Wi-Fi Site Surveys, Analysis, Troubleshooting runs on a MacBook (macOS 11+) or any laptop (Windows 7/8/10/11) with a standard 802.11a/b/g/n/ac/ax wireless network adapter.
How to Get Faster WiFi
We expect our WiFi to work all the time. It can be challenging to figure out how to make WiFi faster. FIND OUT HOW TO TROUBLESHOOT YOUR WIFI.
The allure of fast WiFi is one of the selling points of wireless networks. One can very quickly get addicted to the effortless manner in which you can access the Internet to listen to music, stream videos or engage in online gaming.
We expect our WiFi to work at all times, just like turning on the lights. When it doesn’t work the way it should it can be challenging to figure out the reason for the degraded performance. Obviously, the only thing on your mind will be how to make WiFi faster. And, more importantly, is it possible to make it all happen without spending a single dollar?
How Fast Should My Wi-Fi Be?
Before you embark on the quest for faster WiFi, you should first figure out how fast your WiFi is supposed to be. You might find out that the speeds you’re currently getting are actually the maximum speeds you can reasonably expect to get.
To start with, you should find out how fast your home internet is. If you’re not sure, contact your internet provider and ask. Let’s say you have a 100 Mbps connection going into your house — that’s 100 megaBITS per second. Since nobody except for ISPs thinks in megabits, it’s useful to convert the number to megabytes per second, which gives us 12.5 megaBYTES per second.
In other words, it should take you approximately 1 second to download a 12.5 megabytes-large file from the internet. Under ideal conditions, of course.
But that assumption is only applicable for hard-wired connections and not for wireless networks. When you download a file over WiFi, you introduce several important variables, with your wireless router being the most important one.
WiFi routers broadcast on two main frequencies — 2.4 GHz and 5 GHz — and each of these frequencies is divided into several channels. What’s more, WiFi routers use several different IEEE 802.11 protocols, which provide the basis for wireless network products using the WiFi brand.
The oldest still commonly used WiFi protocol is 802.11g, and it supports transmission speeds of only 54 Mbps, or roughly 6.75 megabytes per second. If you have an older wireless router that only supports the 802.11g WiFi protocol, and you pay for a 100 Mbps internet connection, it’s impossible for you to utilize your connection to its maximum capacity. In that case, your only option is to upgrade to a newer router, which, of course, isn’t free.
But what if you have a newer router, let’s say one that supports the 802.11ac WiFi protocol, which has a multi-station throughput of at least 1 Gbps and single-link throughput of at least 500 Mbps? If that’s the case, consider yourself lucky because you should be able to utilize your internet connection to its maximum capacity even over WiFi.
A Sad Story of Inconsistent Wi-Fi Speed
A great story shared by a great friend of ours. His natural curiosity and determination (and our wonderful brainchild NetSpot) assisted him in figuring out how to get his WiFi working as it was meant to. So here it goes:
After enjoying years of trouble-free WiFi I began to have issues with the system in late December. First a little background on the system. I do not live in a huge house and there are not many devices that are connected at one time. We do use the Internet to stream YouTube TV as well as our other online activities. For the most part, there are only two people using WiFi. We might have four connections going simultaneously if we are both watching TV and on a computer or iPad at the same time.
All was fine until late one Sunday afternoon in December. I am a bit of a sports fan and was watching an NFL game when I was assaulted by the spinning circle in the middle of the YouTube TV picture. This indicates that the app is trying to connect to the Internet, or is experiencing such slow performance that it cannot keep up with the video stream. This would occur sporadically throughout the game, rendering it almost unwatchable.
Since we had not faced any issues like this previously, I was at a loss as to what to do to resolve the problem. I definitely wanted to see the end of the game and tried rebooting the router several times, to no avail. I even considered digging up an old Ethernet cable and plugging it into the back of my cable modem but then that’s not WiFi anymore. Oh, and my iPad doesn’t have an Ethernet port. Does yours? Exactly.
