Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Analysis, Troubleshooting runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax wireless network adapter.
Why Does my WiFi Keep Disconnecting
11 Real Fixes That Actually Work — discover quick solutions to boost stability and Get The Best WiFi Coverage for a seamless online experience.
Tired of your Wi-Fi cutting out at the worst possible moment? You’re not alone — unstable internet is one of the most common (and most annoying) problems in modern life. Whether you’re on a Zoom call, trying to stream your favorite show, or just browsing, a flaky Wi-Fi connection can be a real headache.
The good news? Most Wi-Fi issues aren’t that hard to fix. You don’t need to be a tech genius or spend a fortune on new gear. In fact, many problems can be solved with a few simple tweaks. That’s why we’ve gathered the most effective tips from experts to help you finally put an end to those frustrating disconnects.
- 1. Restart Your Modem and Router — The Classic Fix
- 2. Check Your Cables — It’s Not Always a Wi-Fi Problem
- 3. Move Your Router to a Better Spot
- 4. Watch Out for Signal Interference
- 5. Too Many Devices Are Connected
- 6. Update Your Wi-Fi Adapter Drivers
- 7. Turn Off Auto Network Switching
- 8. Reset Your Network Settings
- 9. Check Background Apps and Antivirus Software
- 10. Test Your Internet Speed
- 11. Consider Replacing Old Equipment — Sometimes It’s Just Time
- Conclusion
- Fix Disconnects and Get Better Coverage — FAQs
1. Restart Your Modem and Router — The Classic Fix
Sometimes your Wi-Fi disconnects due to minor glitches or accumulated background processes in your router and modem. A quick reboot often solves these connectivity issues and restores stable internet. Many users underestimate this simple step, but it’s one of the easiest and most effective solutions you can try.
How to fix it:
Unplug both your modem and router, wait 30 – 60 seconds, then plug them back in. Always restart the modem first, followed by the router.
Expert Tip: Rebooting your equipment at least once a week can prevent unexpected slowdowns and help maintain a stable Wi-Fi connection.
2. Check Your Cables — It’s Not Always a Wi-Fi Problem
If your Wi-Fi keeps disconnecting, the culprit might not be the wireless signal itself. Loose or damaged Ethernet or coaxial cables can silently cause random connection drops, leading to unstable internet and hindering the best WiFi coverage. Over time, cables and their clips can wear out or break, so it’s crucial to double-check all connections before exploring more complex solutions.
How to fix it:
Carefully inspect all cables from your modem to your router for signs of damage, looseness, or broken clips. Replace any that feel wobbly or don’t click securely into place.
Expert Tip: Even a minor bend or fray can affect performance. A new cable is often a simple yet effective fix for intermittent Wi-Fi disconnects.
3. Move Your Router to a Better Spot
A common mistake many people make is placing their Wi-Fi router in the corner of a room, hidden behind furniture, or tucked away inside cabinets. While this might look tidy, it's actually hurting your Wi-Fi coverage and causing connection problems. If you've ever asked yourself, "Why does my Wi-Fi keep disconnecting?", your router’s location could be a big part of the issue.
How to fix it:
Place your router in an open, elevated spot near the center of your home or apartment. Keeping your router out in the open and away from obstructions like furniture or large appliances ensures better Wi-Fi signal strength and stability.
Expert Tip: Think of Wi-Fi like light — open space = better coverage. To pinpoint and eliminate “dead zones” in your home, use a Wi-Fi analyzer such as NetSpot.
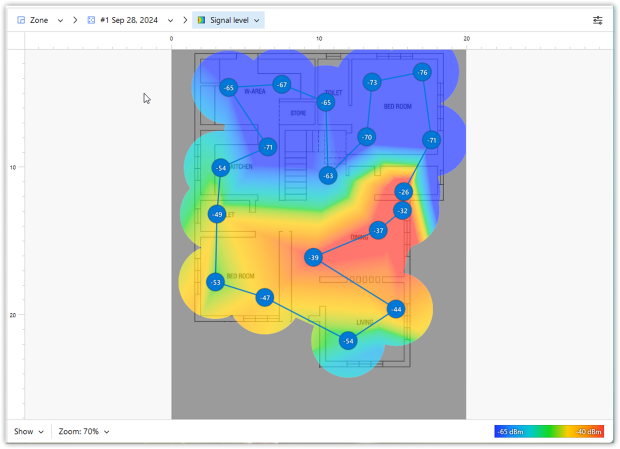
4. Watch Out for Signal Interference
If your Wi-Fi signal frequently drops or gets sluggish, the issue might be interference from household electronics or neighboring wireless networks. Common culprits include microwaves, Bluetooth gadgets, cordless phones, baby monitors, and even neighboring routers that crowd your Wi-Fi channel.
