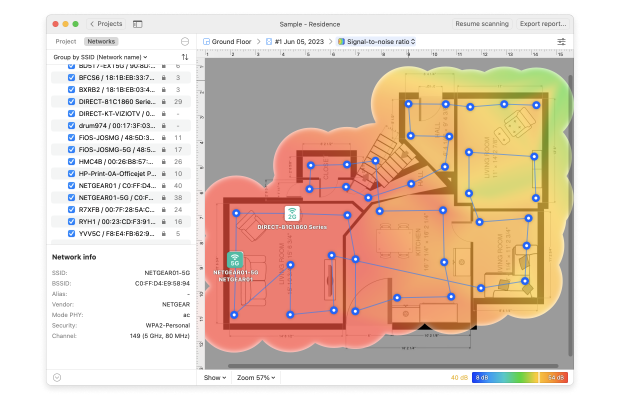
Areas of green are of concern and blue areas are critical. If your wireless network troubleshooting scan shows SNR issues, you will need to consider raising your signal strength or lowering the surrounding noise.
Tip 2. Low signal level
The Low Signal Level heatmap will show you where your signal strength is weak. Causes of weak signal strength include too much distance between the router and the device, or something physically blocking the signal between the router and device.
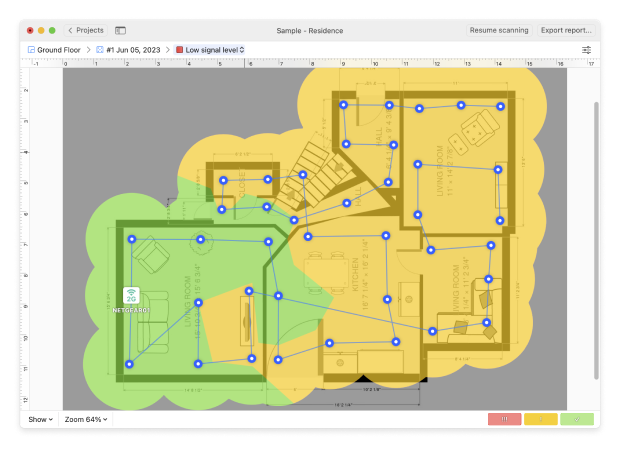
If your WLAN troubleshooting scan shows areas of red and yellow signal levels, you may need to explore ways to boost your signal level.
Tip 3. High noise level
The High Noise Level heatmap will show you where the levels of noise are high. Noise can be caused by electronic devices such as microwave ovens, cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, and wireless video cameras.
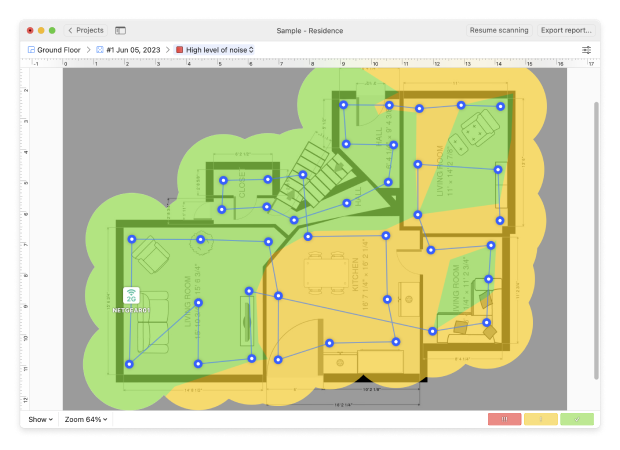
If your wireless network troubleshooting scan shows areas of red and yellow, you may need to explore lowering the noise levels by identifying the interfering devices and removing or shielding them.
Tip 4. Overlapping channels (SIR)
The Overlapping Channels heatmap shows your signal-to-interference ratio and we've touched this topic earlier. This kind of interference is caused by other radio transmitters, such as your neighbor's wireless network.
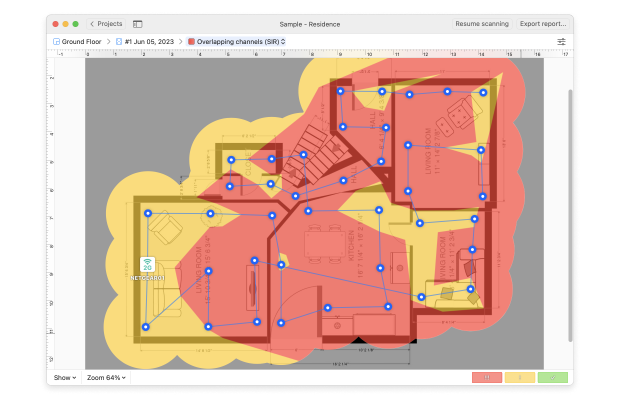
If your Wi-Fi troubleshooter scan shows red and yellow areas, you may need to change your network's WiFi channel to one with less interference.
Follow our recommendations on how to troubleshoot WiFi interference with NetSpot.
Tip 5. Low download and upload rates
If you do an active scan of your network, the Low Download Rate heatmap shows where you might face slow internet downloads, helping you spot and fix problem areas quickly.