So I was forced to actually take the time to track down the culprit in the hope of returning the capability to enjoy my WiFI connected devices to its previous lofty state. I have a feeling that I am not alone in facing this dilemma and that others are afflicted with the scourge of slow WiFi in their home or office.
Therefore, in an attempt to pass on some hard-earned knowledge I am going to describe the steps I took to resolve my issue. I’m going to talk about how to make WiFi faster and we will discuss a number of possible remedies that you can try without spending a dime.
How to Make Your WiFi Faster
These are the no-cost methods that I used to try to improve my Internet speed. Read on to learn how to get better WiFi with their help.
Note: You can also read our article on the top 15 ways to boost your WiFi for additional WiFi optimization tips.
Test the Speed of Your Internet Connection
The first thing I chose to do was to test my Internet connection. The question was how fast is my WiFi. Was I expecting too much from my in-home equipment when in fact the problem was a slow connection to my ISP? There are many speed test tools out there, and I chose one and tested my connection.
Get a perfect WiFi speed with NetSpot
Don’t settle for a decent Internet connection, NetSpot ensures a consistent WiFi speed.So when it was up, the speed of the connection was fine. On to the next step.
To test how fast your WiFi is, NetSpot pops up in many recommendations — it is an industry-leading macOS and Windows software for WiFi analysis and surveys.
Unlike online speed tests, which typically measure only latency, download speed, and upload speed, NetSpot can provide you with the deep insights into the state of your wireless network and help you understand how it fluctuates throughout the day and how it changes from room to room.
NetSpot has three distinct WiFi analysis modes: Inspector, Survey and Planning.
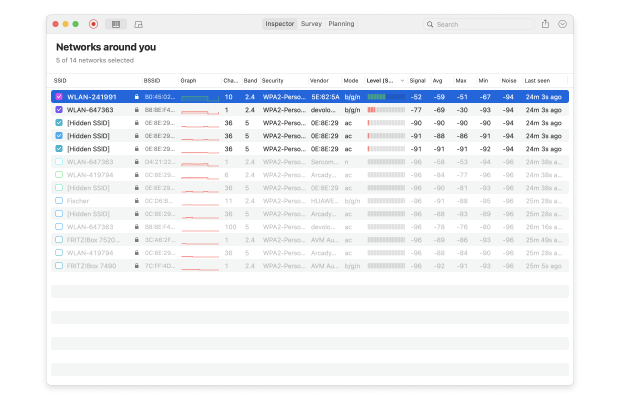
The former mode is offered for Home, Pro, and Enterprise users, and makes it possible to outline your WiFi network on a map and visualize its strength and other parameters. The latter — collects every detail about surrounding WiFi networks and presents wireless data as an interactive table.
NetSpot also offers the Active Scanning feature in Pro and Enterprise editions, which allows you to find out exactly how fast your WiFi is across your space. To use NetSpot’s Active Scanning feature to test WiFi speed in an instant, start a new project. Load an existing map of your area or create a new one.
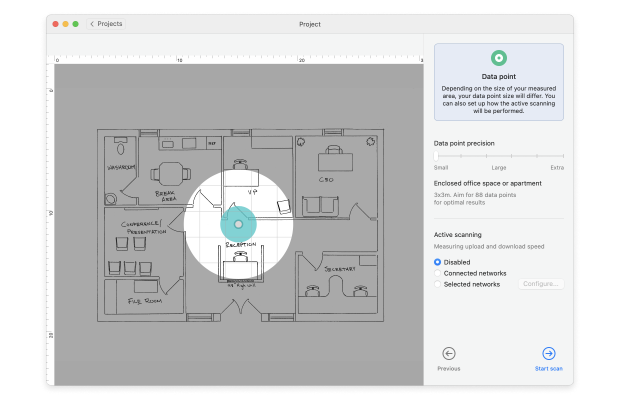
On the Active Scan screen, select your wireless network and click on “Enable active scanning of the selected network(s).” Perform the scan. Once your survey is complete, you will be able to analyze your results and see your upload speed, download speed, wireless transmit rate, as well as other metrics depending on the exact configuration of the scan.