Many people overlook this, not realizing interference can significantly degrade Wi-Fi speed and reliability.
How to fix it:
Use NetSpot, to spot channel overlap and network interference. NetSpot’s intuitive graphs clearly visualize Wi-Fi networks, including hidden ones, helping you find the least crowded channel.
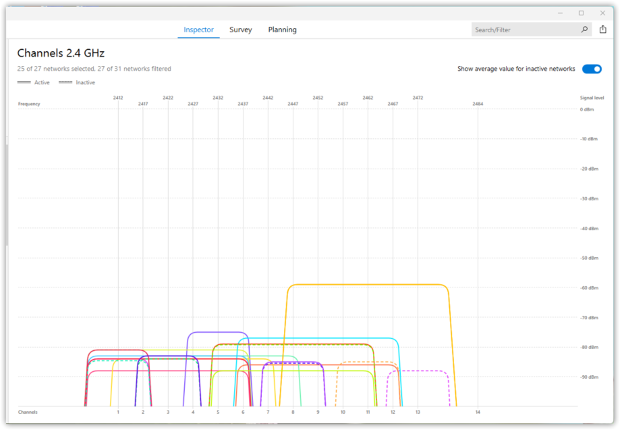
5. Too Many Devices Are Connected
Having too many devices connected at once might seem harmless, but each one competes for your router’s bandwidth — even when they're not actively being used. This silent overload often causes slow speeds, unstable connections, and frequent Wi-Fi drops.
How to fix it:
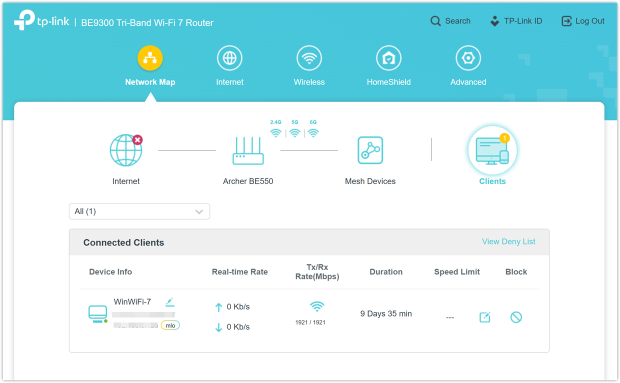
First check your router’s admin interface to identify how many devices are actually connected:
Step 1: Access Your Router’s Admin Panel
- On a device currently connected to your Wi-Fi, launch a web browser.
- Type your router’s IP address into the browser's address bar. Common addresses include 192.168.1.1, 192.168.0.1, or 10.0.0.1.
- (If unsure, you can find this information on the label underneath your router or in its manual.)
Step 2. Log into the Admin Interface
Enter your username and password when prompted. Often, the default login details are:
- Username: admin
- Password: admin, password, or printed on the router label
Tip: If you've changed your login details and forgotten them, you might need to reset your router.
Step-by-step after logging in:
- Navigate to a section like Connected Devices, Attached Devices, Client List, or Network Map.
- Review the list of devices shown, identifying each by their device name, MAC address, or IP address.
- Disconnect or block any unknown or suspicious devices.
6. Update Your Wi-Fi Adapter Drivers
One commonly overlooked reason your Wi-Fi might keep disconnecting is outdated drivers. Many people skip this step, assuming drivers update automatically, but neglecting regular driver updates can lead to connection drops, poor performance, and unreliable internet — even with high-quality routers or devices.