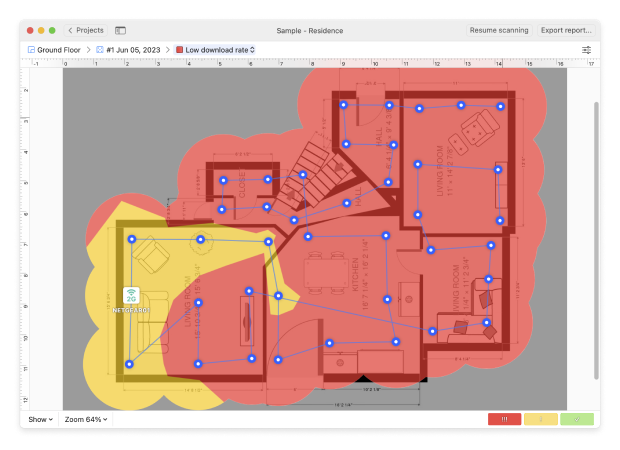
The Low Upload Rate Heatmap shows where uploading files or streaming might be slow, making it easier to find and fix those trouble spots.
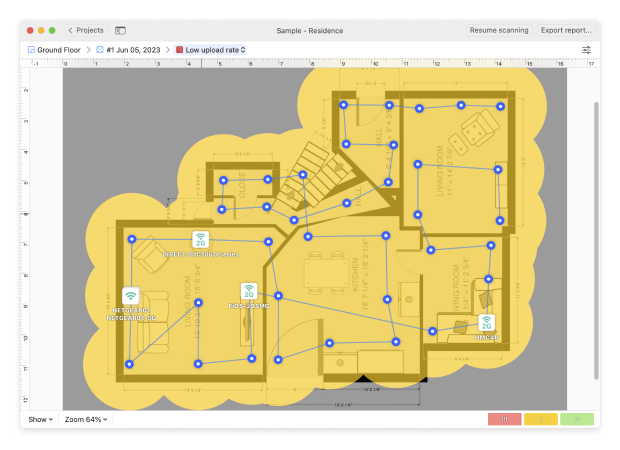
If your troubleshooting scan shows red and yellow areas, you may need to consider boosting your signal strength or changing your hardware, protocols or bandwidth.
NetSpot is a handy Wi-Fi troubleshooting tool that makes it easy to improve and fine-tune your network. It lets you see a visual map of your Wi-Fi signal strength, helping you spot weak spots and areas with interference.
With NetSpot, you can find the best place for your router, choose the right channels, and make sure your Wi-Fi is strong and reliable throughout your home or office. It's perfect for solving connectivity issues, boosting your network speed, and making sure your Wi-Fi works smoothly everywhere you need it.
WiFi Troubleshooting — FAQs
There are many possible answers to this question, which is why you should start by performing an in-depth analysis of your WiFi network using a wireless network analyzer like NetSpot.
Signal bars only indicate connection to the router, not internet access. Check if your ISP is down, or flush your DNS cache. You can also use NetSpot to test signal quality and network stability.
There are several things you can do to fix your WiFi connection, and we recommend that you start by restarting your router. If that doesn’t help, then you need to follow the WiFi troubleshooting techniques described in this article to pinpoint the cause of the problem and resolve it.
First, restart both the phone and router. Forget the network and reconnect. If the problem persists, reset network settings or make sure MAC filtering isn’t blocking your device on the router.
Yes, it’s possible to have a working WiFi connection but no access to the internet. This usually happens when the internet service provider is experiencing technical issues or when there’s something wrong with the internet modem.
To troubleshoot any issues with your WiFi start with performing a WiFi site survey in the NetSpot app. New to NetSpot? Not a problem! Just read "How Do I Start My Survey?" and follow the comprehensive guide. First of all identify the area you are troubleshooting. Then you can either upload a map to NetSpot or draw it from scratch.
Once you have a map, you can start taking data samples of your area. When done, you will be able to see the heatmap NetSpot built based upon the measurements you've taken.
You also may check our top of the best apps for WiFi troubleshooting.
Thanks to the Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) heatmap you can easily see where the signal doesn't have enough strength to overcome the noise created by other electronic devices in the area. Green and blue areas are those of concern, with blue (cold) being critical and needing to be taken care of in the first place.
Refer to the Low Signal Level heatmap to see the areas of weak signal. Weak signal strength might be caused by a router being too far from a device or by an obstacle between router and device physically blocking the signal. If you see green and blue areas on your heatmap, you might want to explore ways to strengthen the signal there.
You'll easily determine the areas with high noise levels thanks to the High Noise Level heatmap. Even such appliances as microwave ovens can cause noise and lower the strength of WiFi signal. If you see green and blue areas on your heatmap — look for electronic devices that might be causing the issue and try moving them to another spot.
Use the Overlapping Channels heatmap to see the areas that have a critical signal-to-interference ratio. The blue and green areas will show you where the interference is the highest. Try changing your network's WiFi channel to eliminate the issue.
To see where your Internet connection speed is slow, perform an active scan of your network, and refer to the Low Download Rate and Low Upload Rate heatmaps. If you see red and yellow areas, you might need to change the protocols or bandwidth, or upgrade your hardware.
Not all devices support 5 GHz. Also, some routers disable 5 GHz by default. Check your router settings and make sure the band is enabled.