Relocate the Router
The way my house is laid out made the northwest corner of the house the logical place for the router. This is where the cable from the ISP enters the house and minimizes the amount of internal cabling required. At this time I was using an Arris modem/router combo that had been provided by the cable company when they installed the Internet connection in the house.
In an attempt to eliminate any obstructions or interference resulting from the router’s location, I spent an afternoon experimenting with various other, more centrally located places to house the router. Following best practices, I kept it away from physical objects and tried to minimize the exposure to other devices such as my microwave that might be causing interference. No luck, as the sporadic WiFi degradation continued.
WiFi signal strength reduces with distance. If you stand just a few feet away from your router, you should be able to enjoy fast WiFi and utilize your internet connection to its maximum capacity. But walk to another room, and your WiFi speeds are most likely going to drop. Depending on the materials used to build your home, the drop could be fairly sharp.
With NetSpot, you can check for signal weak spots and find the most optimum location for your router
That’s why you should always place your router as close to the center of your house as possible. With NetSpot, you can check for signal weak spots and find the most optimum location for your router. As a rule of thumb, avoid placing your router close to large appliances that are likely to emit a lot of electromagnetic interference.

Inspect, compare, survey, and analyze WiFi networks with NetSpot.
Update the Router’s Firmware
Next, I went out to the router’s administration panel and updated the firmware.
While I was there I also set it to update automatically so I would not have to think about this again. There was no noticeable difference in WiFi performance after updating the firmware.
Changing Channel
I wanted to see if I was being impacted by neighboring WiFi installations, so I used the NetSpot WiFi analyzer to discover other nearby networks. There were other networks detected, and they all were using channel 1 or 11 in the 2.4GHz frequency. I did not see other 5GHz networks that might be affecting my router.
FYI, you can try and make your WiFi faster by switching to the least used WiFi channel. This is especially important if you live in a densely populated urban area and have a lot of other wireless networks in your vicinity. If you were to broadcast on the same channel as everyone else, your speeds would suffer because of a phenomenon known as WiFi congestion.
Using NetSpot’s Inspector Mode, you can easily generate a convenient table of all wireless networks around you and see which channels they broadcast on. Simply open the NetSpot app and click Inspector. Click either on “Channels 2.4 GHz” or “Channels 5 GHz” to see which WiFi channels are used the least. You should always prefer non-overlapping channels (1, 6, and 11).

Thinking I had finally found the reason for the problem, I updated the router to use channel 6 for the 2.4 GHz frequency in my home. No other network was using this channel, so if that was the bottleneck it should now be resolved. Unfortunately, the issue persisted. I was out of ideas and had to take it to the next level.
Call in Support to Resolve the Issue
After striking out with my own attempts at fixing my WiFi connection I resorted to contacting the cable company and having a tech sent to my home.
He took one look at the Arris equipment, shook his head, and said they did not support that old device any longer. He did hook it up to some testing equipment and ran the router through its paces. The verdict was that the device was on its last legs and was the most likely reason for my WiFi issues.
We ended up purchasing a Netgear cable modem and a Linksys router to replace the antiquated and malfunctioning Arris modem/router. After configuring the equipment and changing the default passwords we fired up the WiFi and have not had any issues since the new router and modem were installed.
Use an Ethernet Cable
Using an Ethernet cable instead of WiFi can provide a faster and more stable internet connection, as it is not subject to the same interference and signal degradation that can affect WiFi. Keep in mind that you will need to be physically connected to your router with the Ethernet cable in order to use this method.
This is how to make the internet faster using an Ethernet cable:
Locate the Ethernet port on your device and the Ethernet port on your router. Ethernet ports are typically labeled with a symbol that looks like a circle with several diagonal lines inside.
Connect one end of the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port on your device, and the other end of the cable to the Ethernet port on your router.
Once the cable is connected, your device should automatically detect the wired connection and begin using it for internet access.