To solve this, make sure your Wi-Fi drivers are up-to-date. Updating your drivers is one of the simplest and most effective ways to get the best WiFi coverage and maintain a stable connection.
How to fix it:
Open Device Manager → find Network Adapters → right-click your Wi-Fi adapter and choose Update Driver. Follow the instructions to finish the process.
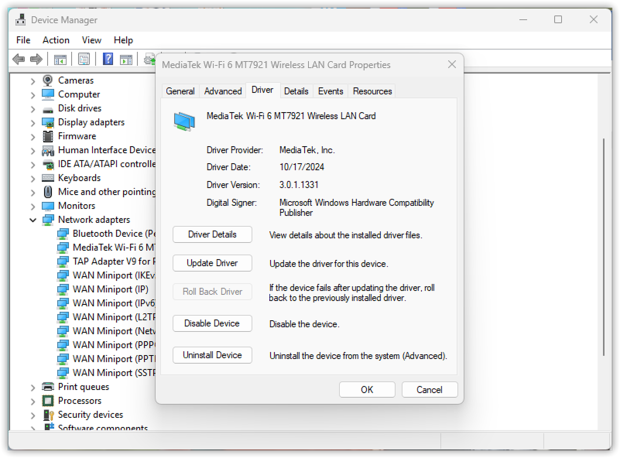
Expert Tip: Don't rely solely on Windows updates; visit your Wi-Fi adapter manufacturer’s website to find the most recent drivers for optimal network stability.
7. Turn Off Auto Network Switching
If your Wi-Fi connection frequently drops, one potential reason might be your device constantly hopping between multiple saved networks. Devices often try connecting to the strongest signal from the saved list — but not always the most stable.
This behavior varies slightly depending on your device or operating system, but the result can be the same: frustrating interruptions during calls, streaming, or gaming.
How to fix it:
Go into your Wi-Fi settings, review your saved networks, and disable Auto-Join or automatic connection for any networks you don't frequently use, or those that consistently have weak or unreliable signals.
On Windows 10:
- Open Settings → Network & Internet → select Wi-Fi.
- Click on Manage known networks, select a network you don’t want to auto-join, click on it, then choose Properties and toggle off Connect automatically.
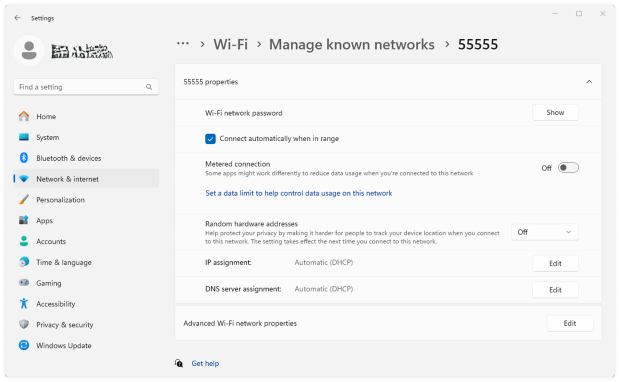
On Windows 11:
- Open Settings → Network & Internet → Wi-Fi.
- Select Manage known networks, click on the network you wish to disable auto-join for, and toggle off Connect automatically.
Expert Tip: The best way to minimize connection conflicts is to regularly clean up your saved networks list, removing outdated or unused entries. This easy practice helps your device consistently choose the strongest, most reliable network, giving you the best WiFi coverage possible.
Cleaning up your network list is an easy way to minimize interference, avoid conflicts, and get the best WiFi coverage possible.
8. Reset Your Network Settings
Another often overlooked culprit is corrupted or outdated network settings. Over time, these settings can accumulate old connections, outdated profiles, or misconfigurations that lead to frequent disconnects. Resetting your network clears away these hidden obstacles, giving your system a fresh start and restoring a stable Wi-Fi connection.
How to fix it:
Go to Settings → Network & Internet → Advanced network settings → Network Reset → Reset Now. Once complete, your PC will reboot, and you’ll need to reconnect to your Wi-Fi network — keep your password handy.
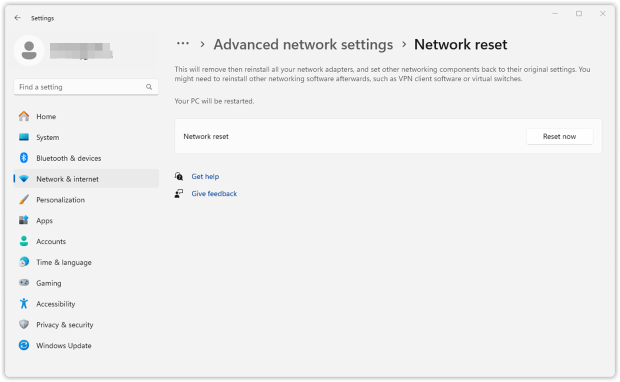
Expert Tip: Performing a network reset every few months can significantly improve Wi-Fi stability, ensuring you get consistent, reliable coverage at home or in the office.
9. Check Background Apps and Antivirus Software
Your Wi-Fi might keep disconnecting because certain background applications or software running quietly on your computer use up more bandwidth than you'd expect. Apps running automatic updates, cloud backups, license verification tools, and antivirus software often silently eat up your bandwidth, making your internet slow, unstable, or prone to frequent disconnections.
Many users overlook this simple yet effective fix, assuming their Wi-Fi hardware is the culprit. However, software like automatic backup services, Adobe Creative Cloud license checks, and cloud synchronization apps can severely strain your network connection, causing frustrating interruptions.
How to fix it:
Open Task Manager (Windows) or Activity Monitor (Mac) and sort processes by network usage to quickly identify which applications use the most bandwidth. Pay particular attention to cloud services, backup software, and subscription license verification tools. Close or temporarily pause non-essential bandwidth-consuming apps, and monitor whether your Wi-Fi stability improves.
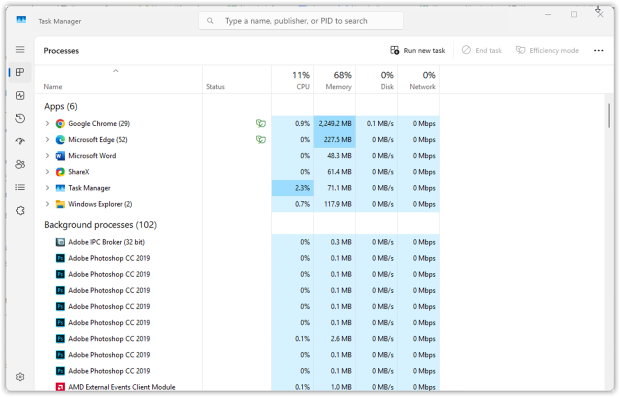
If necessary, temporarily pause or reschedule background backup tasks, or adjust synchronization settings in software such as Dropbox or OneDrive.
Expert Tip: Regularly checking your device’s network activity helps pinpoint problematic software. For optimal results, schedule heavy downloads or backups during off-peak hours to reduce Wi-Fi disconnects.
10. Test Your Internet Speed
Before investing in new gear, make sure you’re actually getting the internet speed you're paying for. Many users skip this crucial step, assuming slowdowns or disconnects are due to Wi-Fi hardware or interference issues, but your actual internet bandwidth might simply be insufficient.
A quick Wi-Fi speed test helps identify bottlenecks and reveals if your connection meets your provider’s promised speeds.
How to fix it:
Run an online speed test and you'll quickly see your current download, upload speeds, and latency. If your measured speeds fall significantly short of what you're paying for, the problem might be with your ISP or your plan rather than your home Wi-Fi setup.
With NetSpot, you can do more than just a quick speed test — you can create detailed Wi-Fi heatmaps showing your actual download and upload speeds throughout your home or office.
Run an active survey in NetSpot’s Survey Mode. Collect precise download and upload speed data across various locations in your home or office with NetSpot as you move around the space.