If your device does not automatically detect the wired connection, you may need to manually configure your network settings. Open the settings menu on your device and navigate to the network settings. Select the Ethernet connection and follow the prompts to connect to the internet.
You may also need to use a longer Ethernet cable if your device is not located near your router.
Thinking I had finally found the reason for the problem, I updated the router to use channel 6 for the 2.4 GHz frequency in my home. No other network was using this channel, so if that was the bottleneck it should now be resolved. Unfortunately, the issue persisted. I was out of ideas and had to take it to the next level.
Secure Your Wi-Fi
Securing a WiFi network is a great way how to make WiFi faster for several reasons. Firstly, encrypting the network with a strong password can prevent unauthorized users from accessing the network and using up bandwidth, which can slow down the internet for authorized users. This can also prevent malicious users from potentially accessing or tampering with your network.

Secondly, using a strong WiFi password can also prevent others from "piggybacking" on your network, which can further reduce the available bandwidth and slow down your internet speeds.
Thirdly, securing your network can also improve coverage by preventing unauthorized users from accessing the network and using up bandwidth in areas that are outside the range of your WiFi signal. This can help ensure that the available bandwidth is being used exclusively by authorized users within the range of your signal.
There are several WiFi encryption standards that are commonly used to secure WiFi networks. These include:
- Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP): WEP is an older encryption standard that is no longer considered secure. It uses a 64-bit or 128-bit key to encrypt data transmitted over a WiFi network, but it has been widely criticized for its vulnerability to hacking and other security breaches.
- WiFi Protected Access (WPA): WPA is a more secure encryption standard that was developed to address the weaknesses of WEP. It uses a stronger encryption algorithm and a longer, more complex key to encrypt data transmitted over a WiFi network. WPA is generally considered to be more secure than WEP, but it is not as strong as some of the newer encryption standards.
- WiFi Protected Access 2 (WPA2): WPA2 is the most widely used encryption standard for WiFi networks. It uses a stronger encryption algorithm and a longer, more complex key to encrypt data transmitted over a WiFi network. WPA2 is considered to be the most secure encryption standard for WiFi networks, but it has also been criticized for its vulnerability to certain types of attacks.
- WiFi Protected Access 3 (WPA3): WPA3 is the latest WiFi encryption standard. It uses a stronger encryption algorithm and a longer, more complex key to encrypt data transmitted over a WiFi network. WPA3 is considered to be the most secure encryption standard for WiFi networks, and it is not vulnerable to the same types of attacks that can affect WPA2.
You should always use the latest standard (and get a new router if your existing one doesn’t support it) and combine it with a strong password that adheres to the following password best practices:
- Use a password that is at least 8 characters long and contains a combination of letters, numbers, and special characters.
- Avoid using common words or personal information in your password.
- Do not use the same password for multiple accounts or websites.
- Use a password manager to generate and store complex, unique passwords for each of your accounts.
- Regularly update your password and avoid sharing it with others.
Adopt modern Wi-Fi solutions
Current Wi-Fi technologies have significantly advanced to offer faster and more reliable connections, benefitting both home users and businesses. Here's an overview of how these technologies help achieve faster Wi-Fi speeds:
- Wi-Fi 6 and 6E (802.11ax)
- Increased Capacity and Efficiency: Wi-Fi 6 introduces Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access (OFDMA) and Multi-User MIMO (MU-MIMO), allowing more devices to connect simultaneously without impacting speed.
- Improved Performance in Crowded Areas: By dividing channels into smaller sub-channels, Wi-Fi 6 can serve multiple users in dense environments more efficiently, reducing wait times and increasing throughput.
- Target Wake Time (TWT): This feature extends battery life in Wi-Fi devices by scheduling wake times, which is particularly beneficial for mobile and IoT devices.
- Wi-Fi 6E: Extends Wi-Fi 6 capabilities into the 6 GHz band, offering more bandwidth and reducing interference from legacy devices.