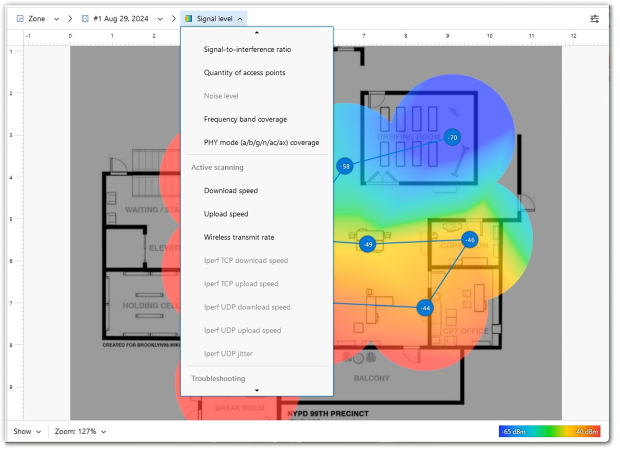
Once the survey is complete, you'll receive detailed heatmaps of your Wi-Fi performance, visually highlighting problem areas and speed bottlenecks.
Expert Tip: Run the speed test several times throughout the day to check for peak-hour slowdowns. Test multiple devices to confirm whether the issue is with your network or a specific gadget.
Perform surveys regularly to track network performance changes over time, especially after repositioning equipment or adjusting settings.
Conduct surveys at peak usage times to understand how your network handles maximum load, helping you plan any necessary upgrades effectively.
Get a perfect WiFi speed with NetSpot
Don’t settle for a decent Internet connection, NetSpot ensures a consistent WiFi speed.11. Consider Replacing Old Equipment — Sometimes It’s Just Time
If you've already tried all the fixes and your Wi-Fi still keeps disconnecting or slowing down, the problem might be your equipment. Older routers and modems often can’t handle modern network demands — too many devices, higher speeds, and new Wi-Fi standards.
How to fix it:
- Check how old your modem and router are. If they’re over 4 – 5 years old, it’s probably time to upgrade.
- Look for devices that support Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) or Wi-Fi 6/6E (802.11ax) — they’re faster, more stable, and better with multiple devices.
- For more expansive homes or offices, a Mesh Wi-Fi setup can be a great option — it gives you strong coverage across all rooms.
- If you’re renting equipment from your ISP, ask them for a newer model.
Expert Tip: Before spending money on new gear, try using the NetSpot app in Planning Mode. It offers a virtual Wi-Fi equipment selection tool — you can simulate different routers and access point placements before you buy anything.
This smart feature helps you test and find the best setup for your space.
Conclusion
If you've ever found yourself wondering, “Why does my Wi-Fi keep disconnecting?” — now you know it’s not just bad luck. Most Wi-Fi problems have simple, practical solutions. A few smart tweaks can make a huge difference — and you don’t need to be a tech wizard to fix things.
But here’s the deal: if your internet connection is critical for work, study, or just your everyday life, it’s worth keeping an eye on your network regularly — not only when something breaks. That’s where tools like NetSpot come in handy. They help you analyze your Wi-Fi coverage, find weak spots, detect interference, and even simulate new router placements before you buy anything.
Staying connected doesn’t have to be a constant struggle — just keep your setup optimized, monitor your network from time to time, and your WiFi will thank you.
Fix Disconnects and Get Better Coverage — FAQs
Random Wi-Fi drops usually happen due to interference, crowded channels, outdated drivers, background apps, or hardware issues. Follow our expert tips above to quickly fix these common problems.
Absolutely! Many users underestimate this solution, but regularly rebooting your modem and router can clear glitches and processes that cause random Wi-Fi drops.
Use a Wi-Fi analyzer like NetSpot to scan your environment and identify crowded channels. Then, manually select the least crowded channel in your router’s admin panel to drastically reduce interference.
Resetting network settings every few months can clear out outdated network profiles and corrupted settings that lead to Wi-Fi instability, significantly improving your Wi-Fi experience.
Placing your router in an elevated, central, and open location significantly improves signal strength and stability. Avoid hiding it behind furniture or appliances.
Yes, 5 GHz bands are generally less crowded and offer better speed and reliability, making them ideal for apartments or densely populated areas. If available, 6 GHz (Wi-Fi 6E) provides even better performance.
Outdated Wi-Fi adapter drivers often lead to connection drops and slowdowns. Regular updates ensure compatibility, stability, and optimal network performance.