- Wi-Fi 7 (802.11be) — Emerging
- Higher Throughput and Efficiency: Wi-Fi 7 is poised to further increase the maximum throughput by utilizing broader channels (up to 320 MHz) and more complex QAM (4096-QAM), pushing the boundaries of wireless transmission speeds.
- Improved Latency: The introduction of Multi-Link Operation (MLO) enables devices to concurrently send data over several frequency bands, significantly reducing latency and improving performance in congested networks.
- Beamforming and MU-MIMO
- Direct Signal Delivery: Beamforming technology allows the Wi-Fi signal to be directed towards specific devices rather than broadcasting in all directions, improving signal strength and speed.
- Simultaneous Data to Multiple Devices: MU-MIMO (Multi-User, Multiple Input, Multiple Output) allows a Wi-Fi router to interact with several devices at the same time, cutting down on delays and enhancing the total efficiency of the network.
- Wi-Fi Mesh Systems
- Expanded Coverage with Seamless Roaming: Mesh systems use multiple router-like devices to cover large areas with Wi-Fi, ensuring devices can move across large spaces without losing connection by seamlessly transitioning between mesh nodes.
- Use of AI and Machine Learning
- Network Optimization: Some modern routers employ AI to monitor network conditions and automatically adjust settings for optimal performance, including channel selection, band steering, and load balancing.
Adoption of these technologies requires compatible hardware and sometimes software updates. Users seeking to upgrade their Wi-Fi speeds should consider devices that support these standards and features. As previously highlighted, the right network configuration and upkeep, including ideal router positioning and consistent firmware upgrades, are essential for attaining peak performance.
Cut Off Unused Devices
Cutting off unused devices can improve WiFi performance by reducing the number of devices that are connected to the network and using up bandwidth. When there are fewer devices connected to the network, the available bandwidth is more evenly distributed among the remaining devices, which can result in faster internet speeds.

Other devices that use WiFi, such as smartphones, laptops, and tablets, can continue to access your Wi-Fi while they are idle. When these devices are connected to your WiFi network but not actively being used, they will continue to use up a small amount of bandwidth, which can slow down your internet speeds. Disconnecting these devices from your Wi-Fi network when they are not in use can help improve your Wi-Fi performance.
Keep in mind that some devices, such as smart home devices and security cameras, may need to remain connected to your WiFi network in order to function properly. In these cases, disconnecting the device from the network may not be an option.
Restart Your Router
Restarting your router can improve WiFi speeds by resetting the connection between the router and your internet service provider (ISP). This can help clear any temporary glitches or errors that may be causing slowdowns or other issues with your WiFi connection.
When you restart your router, it will shut down and then restart, which can take a few minutes. During this time, your devices will be disconnected from the WiFi network, but they will automatically reconnect once the router has restarted.
Once your router has restarted, it will establish a new connection with your ISP and begin routing internet traffic to your devices. This can help improve your WiFi speeds by clearing any temporary issues that may have been causing slowdowns or other issues with your connection.
How to get faster WiFi by restarting your router:
Locate the power cord for your router.
Unplug the power cord from the back of the router and from the power outlet. This will shut down the router and disconnect all devices from the WiFi network.
Wait for a few minutes before plugging the power cord back into the power outlet and into the back of the router.
Once the power cord is plugged in, the router will automatically restart and begin establishing a connection with your internet service provider (ISP). This can take a few minutes.
Once the router has restarted, your devices will automatically reconnect to the WiFi network. You may need to enter the WiFi password on each device to reconnect.
It is important to note that restarting your router will not necessarily fix all WiFi issues or guarantee faster speeds.
However, it can be a helpful troubleshooting step to try if you are experiencing slowdowns or other issues with your WiFi connection.
Paid Solutions for Boosting WiFi Speeds
If you are tired of slow and unreliable WiFi speeds, there are several paid solutions that can help boost your internet performance. These solutions range from simple hardware adjustments and upgrades to more complex networking solutions, and they are among the most best ways to extend WiFi range.
Adjust the Antennas
Adjusting the antennas on your router can help improve WiFi performance by directing the wireless signal in specific directions.
For example, if you have a large, open floor plan in your home, you can position the antennas on your router to extend the signal horizontally, covering more area and providing better coverage for your devices. Alternatively, if you have a multi-story home with thick walls, you may want to position the antennas vertically to extend the signal upwards and downwards, penetrating the walls and providing better coverage on each floor.
Just know that some routers, such as older or low-end models, may not have any antennas at all. Other routers, such as newer or higher-end models, may have two or more antennas.
Use a Wi-Fi Extender
A WiFi extender, also known as a WiFi repeater or WiFi booster, is a device that can improve the speeds and coverage of your WiFi network. WiFi extenders work by connecting to your existing WiFi network and then rebroadcasting the signal, effectively extending the range and coverage of your WiFi network.
For example, if you have a large home with thick walls and poor WiFi coverage in some areas, a WiFi extender can help improve your internet speeds and coverage by rebroadcasting the WiFi signal and filling in dead spots in your home. This can help reduce the number of dropped connections and improve the overall performance of your internet connection.
Additionally, WiFi extenders can also improve the speeds of your internet connection by providing additional bandwidth for your devices to use. By adding more bandwidth to your network, a WiFi extender can help reduce congestion and improve the speed of your internet connection, allowing you to enjoy faster and more reliable internet speeds.
The biggest disadvantage of WiFi extenders is that they can introduce additional latency and slow down your internet speeds. This is because WiFi extenders work by connecting to your existing WiFi network and then rebroadcasting the signal, which can add an extra "hop" for your devices to connect to the internet.
Buy a New Wi-Fi Router
A new WiFi router can improve your internet experience in several ways. First and foremost, a new WiFi router can provide faster and more reliable internet speeds. Newer routers are typically designed to support the latest WiFi standards and technologies, such as WiFi 6 and MU-MIMO, which can provide faster and more efficient internet speeds compared to older routers.
A new WiFi router can also improve your internet experience by providing additional features and capabilities. For example, newer routers may support advanced networking technologies, such as Quality of Service (QoS) or VPN support, which can help prioritize and secure your internet traffic. They may also support advanced management and security features, such as parental controls or guest networks, which can help you customize and protect your home network.
Overall, upgrading to a new WiFi router is a great way how to fix a weak WiFi signal, but it’s certainly not the cheapest.
What to Do If This Happens to You
As you can see, pinpointing the issue that is degrading your WiFi speed can be a challenge. I would suggest that if you are faced with this problem, you follow the steps discussed above to try and resolve the issue. In most cases, you will see an improvement by changing channels or moving your router.
With these simple tips, you should be able to enjoy a fast WiFi hotspot even with an older wireless router. Of course, there is only so much you can accomplish with outdated technology, especially if you live in a larger home and your WiFi requirements are high.
Unfortunately, not all WiFi issues can be resolved at no cost. When faced with the prospect of continued sporadic Internet problems or spending a few dollars, the choice was easy. We are back to enjoying our WiFi without interruptions. Isn’t that what we all really want?
How to Get Faster WiFi — FAQs
Here are some ways how to get better internet by increasing your WiFi speed:
- position your router in a central, open location;
- avoid interference from other electronic devices;
- update the firmware on your router;
- use a wired connection for devices that are close to the router;
- disconnect any unused devices;
- upgrade to a more powerful router or use WiFi extenders.
There are many potential reasons why your WiFi may be slow:
- Interference from other electronic devices
- Weak or unreliable signal
- Outdated hardware or firmware
- Large number of devices connected to the WiFi network
- Network congestion or bandwidth limitations
- Slow internet connection from your service provider
To improve a weak WiFi signal, there are a few steps you can take. These include positioning your router in a central, open location, avoiding interference from other electronic devices, updating the firmware on your router, using a wired connection for devices that are close to the router, disconnecting unused devices, and upgrading to a more powerful router or using WiFi extenders.
